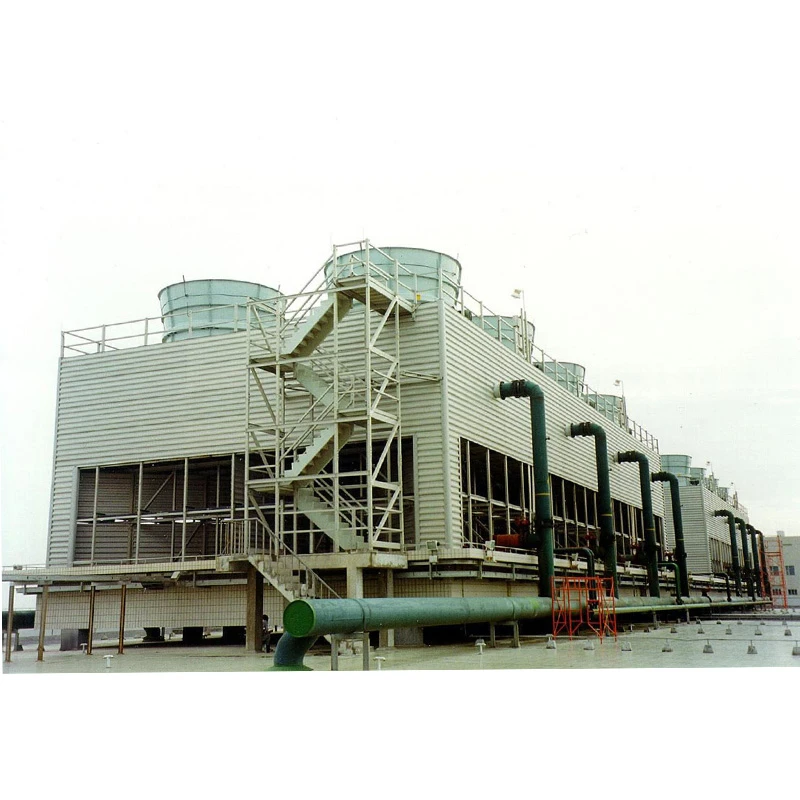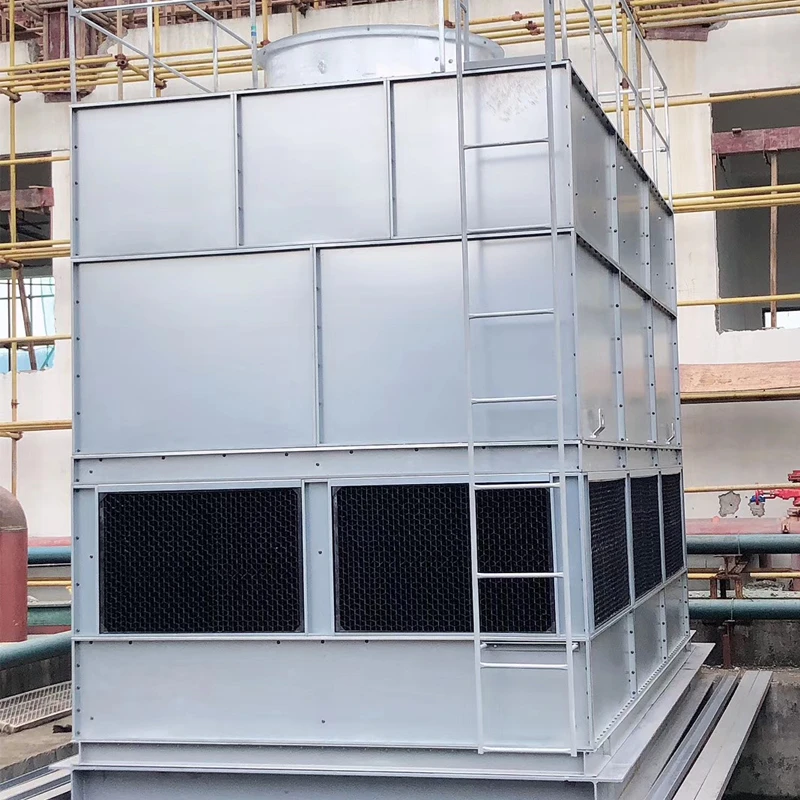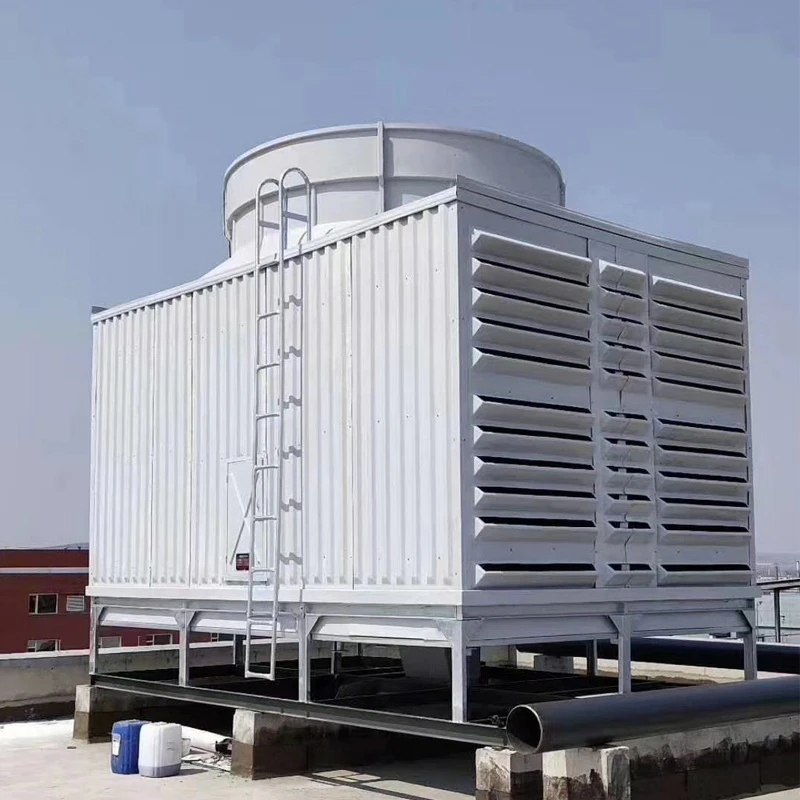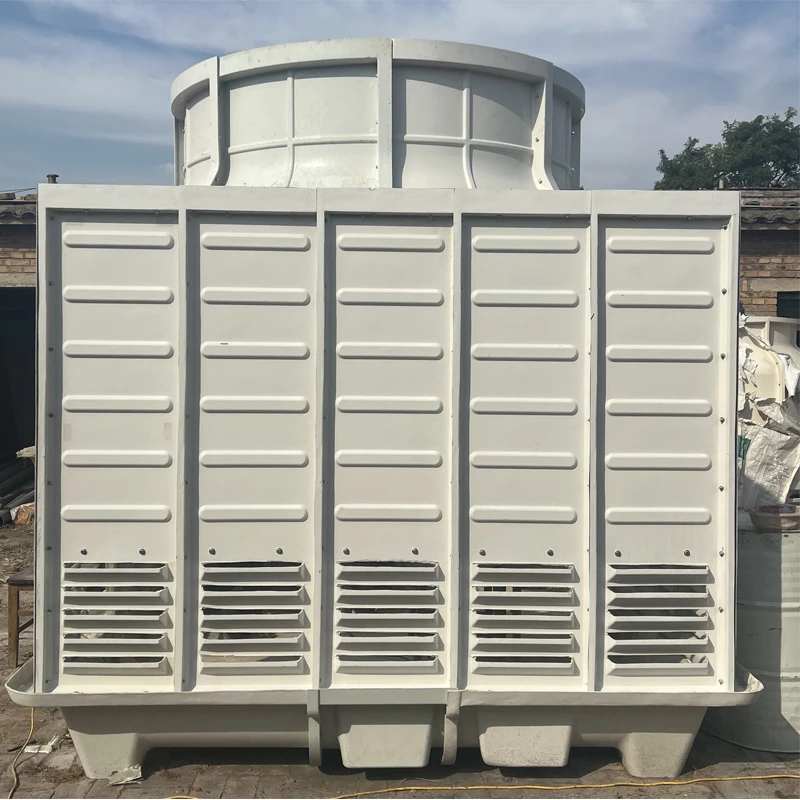
We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
Here’s a professional English technical introduction to FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) Tanks, structured for engineering specifications, industrial procurement, or technical documentation:
FRP Tank Technical Introduction
