We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
Square Counter Current Cooling Tower Technical Introduction
-
1.Overview
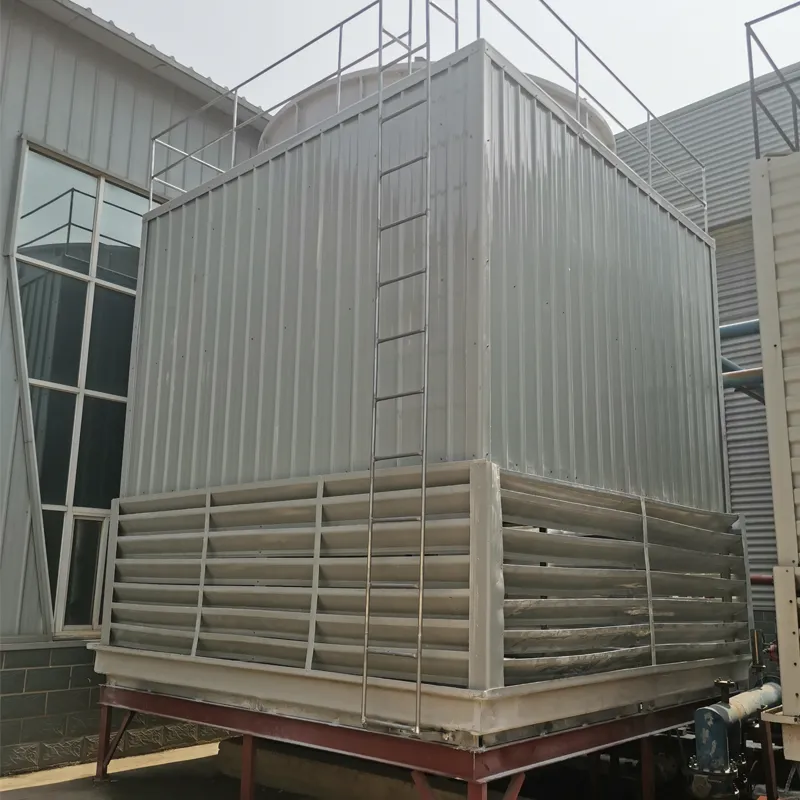
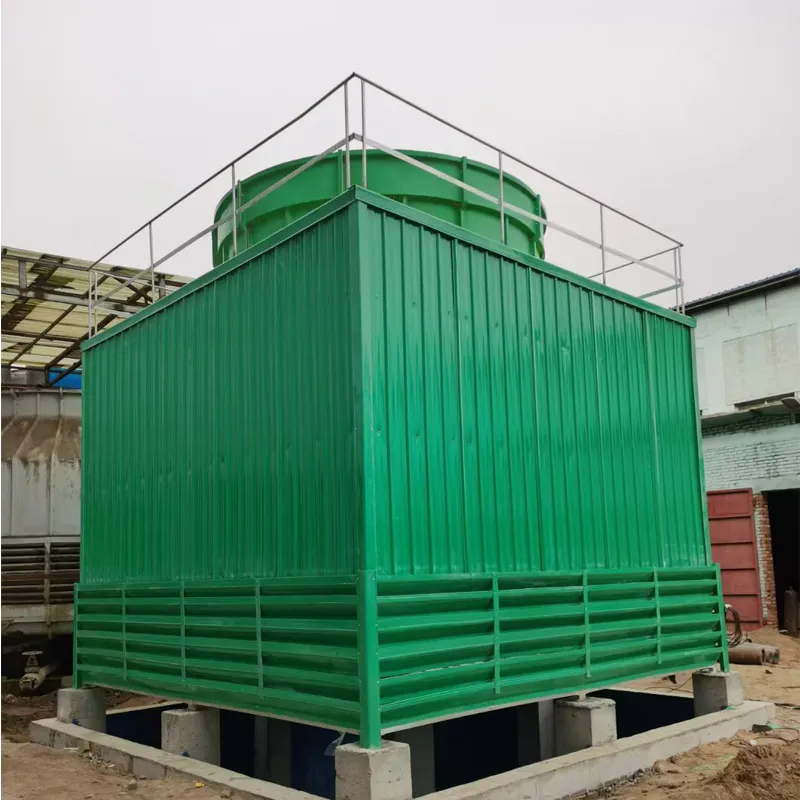
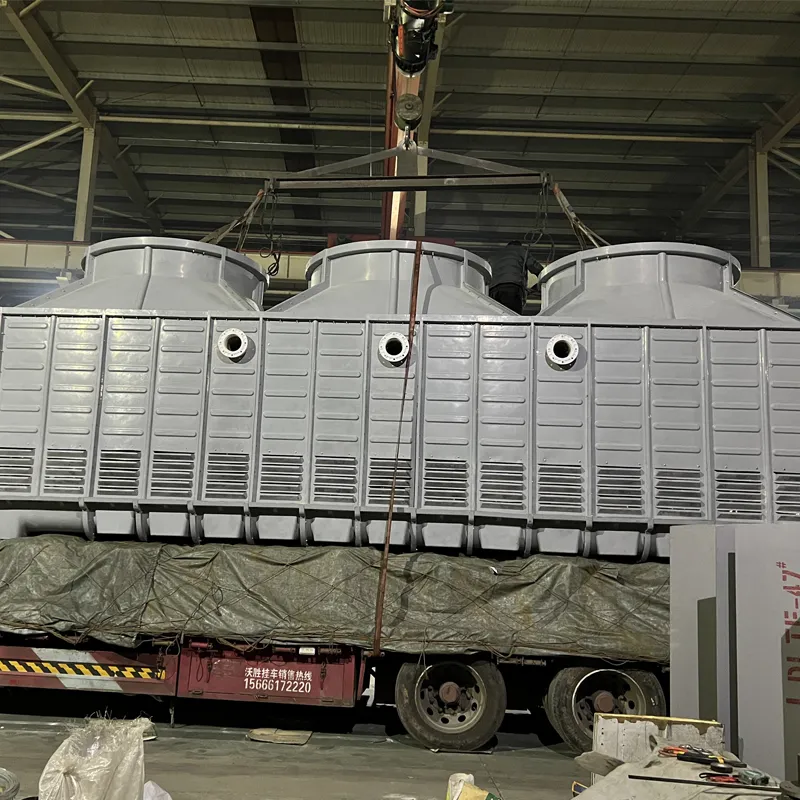
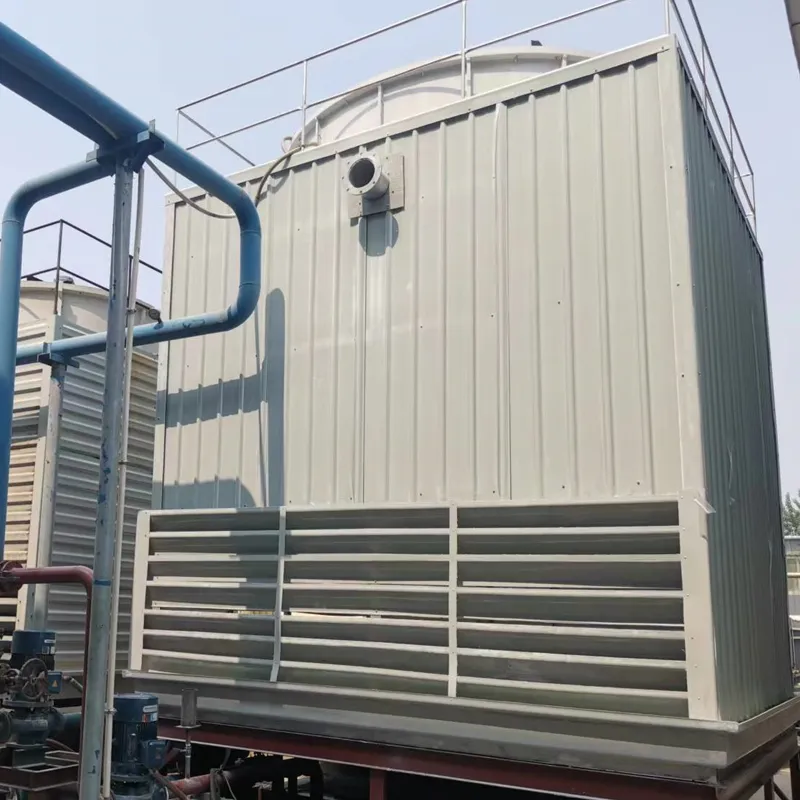
