We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
Introduzione tecnica alla torre di raffreddamento dell'aria condizionata
1. Overview
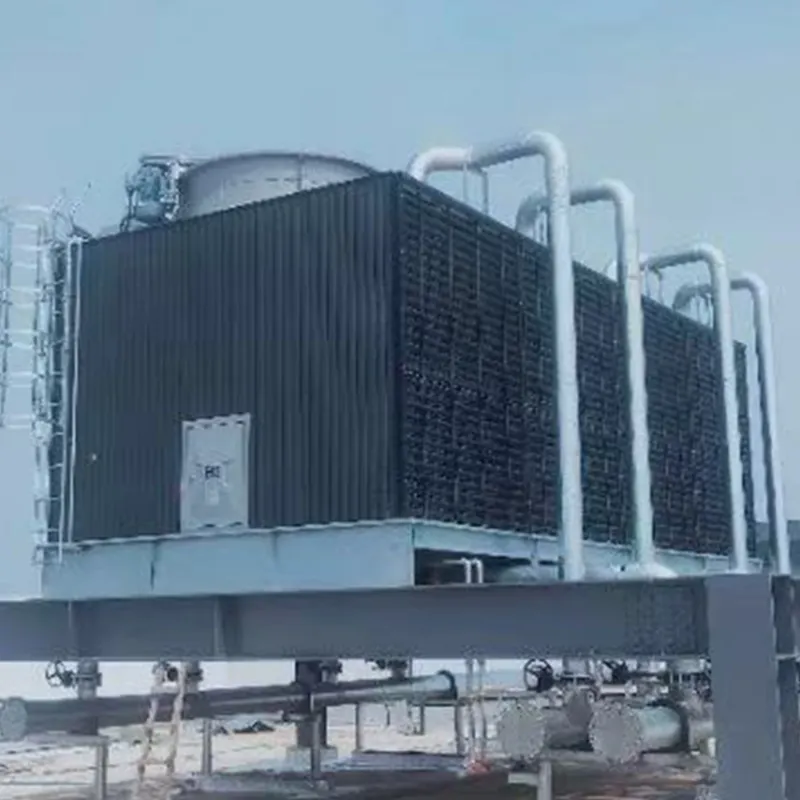
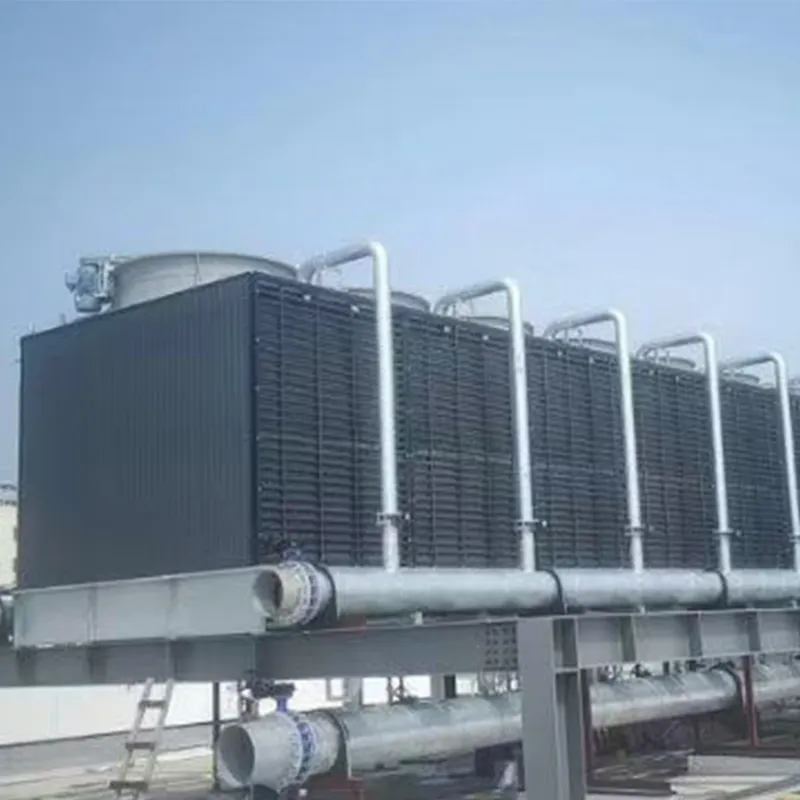
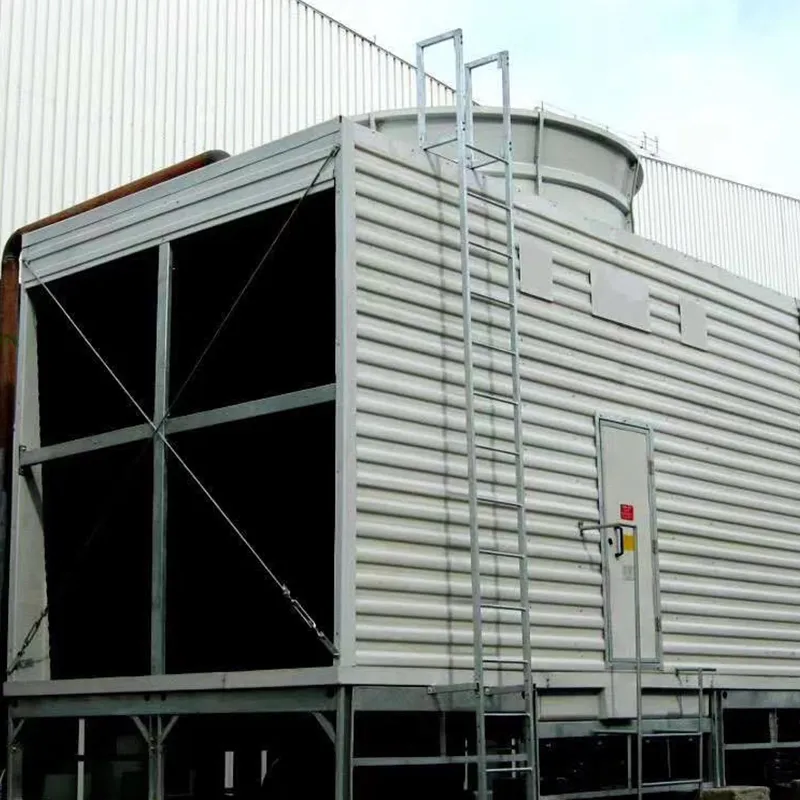