- 1.Overview
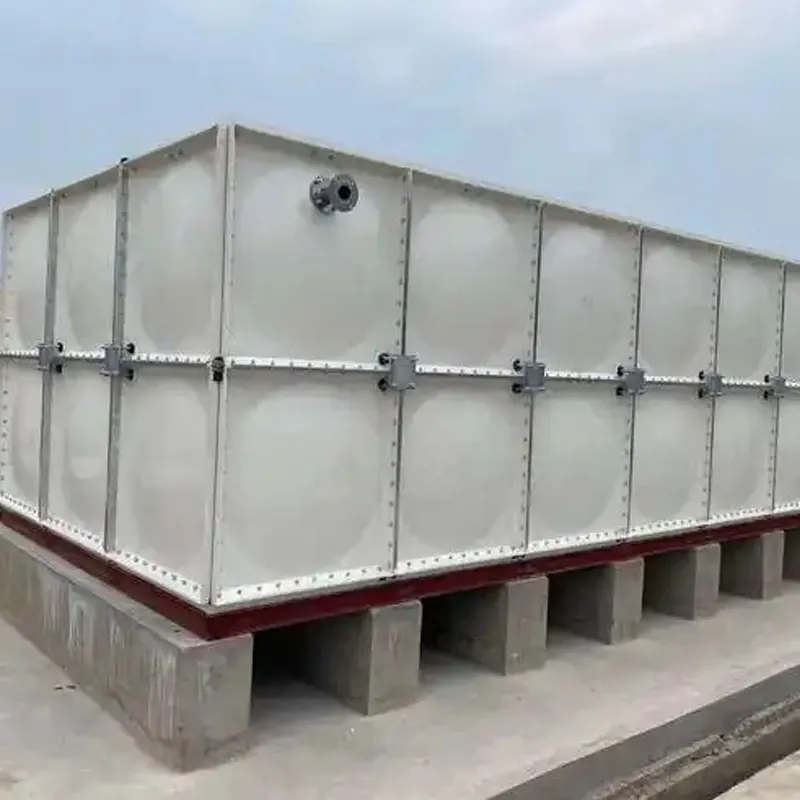
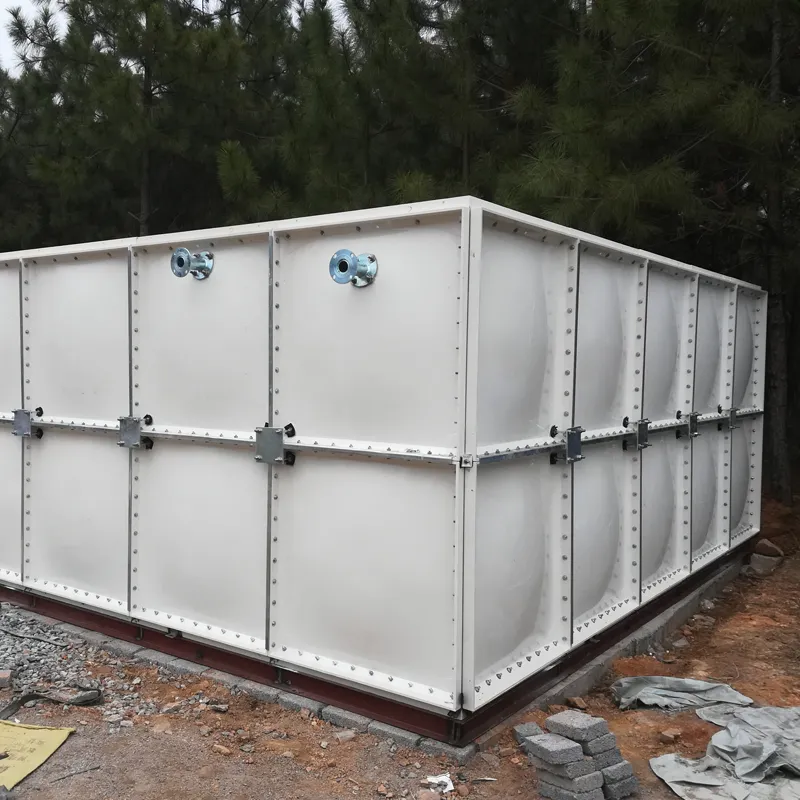
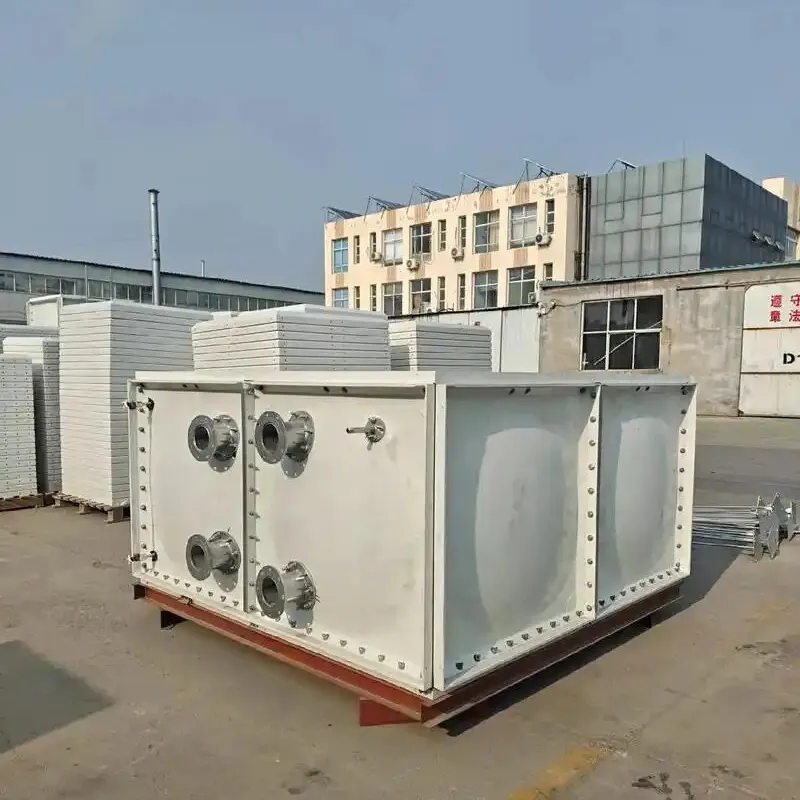
FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) Tanks are composite storage vessels manufactured by combining glass fiber reinforcements with thermosetting resins (e.g., polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy). Renowned for their corrosion resistance, lightweight design, and customizable