We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
1. Definition
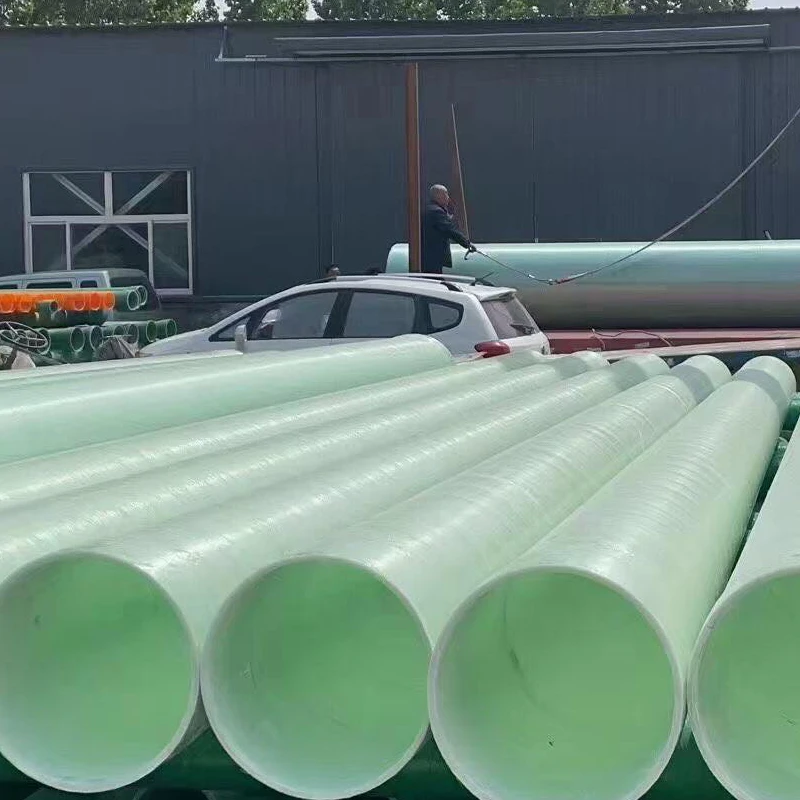
FRP pipe, short for Fiber Reinforced Plastic pipe, is a composite pipe made by combining resin matrix with fiber reinforcements such as glass fiber, carbon fiber, or aramid fiber. This combination endows the pipe with unique mechanical and chemical properties, making it a popular choice in various industries.
2. Manufacturing Process
- Filament Winding: This is a common method. Continuous fibers impregnated with resin are wound onto a rotating mandrel in a specific pattern. The winding angle and layer thickness are precisely controlled to ensure the pipe has the required strength and performance characteristics. After winding, the pipe is cured under certain temperature and pressure conditions to form a solid structure.
- Centrifugal Casting: In this process, resin and fiber materials are poured into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force distributes the materials evenly along the inner wall of the mold. As the materials solidify during rotation, a uniform - wall - thickness pipe is formed. This method is suitable for producing pipes with larger diameters.
3. Physical and Chemical Properties
- High Strength - to - Weight Ratio: FRP pipes are lightweight yet possess high tensile and compressive strength. The reinforcement fibers carry the major part of the load, allowing the pipe to withstand high internal and external pressures while being much lighter than traditional metal pipes. This property makes transportation and installation more convenient, especially for large - scale pipeline projects.
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: The resin matrix in FRP pipes provides outstanding resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and salts. This makes FRP pipes ideal for applications in chemical processing plants, sewage treatment systems, and coastal areas where corrosion is a major concern. They can maintain their integrity and performance over a long service life without significant degradation due to chemical attacks.
- Good Insulating Properties: FRP pipes are excellent electrical and thermal insulators. They do not conduct electricity, which is crucial in applications where electrical safety is required, such as in power plants and electrical utility systems. In terms of thermal insulation, they can help reduce heat loss or gain, saving energy in heating and cooling systems.
4. Performance Advantages
- Long Service Life: Due to their corrosion - resistant and durable nature, FRP pipes can last for 20 - 50 years or even longer under normal operating conditions. This significantly reduces the need for frequent replacements, resulting in lower maintenance and replacement costs over time.
- Smooth Inner Surface: The inner surface of FRP pipes is extremely smooth, which reduces the friction coefficient during fluid flow. As a result, fluids can flow through the pipes with less energy consumption, improving the overall efficiency of the pipeline system. This property is beneficial for transporting various fluids, such as water, oil, and gas.
- Design Flexibility: FRP pipes can be customized in terms of diameter, length, wall thickness, and mechanical properties according to specific project requirements. Different fiber - resin combinations and winding patterns can be selected to meet different engineering needs, providing a high degree of adaptability to various applications.