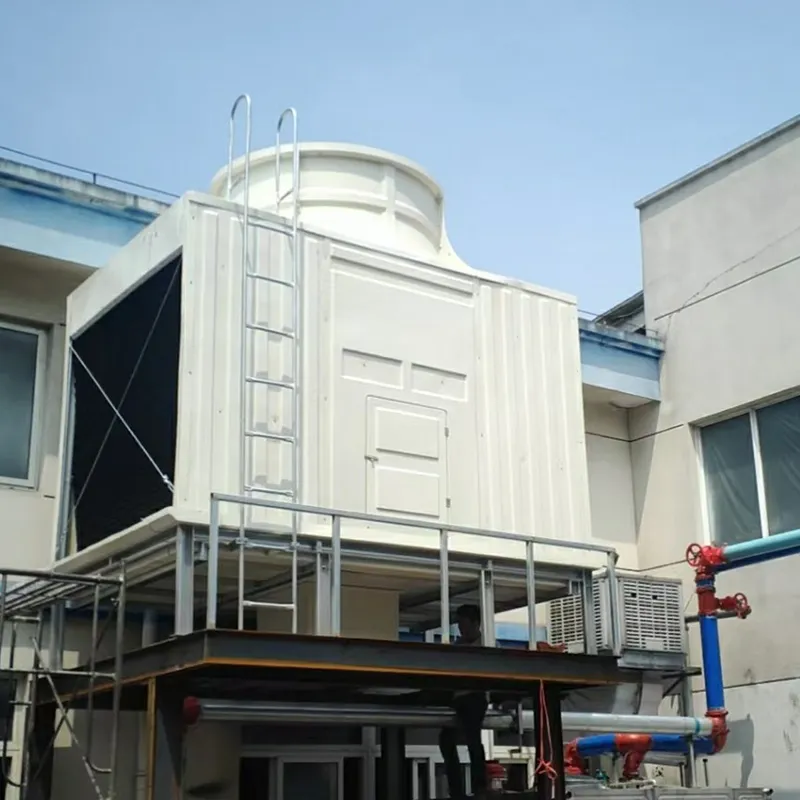
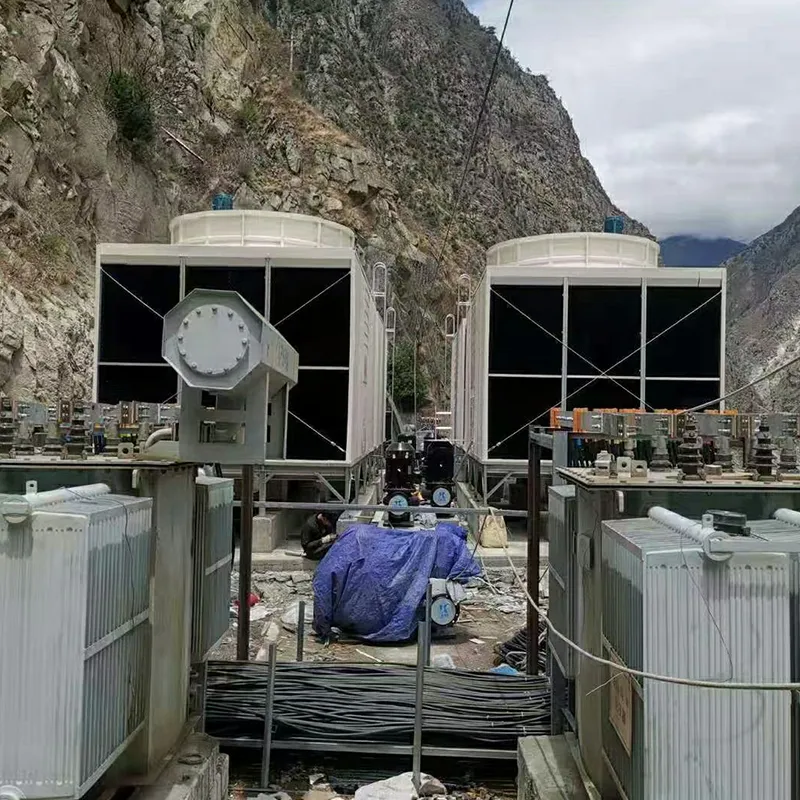
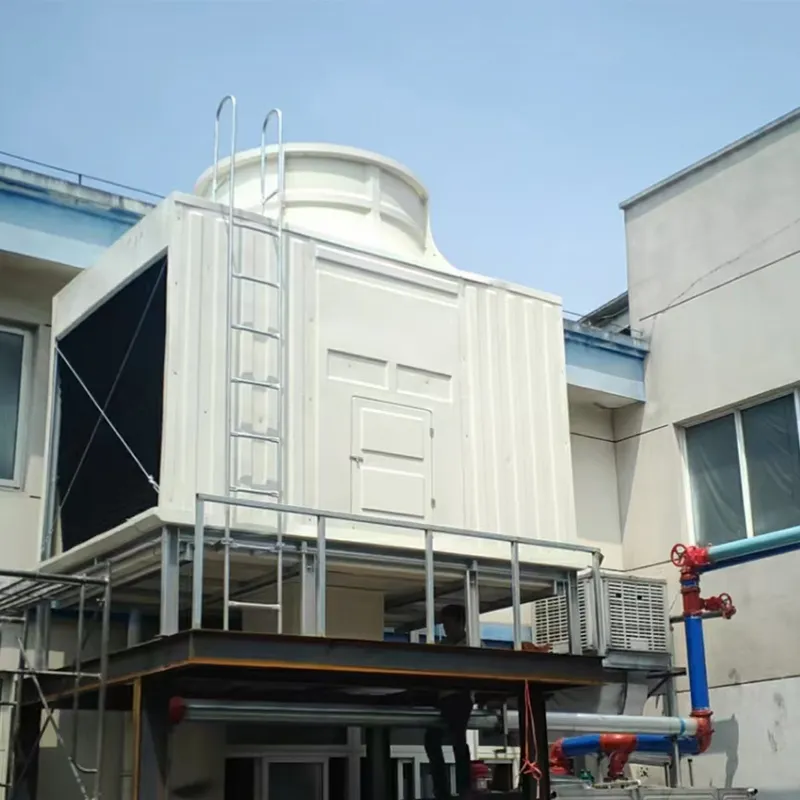
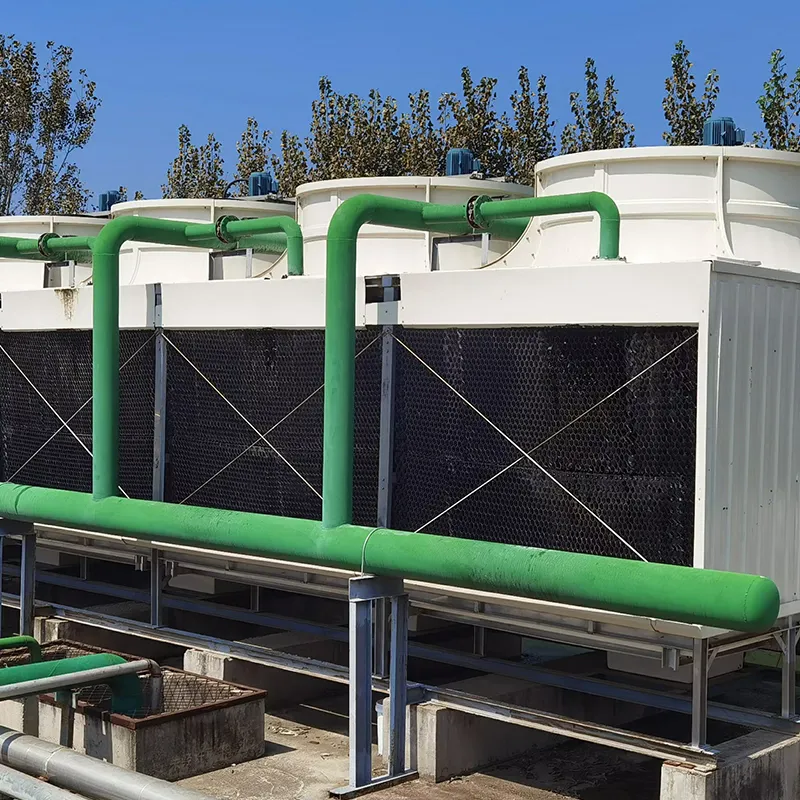
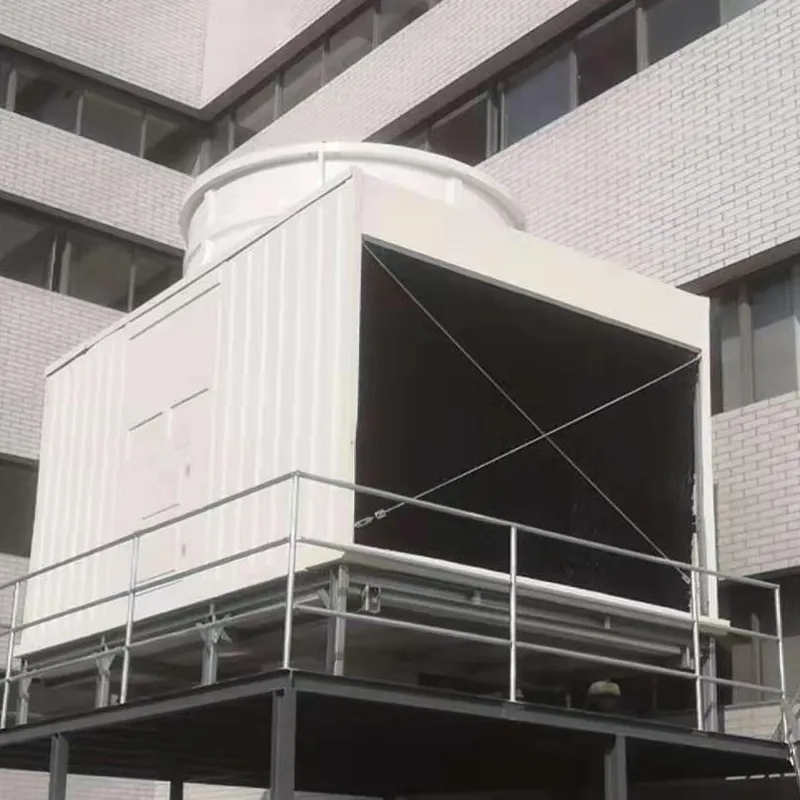