configurations, FRP tanks are widely used in industries requiring durable chemical storage, water treatment, and industrial process solutions.
- 2.Structure & Manufacturing
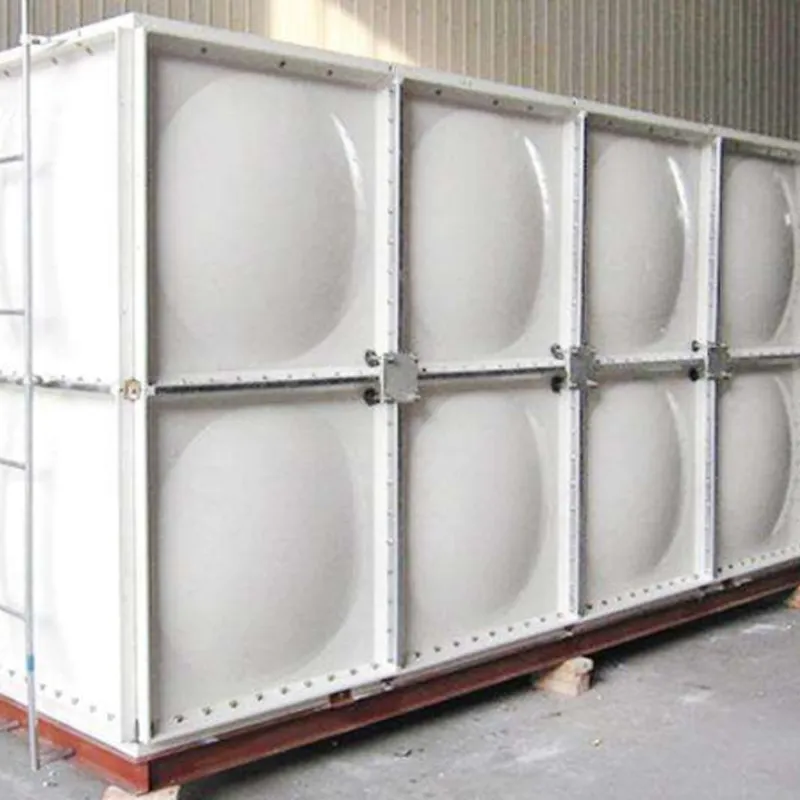
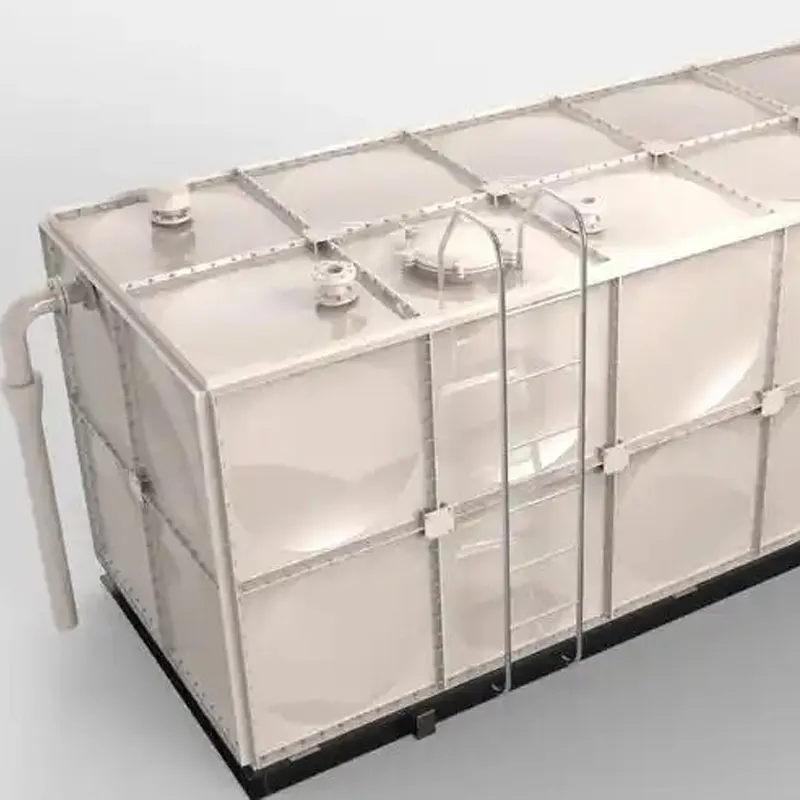
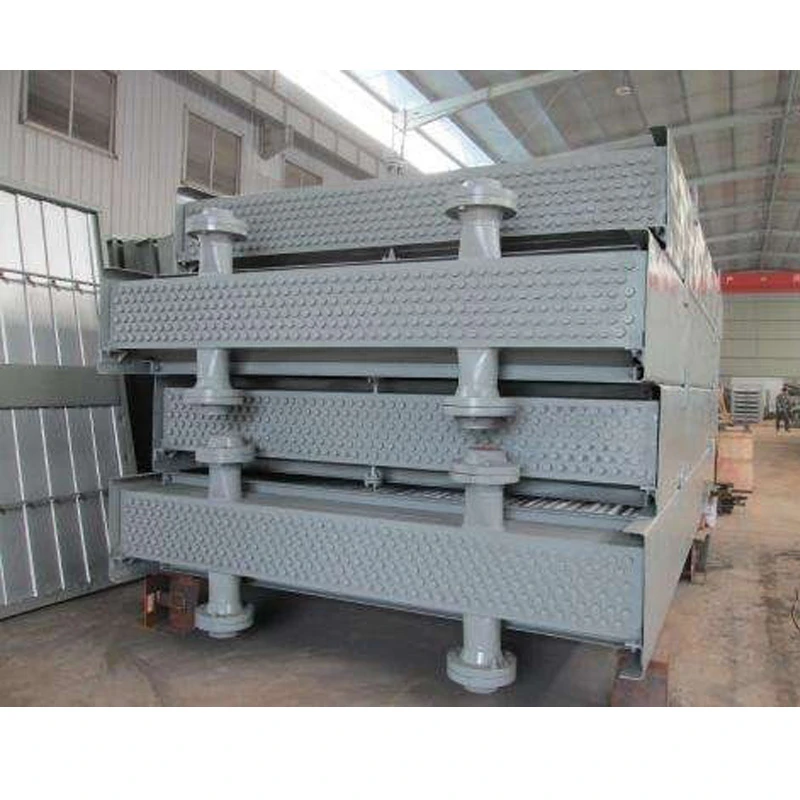
2.1 Layered Construction
Layer Material/Function Inner Liner Resin-rich layer with additives (e.g., graphite or veils) for chemical/abrasion resistance. Structural Wall Glass