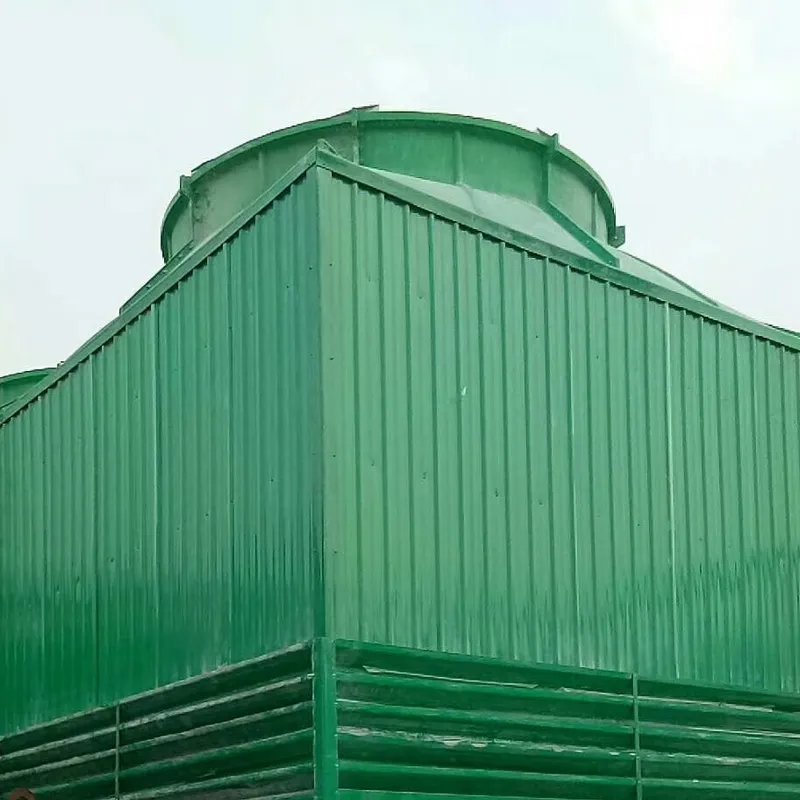
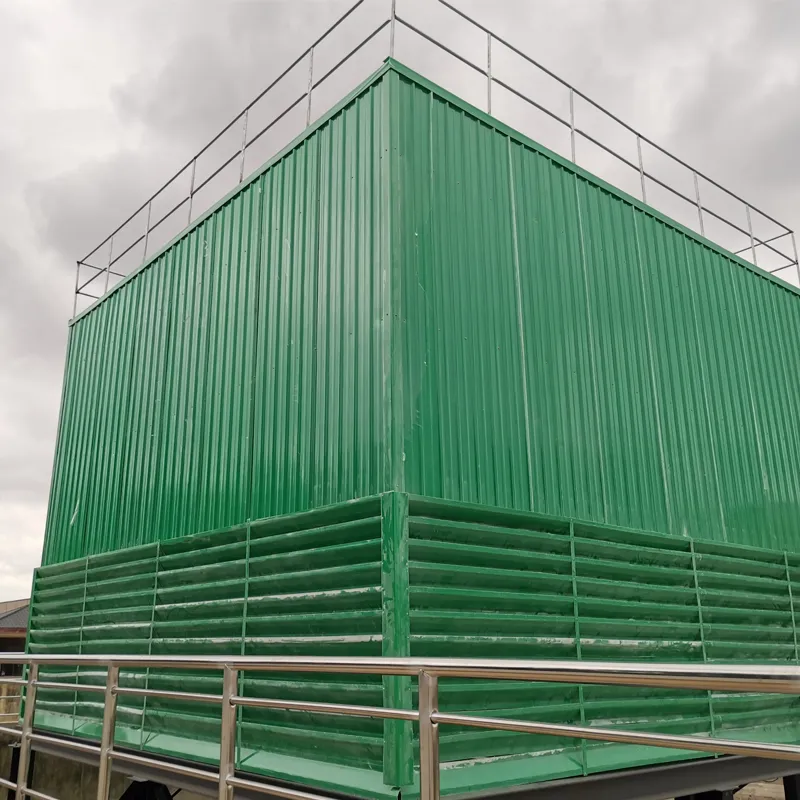
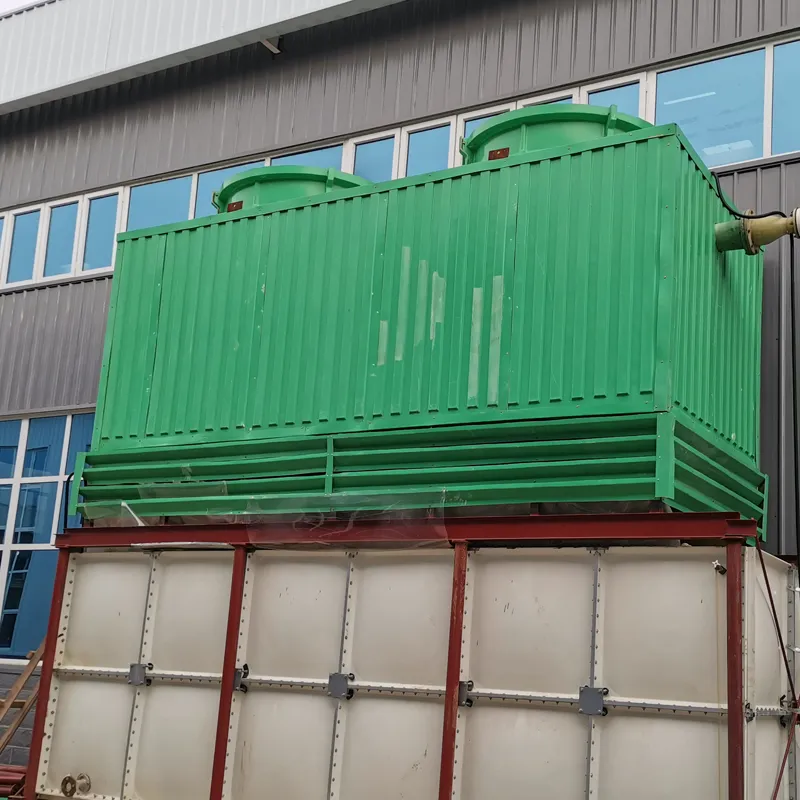
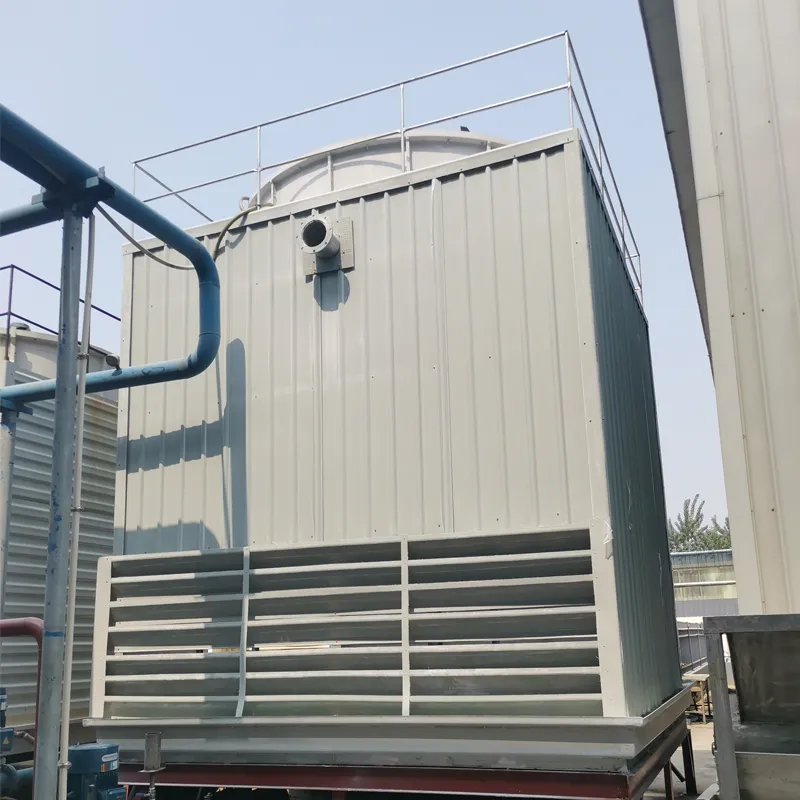
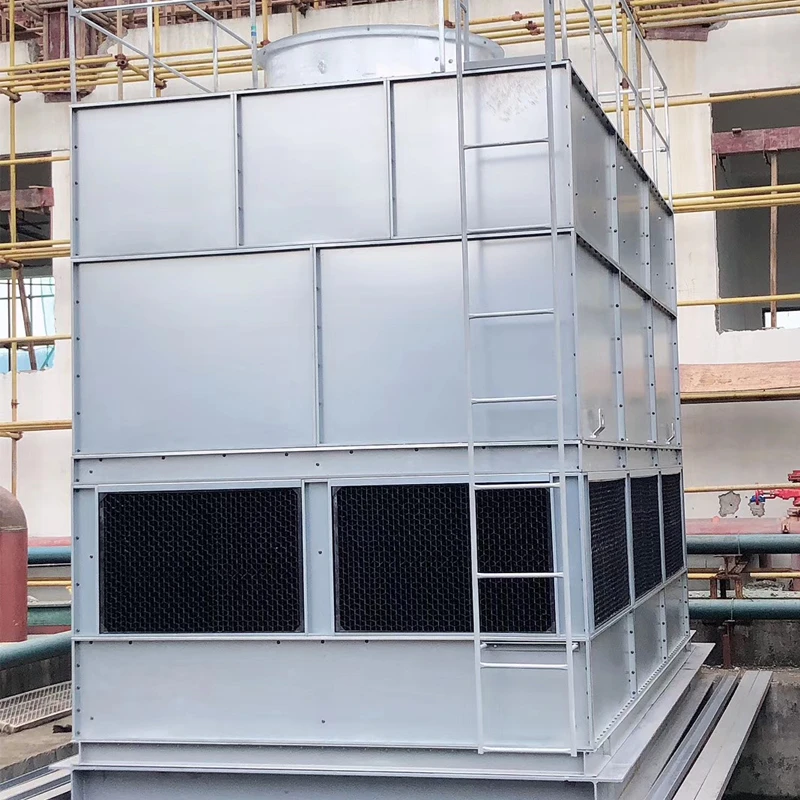
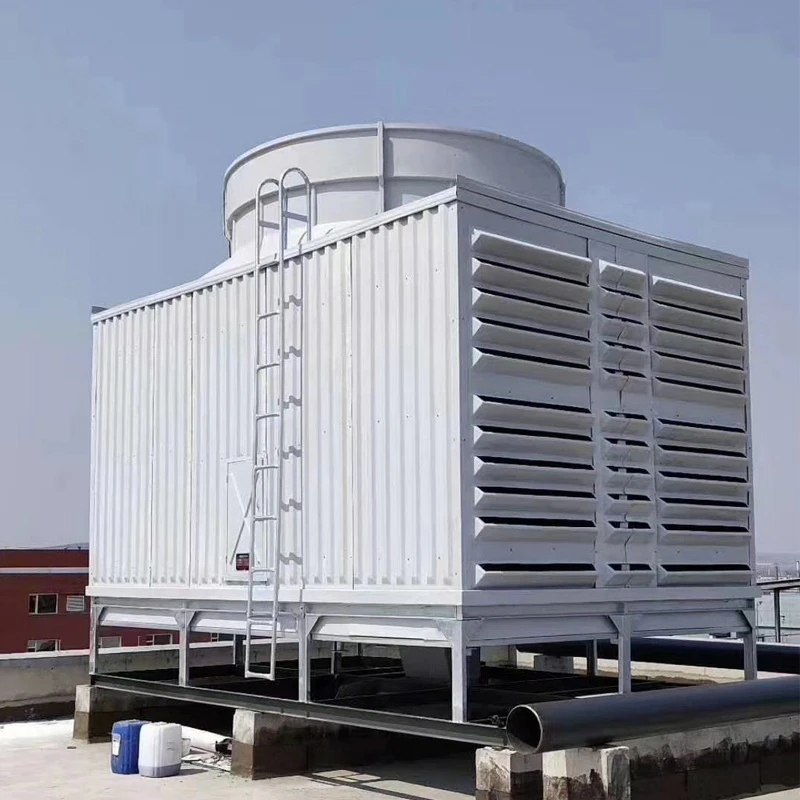
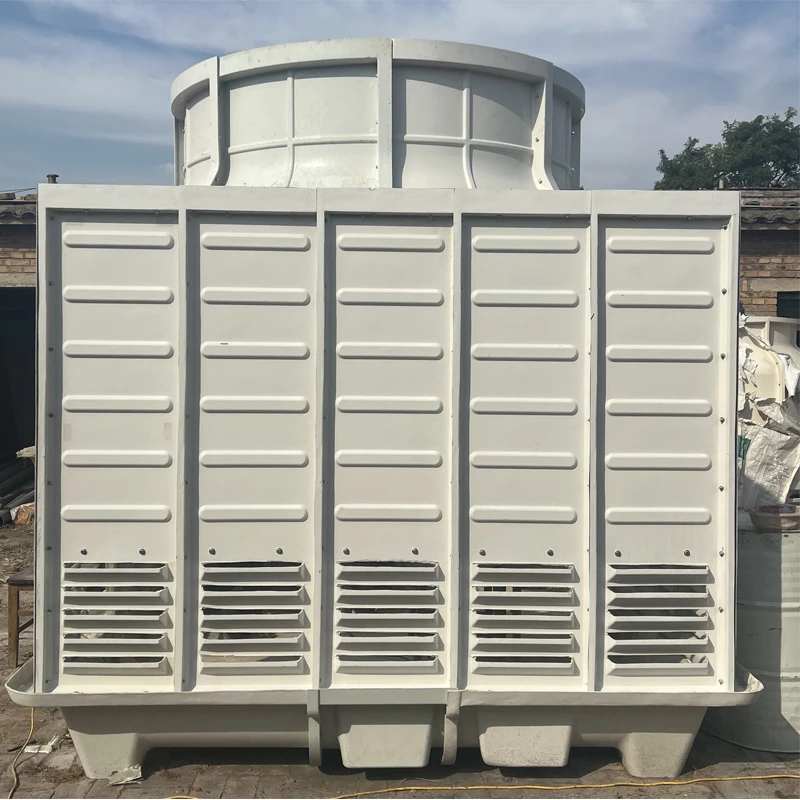