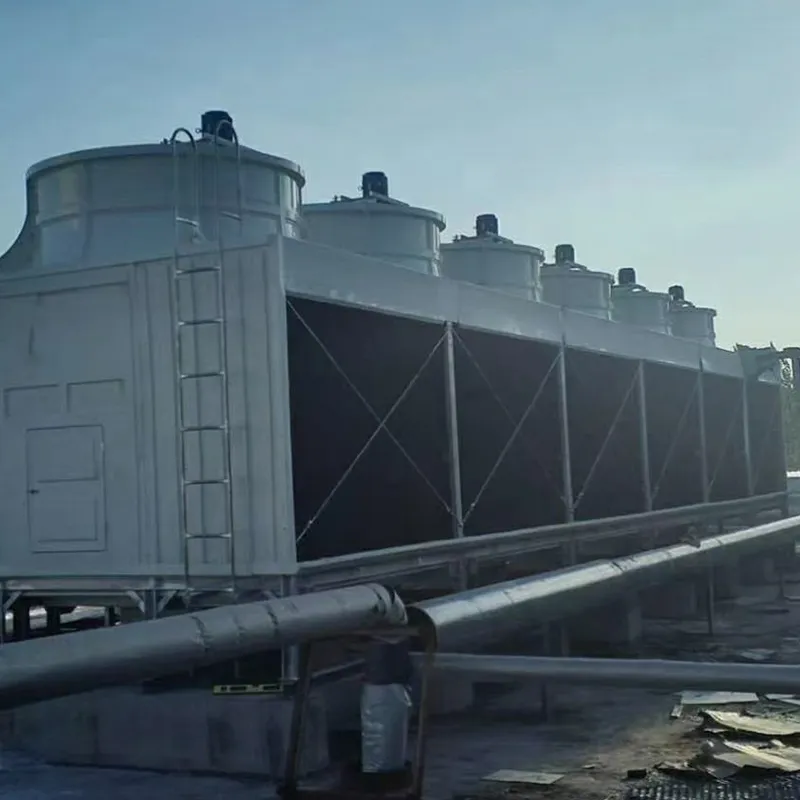
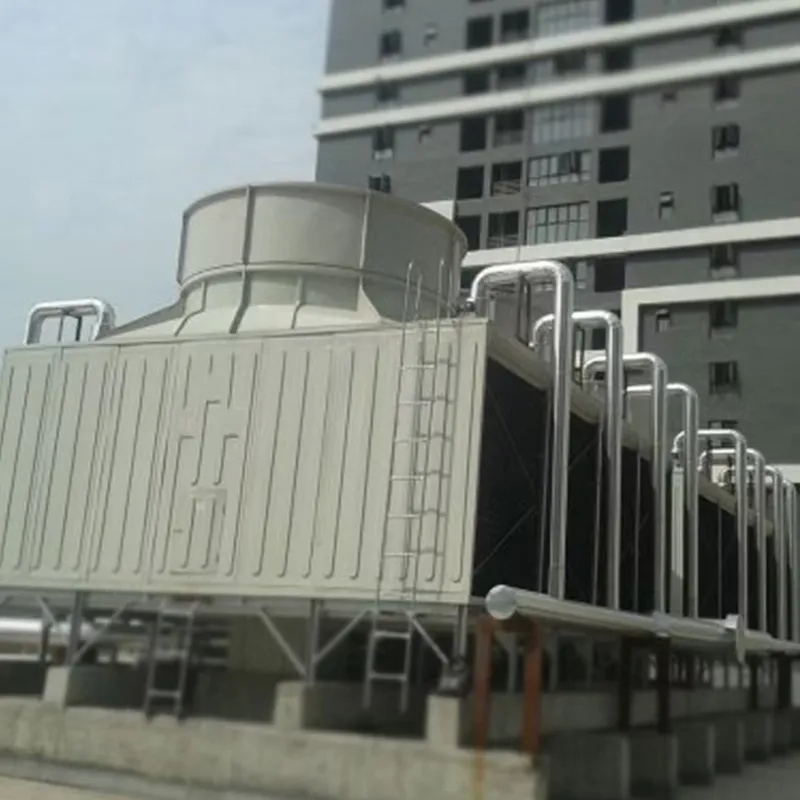
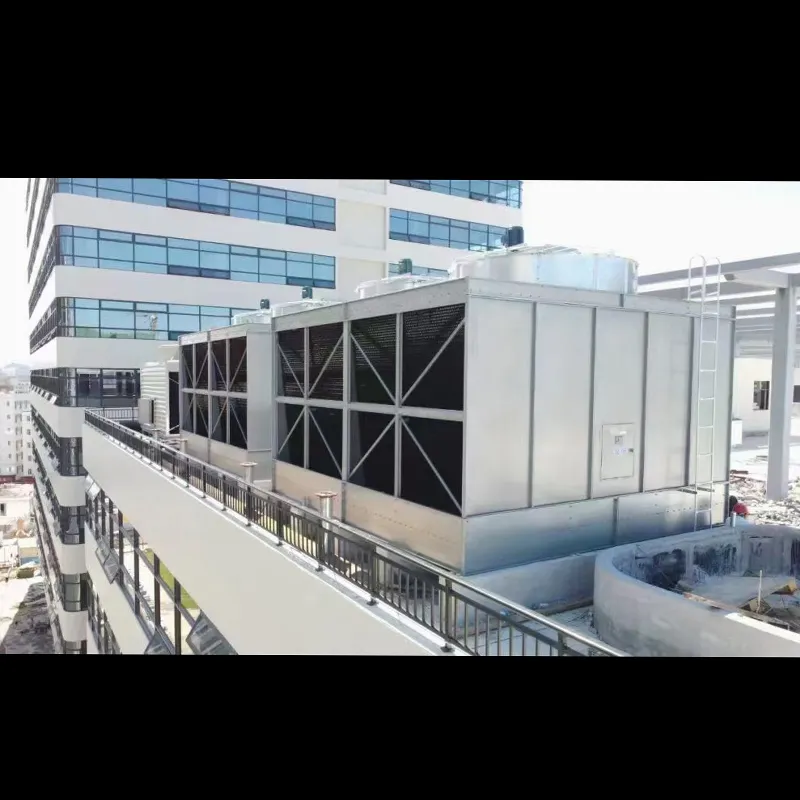
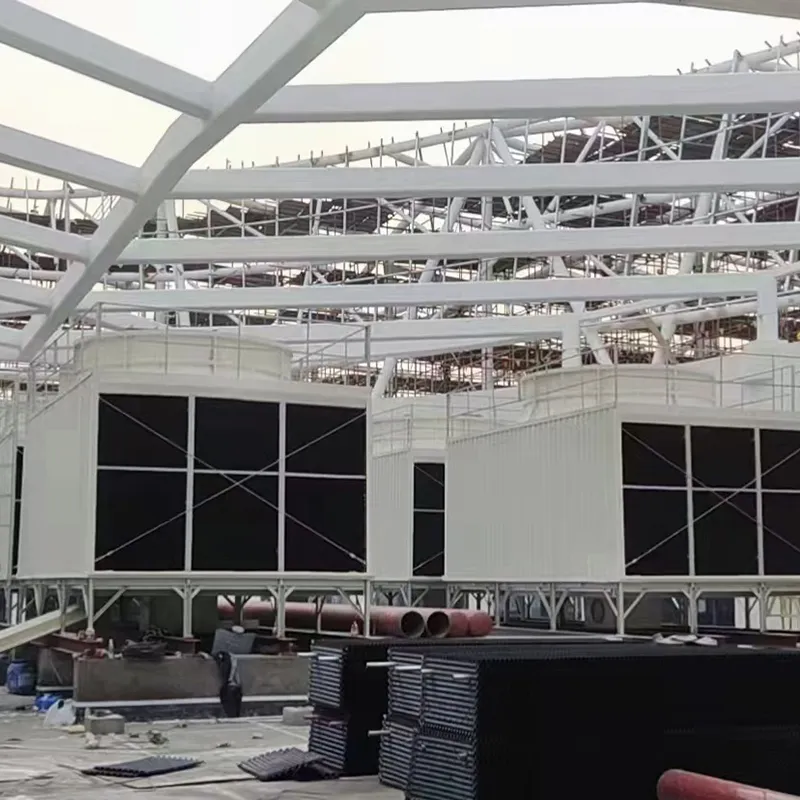
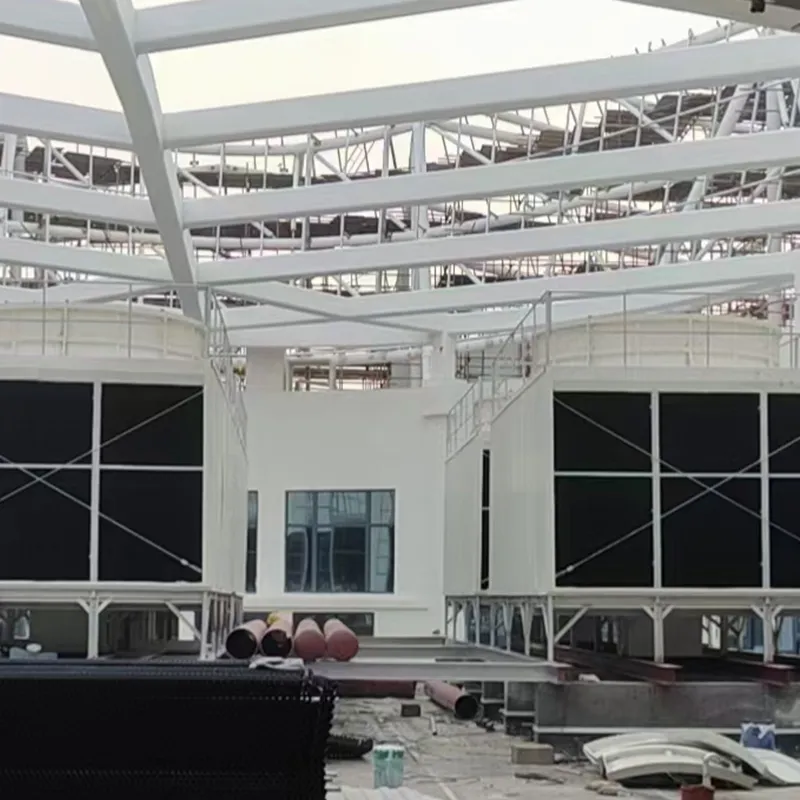
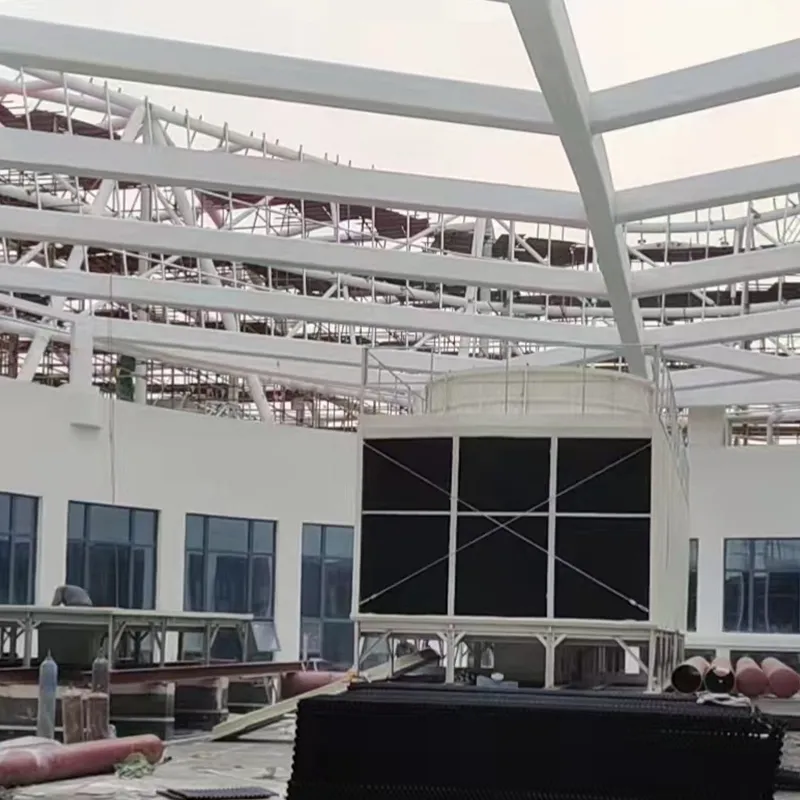