fiber mats/woven rovings + resin matrix (hand lay-up or filament winding). Outer Layer UV-resistant gel coat or resin for weatherproofing and mechanical protection.
2.2 Manufacturing Processes
Filament Winding: Automated fiber winding for uniform strength (ideal for cylindrical tanks).
Hand Lay-Up: Manual layering for complex shapes (e.g., conical or rectangular tanks).
Spray-Up: Quick production for non-critical applications (limited structural consistency).
- 3.Key Advantages
Feature Benefit Corrosion Resistance Resists acids, alkalis, solvents, and salts (pH range: 1–14).
High Strength Tensile strength up to 300 MPa, comparable to steel at 1/4 the weight.
Customizable Design Adaptable to non-standard shapes, fittings, and mounting configurations.
Low Maintenance No rust, coatings, or cathodic protection required; lifespan ≥30 years.
Thermal Insulation Low thermal conductivity (0.04–0.06 W/m·K) minimizes heat transfer.
- 4.Technical Specifications
4.1 Standard Parameters
Capacity: 100 L to 500,000 L (customizable).
Pressure Rating: Atmospheric to 10 bar (special designs up to 25 bar).
Temperature Range: -50°C to 120°C (vinyl ester resin); higher with epoxy.
Wall Thickness: 6–25 mm (varies with diameter and pressure requirements).
4.2 Common Configurations
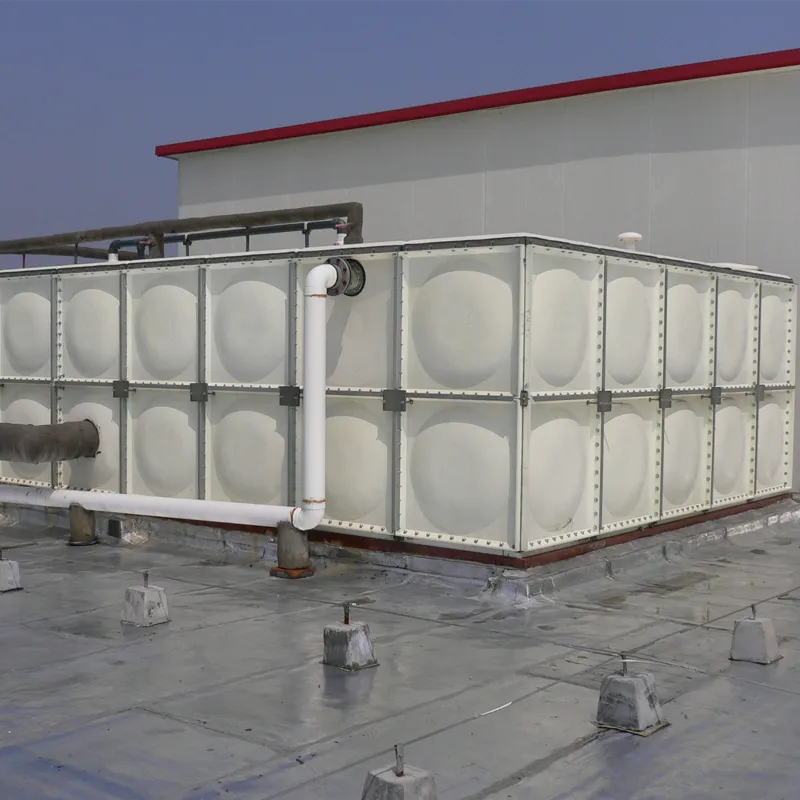
Vertical/Cylindrical: For general-purpose storage (chemicals, water).