5. Application Areas
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: FRP pipes are widely used in water supply systems, including potable water pipelines and water treatment plants. In wastewater treatment, they can handle the transportation of sewage and industrial effluents, with their corrosion - resistance ensuring the long - term operation of the treatment facilities.
- Chemical Industry: In chemical plants, FRP pipes are used to transport a variety of corrosive chemicals, such as strong acids, alkalis, and solvents. Their ability to withstand chemical reactions without contamination makes them an essential component in chemical production processes.
- Oil and Gas Industry: For the transportation of oil, gas, and other hydrocarbons, FRP pipes are used in some specific applications, especially in offshore platforms and sub - sea pipelines. Their corrosion resistance and light weight are advantageous in harsh marine environments.
In summary, FRP pipes, with their remarkable properties, performance advantages, and wide - ranging applications, play an important role in modern infrastructure and industrial development.
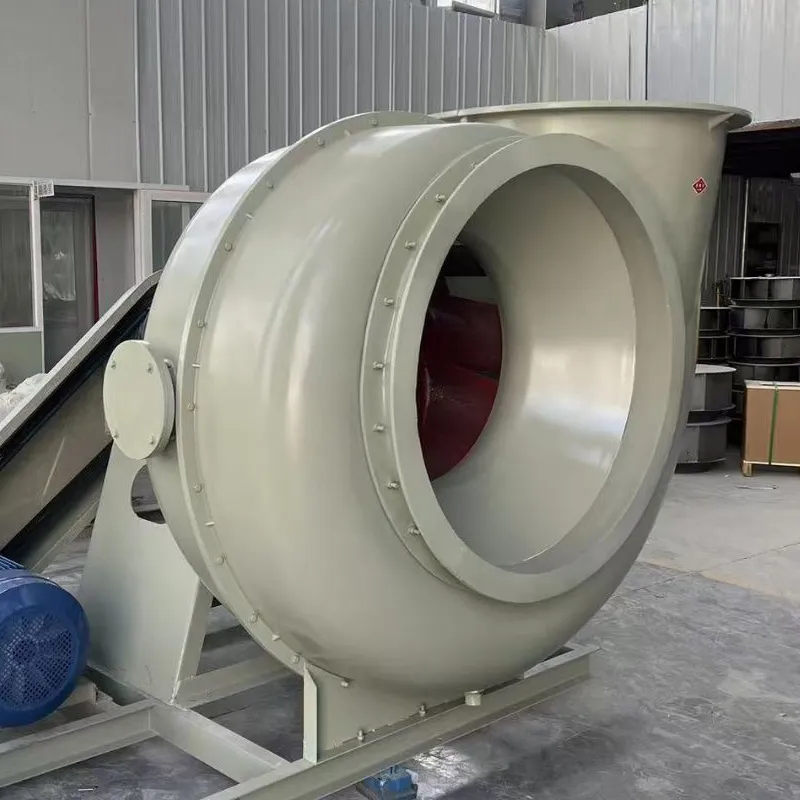
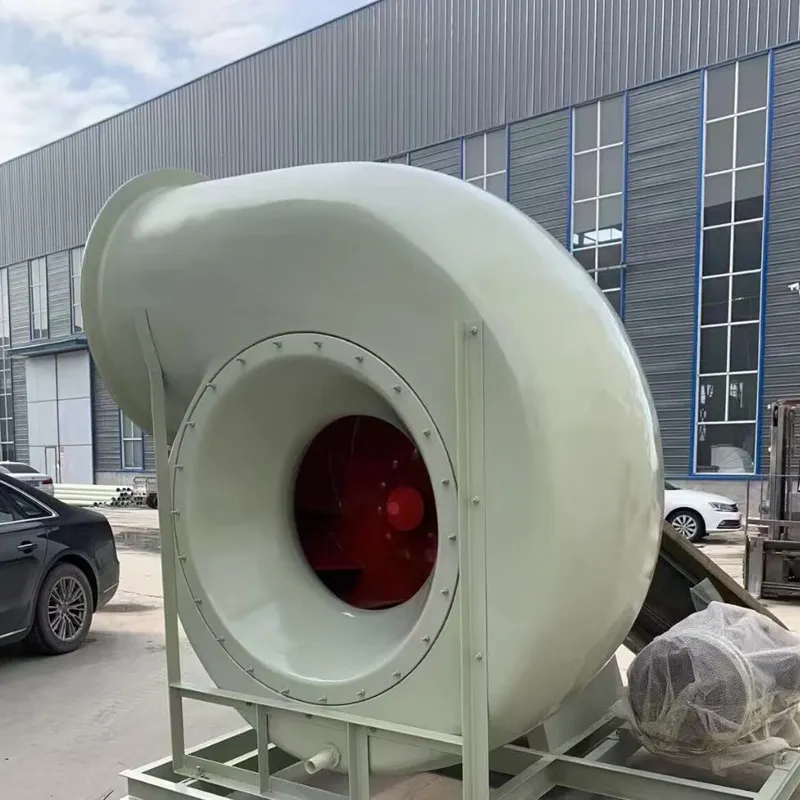
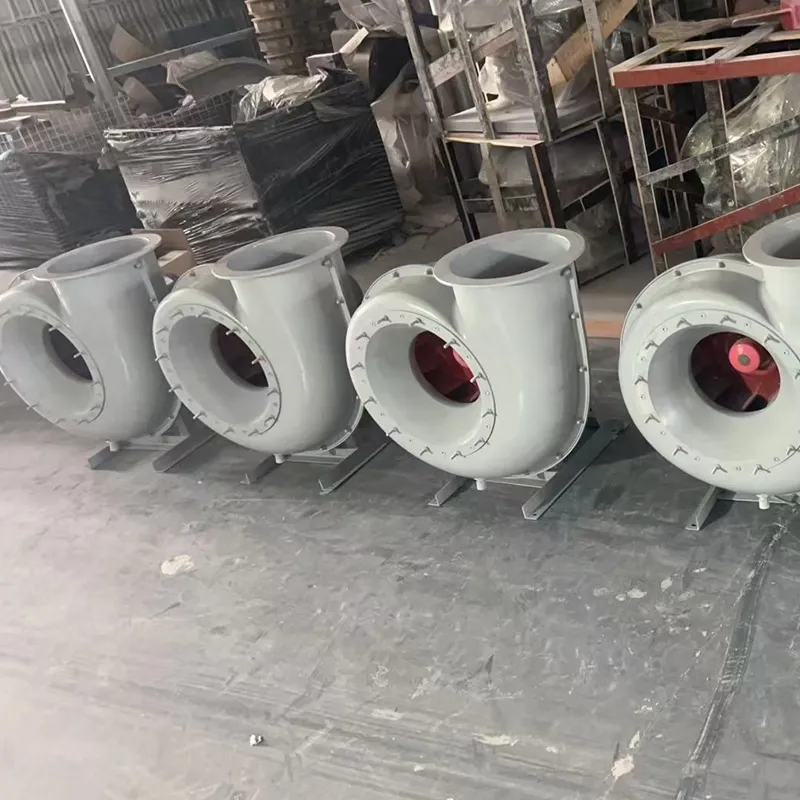
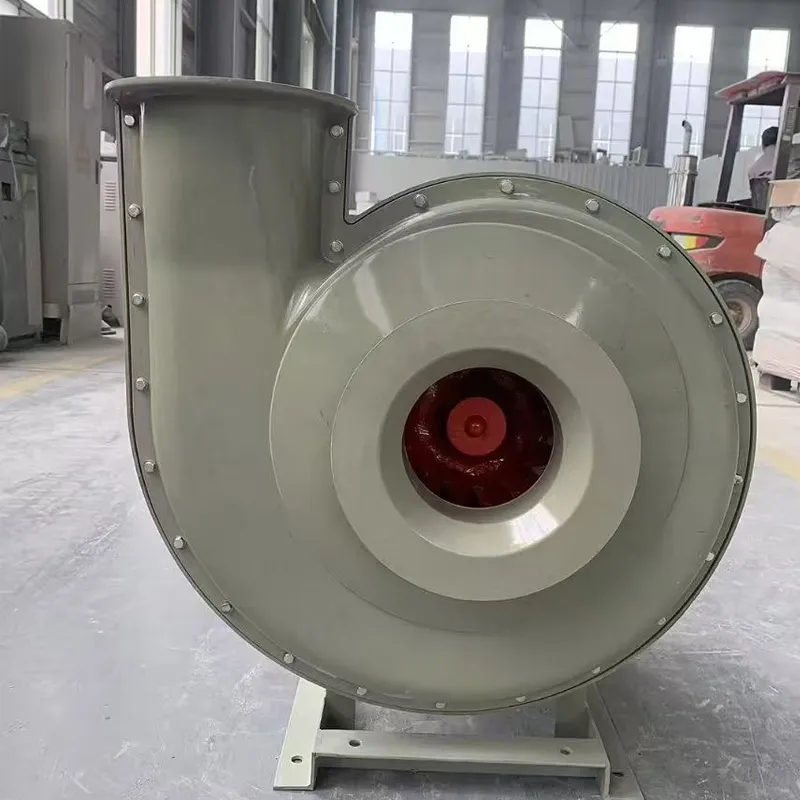
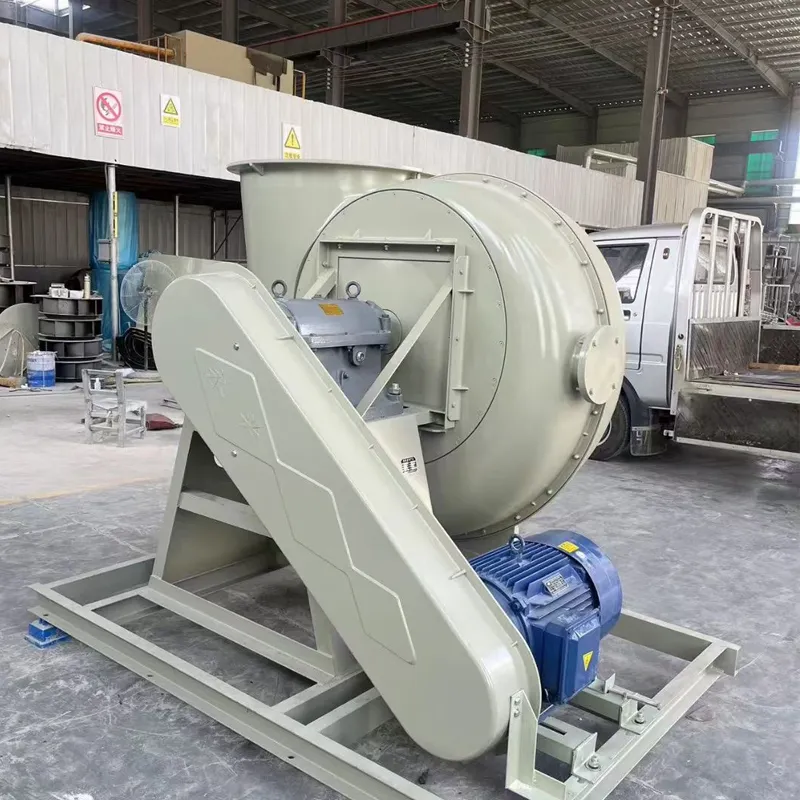
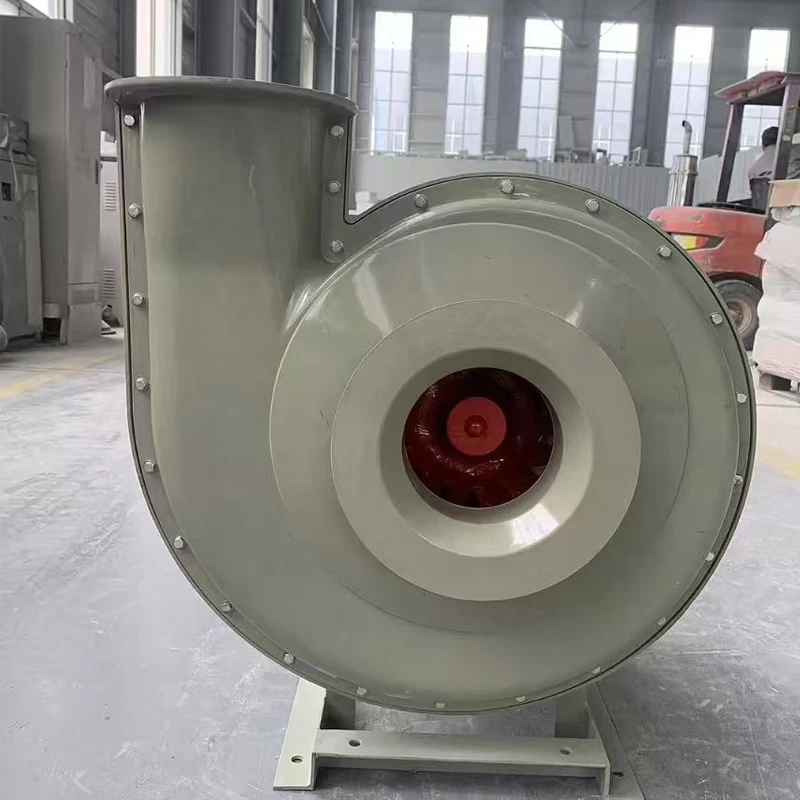
What Our Customers Say About FRP Centrifugal Fan
Frp Centrifugal Fan FAQ
-
Q: What is an FRP centrifugal fan?
A: An FRP centrifugal fan is a high-performance fan made from fiberglass reinforced plastic, designed for moving air in ventilation and cooling systems.
-
Q: Why are FRP centrifugal fans preferred in certain industries?
A: They offer excellent corrosion resistance, high airflow capacity, and energy efficiency, making them ideal for chemical and power plant environments.
-
Q: Where are FRP centrifugal fans used?
A: They are used in ventilation systems, dust collection systems, and cooling towers in heavy industries.
-
Q: How do FRP centrifugal fans improve system efficiency?
A: Their high efficiency and corrosion resistance help reduce energy consumption and maintenance costs, improving overall system performance.







Address
20 Xingyuan South Street, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province, China