A Square Counter Current Cooling Tower is a mechanical draft cooling tower characterized by its rectangular/cuboidal structure, where air and water flow in opposite directions (counter current) to maximize heat transfer efficiency. Widely used in power plants, chemical processing, data centers, and other industrial applications requiring high-efficiency heat dissipation, it is particularly suited for space-constrained sites or projects requiring modular scalability.
2. Core Structure & Design
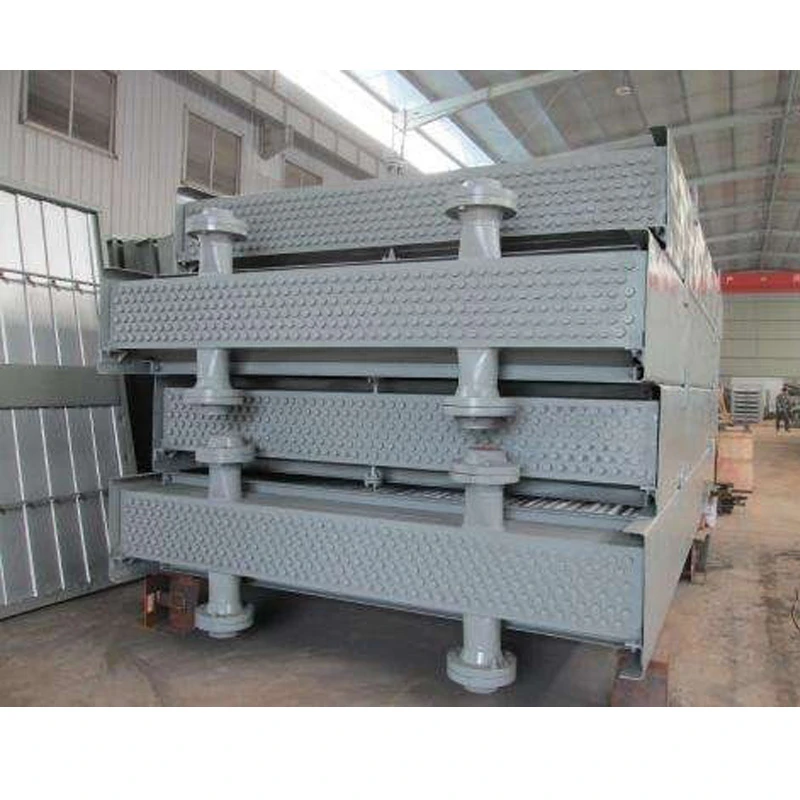
2.1 Main Components
|
Component |
Material/Design |
Function |
|
Tower Frame |
Galvanized steel/FRP |
Structural support, corrosion-resistant |
|
Fill Media |
PVC or PP modules |
Maximize air-water contact surface area |
|
Water Distribution |
Rotary nozzles/fixed spray pipes |
Evenly distribute hot water over fills |
|
Fan System |
Axial fans (top-mounted) |
Force air upward from the base |
|
Drift Eliminators |
Corrugated PVC sheets |
Reduce water drift loss (>99.9% efficiency) |
|
Cold Water Basin |
Stainless steel/FRP |
Collect cooled water for recirculation |
2.2 Design Features
Counter Current Flow: Air moves upward against descending water, maximizing thermal gradient.