Horizontal: Transportable tanks for fuel or liquid bulk handling.
Underground: Leak-proof designs for fuel or wastewater storage.
- 5.Applications
Industry Use Case Chemical Processing Storage of HCl, H₂SO₄, NaOH, and organic solvents. Water Treatment Chlorine, alum, and brine storage; RO system vessels. Oil & Gas Fuel storage, produced water tanks, and offshore brine containment.
Food & Beverage FDA-compliant tanks for vinegar, juices, and edible oils.
- 6.Standards & Certifications
ASTM D4097: Standard for contact-molded FRP tanks.
ASME RTP-1: Reinforced thermoset plastic corrosion-resistant equipment.
NSF/ANSI 61: Certification for potable water contact.
EN 13121: GRP tanks and vessels for underground storage.
- 7.Comparison with Alternative Materials
Parameter FRP Stainless Steel Polyethylene (PE) Corrosion Resistance Excellent (broad chemical compatibility) Moderate (depends on grade) Limited (susceptible to organics) Weight 1.8–2.0 g/cm³ 7.9–8.0 g/cm³ 0.95–0.98 g/cm³ Installation Cost Low (prefabricated modules) High (welding/coating) Moderate Lifespan 30+ years 15–25 years 10–20 years
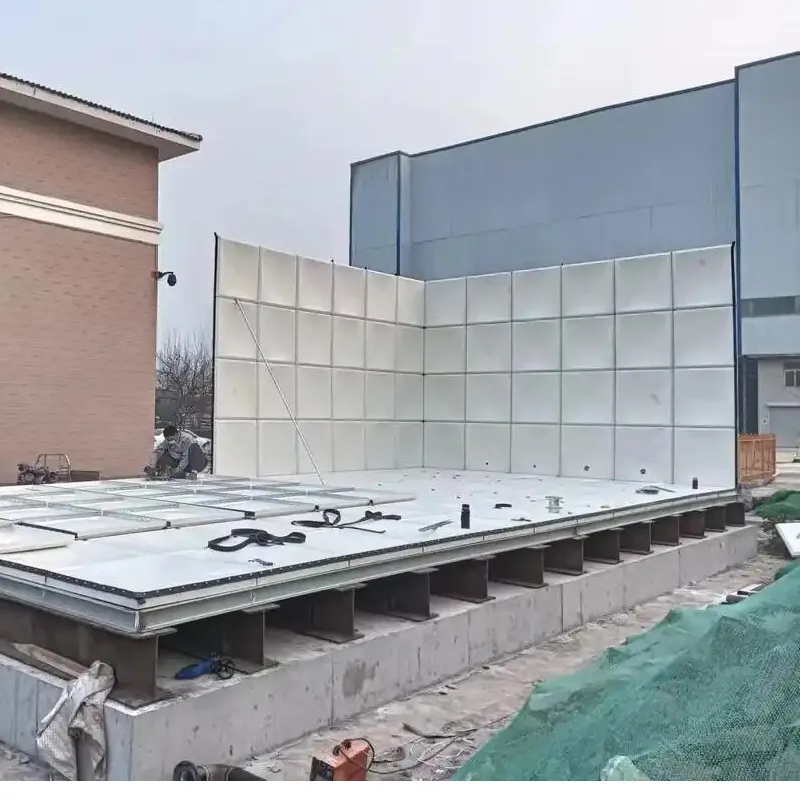
- 8.Installation & Maintenance
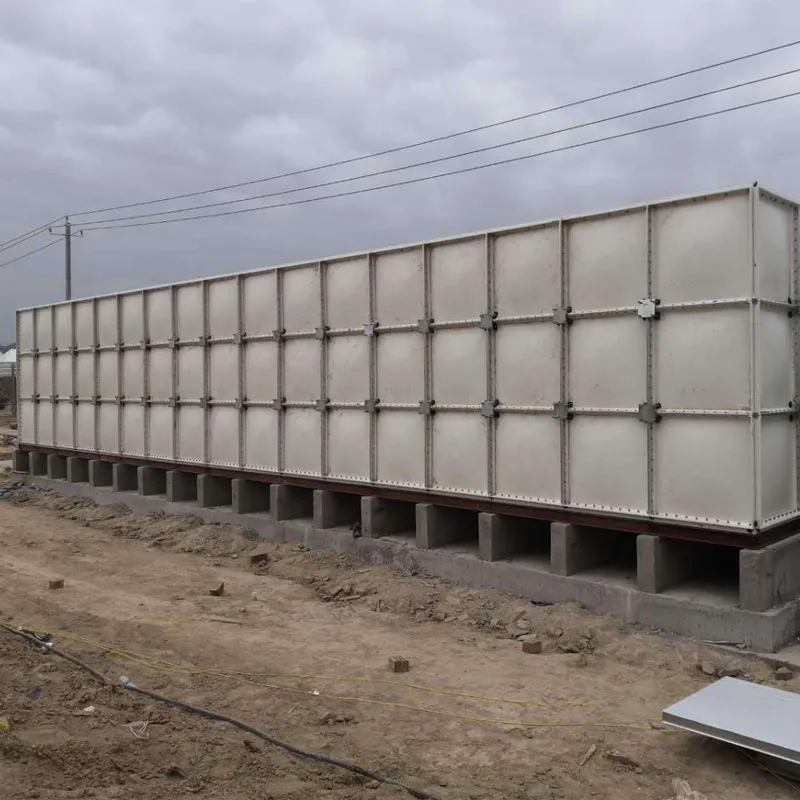
Foundation: Ensure flat, reinforced concrete base (load capacity ≥1.5× tank weight).
Anchoring: Use stainless steel straps for seismic/storm-prone areas.
Inspection:
Annual: Check for surface cracks, joint integrity, and liner wear.
5-Year: Hydrostatic testing for pressure vessels.
- 9.Cost Analysis
Initial Cost: 20–40% higher than PE tanks, but 50–70% lower than stainless steel.
Lifecycle Cost: 30–50% savings over 20 years due to zero corrosion maintenance.
- 10.Leading Manufacturers