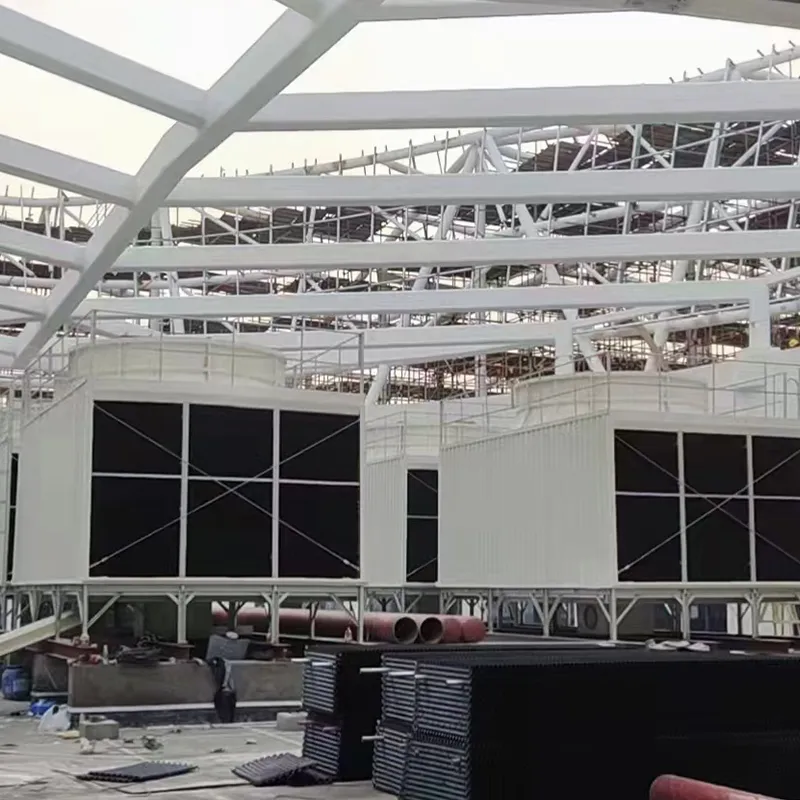
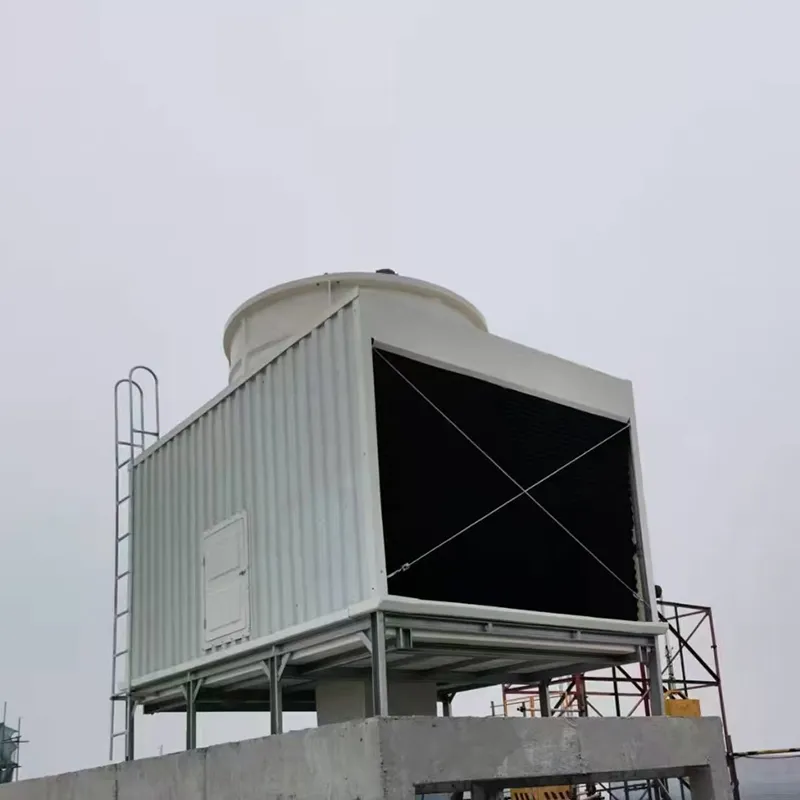
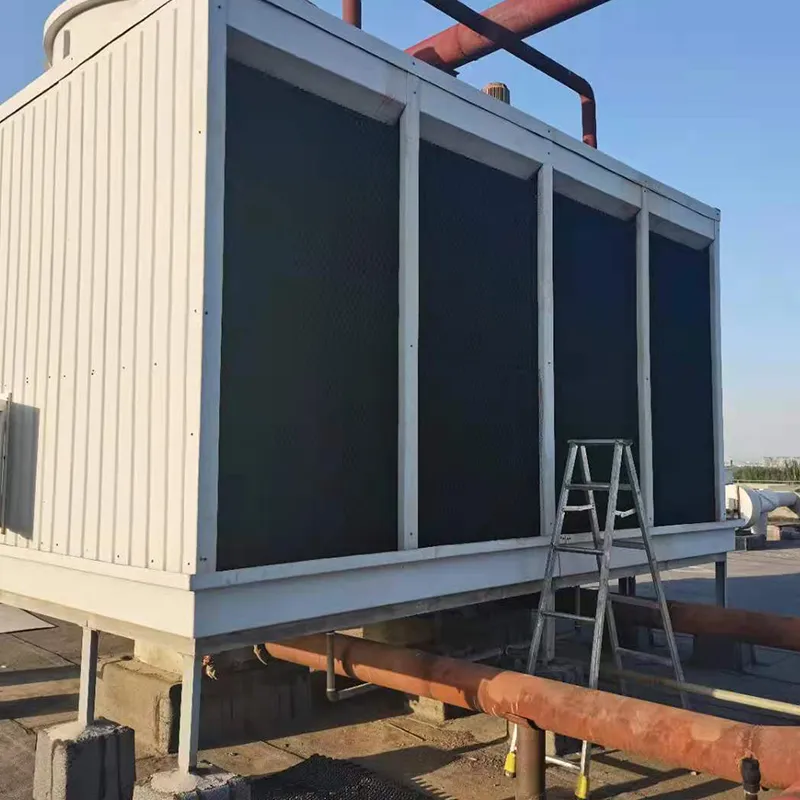
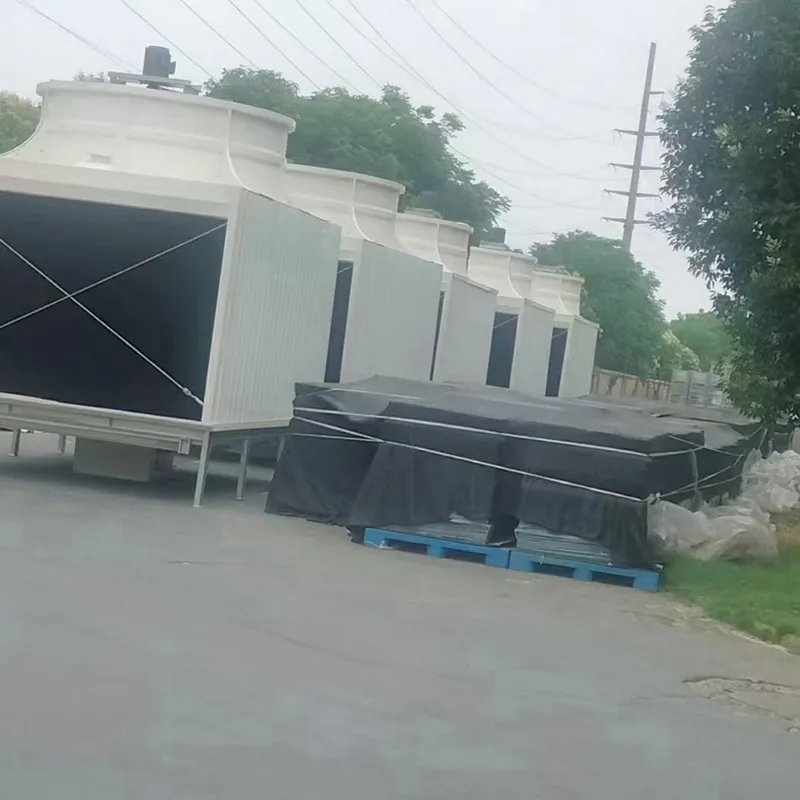
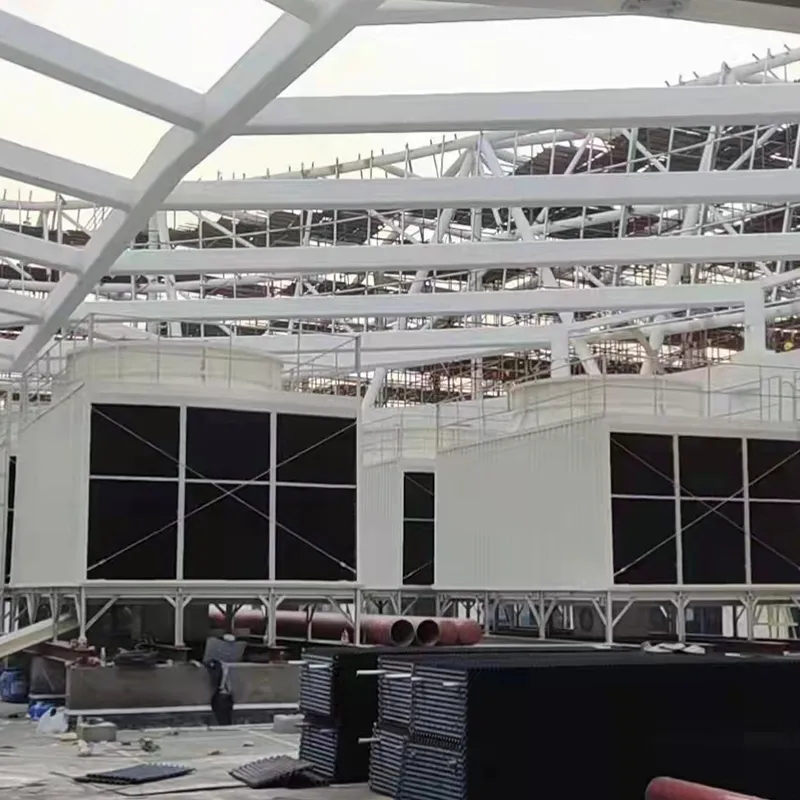
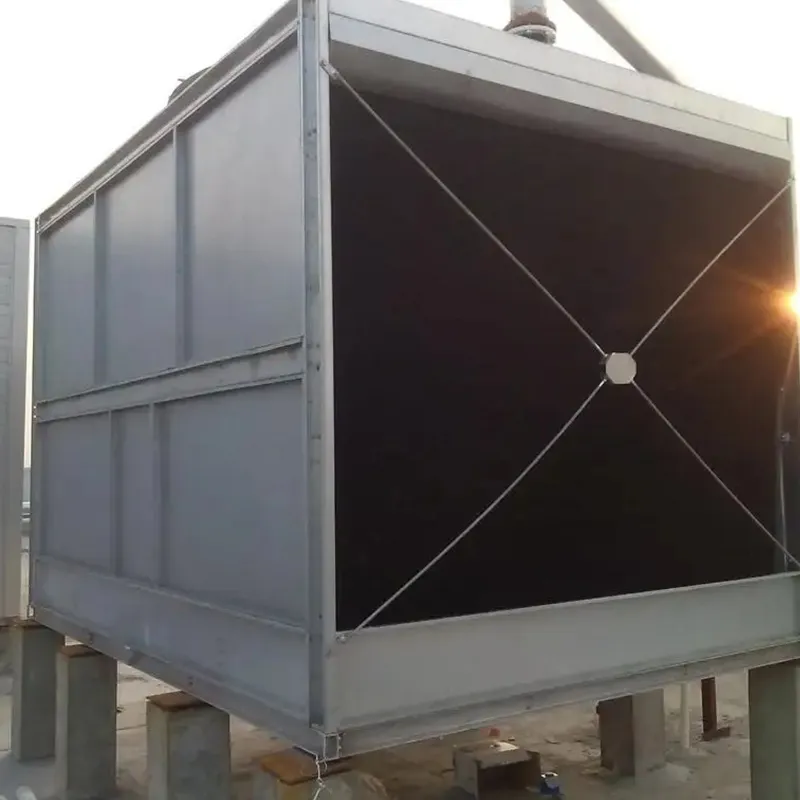