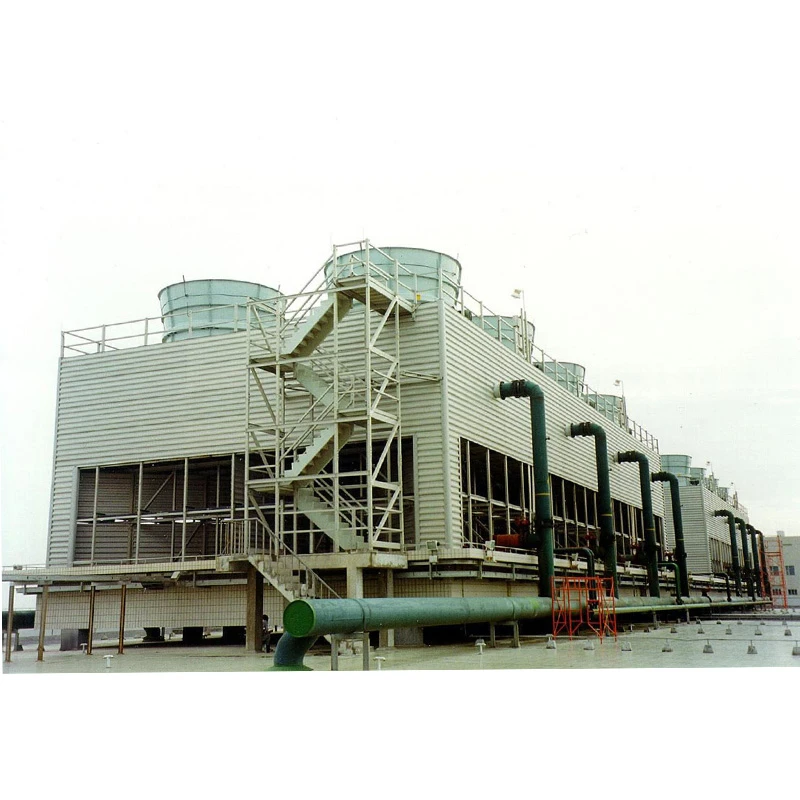
Modular Configuration: Supports parallel installation for flexible capacity expansion.
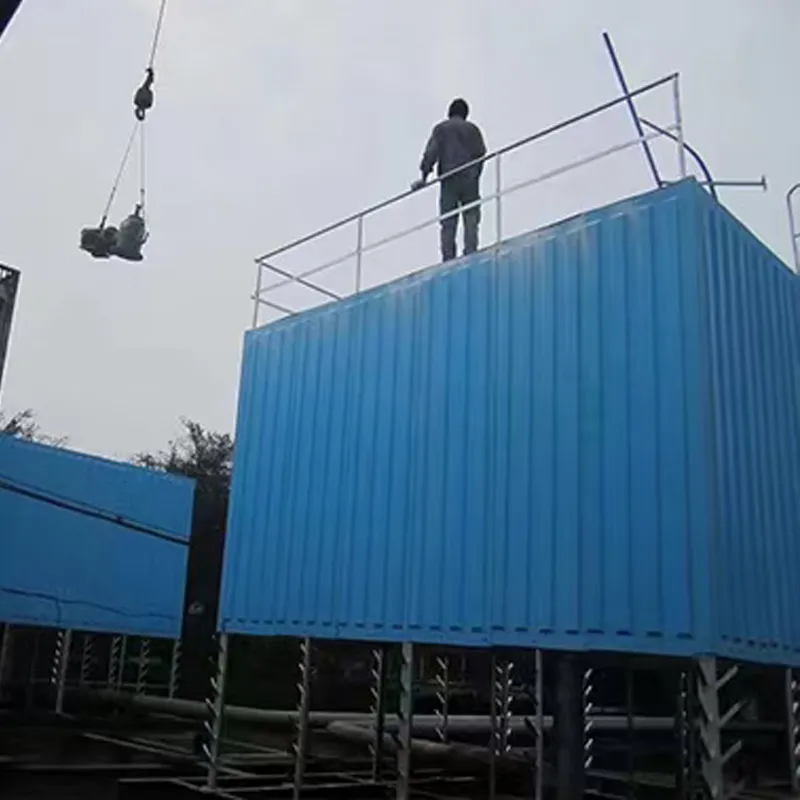
Ease of Maintenance: Removable side panels allow easy access to fills and internal components.