ZCL Composites (Canada): Specializes in double-walled FRP tanks for fuel storage.
Liquid Containment (U.S.): NSF-certified tanks for water treatment.
Belco Manufacturing (U.S.): Custom FRP vessels for chemical processing.
Conclusion
FRP tanks provide unmatched durability and cost efficiency for corrosive and high-purity storage applications. When specifying FRP tanks, prioritize resin compatibility with stored media, validate structural calculations for seismic loads, and adhere to industry standards (e.g., ASME RTP-1). For aggressive chemicals (e.g., HF acid), consult manufacturers for specialized liner materials like PVDF or PTFE.
For detailed quotations or engineering drawings, provide operational parameters (chemical composition, temperature, capacity) and site-specific requirements.
Let me know if you need additional details on resin selection, retrofitting existing systems, or failure case studies!
What Our Customers Say About FRP Water Tank
Frp Water Tank FAQ
-
Q: What is an FRP water tank?
A: An FRP water tank is a storage tank made from fiberglass reinforced plastic, designed to store both potable and non-potable water.
-
Q: What are the advantages of using an FRP water tank?
A: FRP water tanks are corrosion-resistant, lightweight, and have a long lifespan with minimal maintenance.
-
Q: Where are FRP water tanks typically used?
A: They are used in industrial water storage, agriculture, and municipal water systems.
-
Q: How do FRP water tanks compare to other types of water tanks?
A: FRP water tanks offer better durability, resistance to chemicals, and long-term cost-effectiveness compared to steel or concrete tanks.







Address
20 Xingyuan South Street, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province, China