3. Working Principle
Hot Water Inlet: Process hot water is pumped to the distribution system.
Water Distribution: Nozzles spray water uniformly over the fill media.
Airflow: Top-mounted fans draw ambient air upward through the tower.
Heat Exchange: Evaporative cooling occurs as air and water interact counter-currently.
Cooled Water Recovery: Chilled water collects in the basin for reuse.
4. Performance Advantages
|
Parameter |
Advantages |
|
Cooling Efficiency |
10–15% higher ΔT (temperature difference) compared to crossflow designs. |
|
Space Efficiency |
Vertical design minimizes footprint, ideal for narrow or rectangular spaces. |
|
Maintenance Cost |
Modular components reduce downtime by 30%. |
|
Water Conservation |
Advanced drift eliminators limit water loss to <0.001% of circulation flow. |
|
Noise Control |
Low-speed fans + acoustic insulation ensure noise ≤65 dB(A) at 1m distance. |
5. Typical Applications
Power Generation: Cooling condenser water in thermal/nuclear plants.
Chemical & Petrochemical: Heat dissipation for reactors and distillation columns.
Data Centers: Auxiliary cooling for liquid-cooled server systems.
Manufacturing: Cooling for injection molding machines and die-casting systems.
6. Comparison with Circular Cooling Towers
|
Feature |
Square Counter Current Tower |
Circular Cooling Tower |
|
Airflow Uniformity |
Requires airflow guides to minimize dead zones |
Naturally uniform airflow |
|
Scalability |
Modular parallel expansion |
Limited to single-unit capacity upgrades |
|
Wind Resistance |
Reinforced framing needed for high-rise sites |
Superior inherent wind resistance |
|
Installation Flexibility |
Fits rectangular spaces, wall-mountable |
Requires dedicated circular area |
7. Selection & Maintenance Guidelines
7.1 Key Selection Parameters
Cooling Capacity (RT): Calculate based on thermal load (1 RT ≈ 3.5 kW).
Wet Bulb Temperature: Design for local extreme conditions (e.g., 28°C wet bulb).
Water Quality: Maintain TDS <500 ppm with regular corrosion inhibitors.
7.2 Maintenance Protocol
Quarterly: Clean fill media, check fan balance.
Annual: Replace bearing lubricants, test motor insulation.
Winterization: Drain basins and install electric heating tapes in freezing climates.
8. Sustainability & Energy Efficiency
Energy Savings: Variable-frequency drives (VFDs) reduce fan power consumption by 20–30%.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Recyclable FRP reduces lifecycle carbon footprint.
Zero Liquid Discharge: Closed-loop systems with softened/filtered water reuse.
Conclusion
Square counter current cooling towers excel in high-efficiency heat exchange, modular scalability, and space optimization, making them ideal for industrial cooling systems. For optimal performance, prioritize models with IoT-enabled monitoring systems and tailor configurations to site-specific thermal and spatial requirements.
What Our Customers Say About Square Counter Current Cooling Tower
Square Counter Current Cooling Tower FAQ
-
Q: What is a square counter current cooling tower?
A: A square counter current cooling tower is a cooling system where water and air flow in opposite directions, providing efficient heat exchange.
-
Q: How is a square counter current cooling tower different from a crossflow type?
Q: How is a square counter current cooling tower different from a crossflow type?
-
Q: What are the applications of square counter current cooling towers?
A: They are used in power plants, chemical factories, and large-scale HVAC systems to improve cooling efficiency.
-
Q: Are square counter current cooling towers easy to maintain?
A: Yes, these towers are designed for easy maintenance with accessible components and durable materials.







Address
20 Xingyuan South Street, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province, China