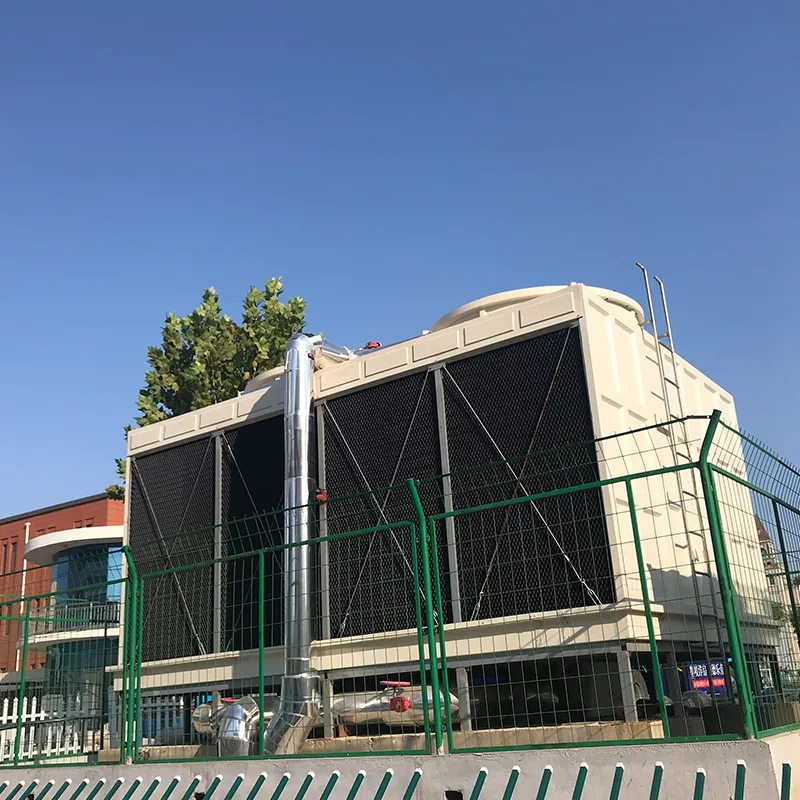
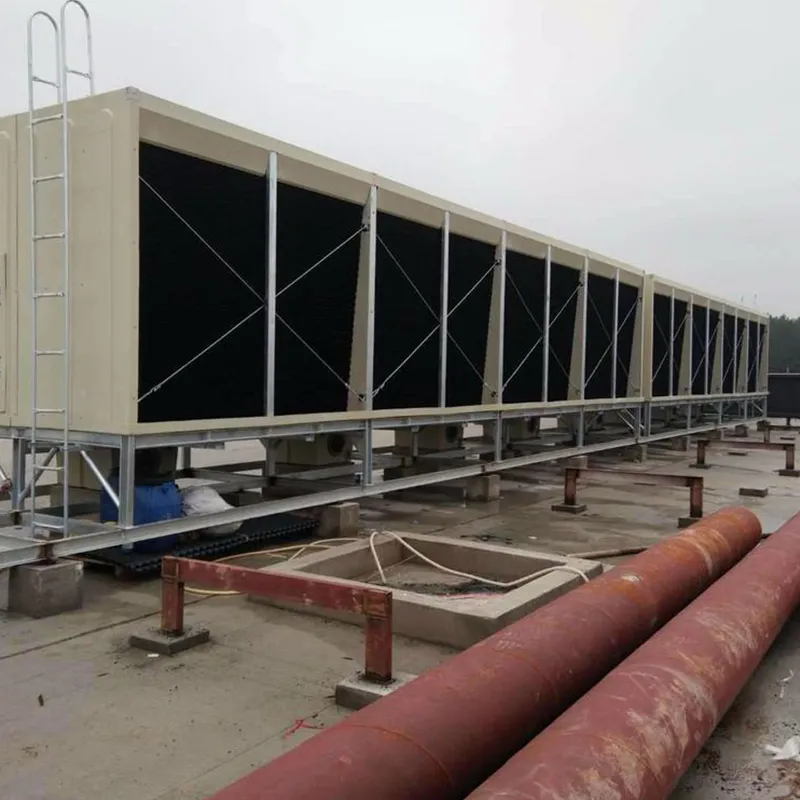
An air conditioning cooling tower is a critical heat rejection component in central HVAC systems, designed to dissipate waste heat from condensers into the atmosphere via **evaporative cooling**. It ensures efficient operation of refrigeration cycles and is widely used in commercial buildings (e.g., offices, hospitals, hotels) and industrial facilities (e.g., data centers). Key design considerations include chiller capacity, ambient wet-bulb temperature, and spatial constraints.
2. Principio di funzionamento
1. Hot Water Inlet: Hot water (typically 37°C) from the chiller condenser enters the cooling tower.
2. Water Distribution: Spray nozzles evenly distribute water over the fill media.
3. Air-Water Heat Exchange: Fans drive air to interact with water in counterflow or crossflow configurations, enabling evaporative cooling.
4. Cooled Water Return: Chilled water (≈32°C) recirculates to the condenser.
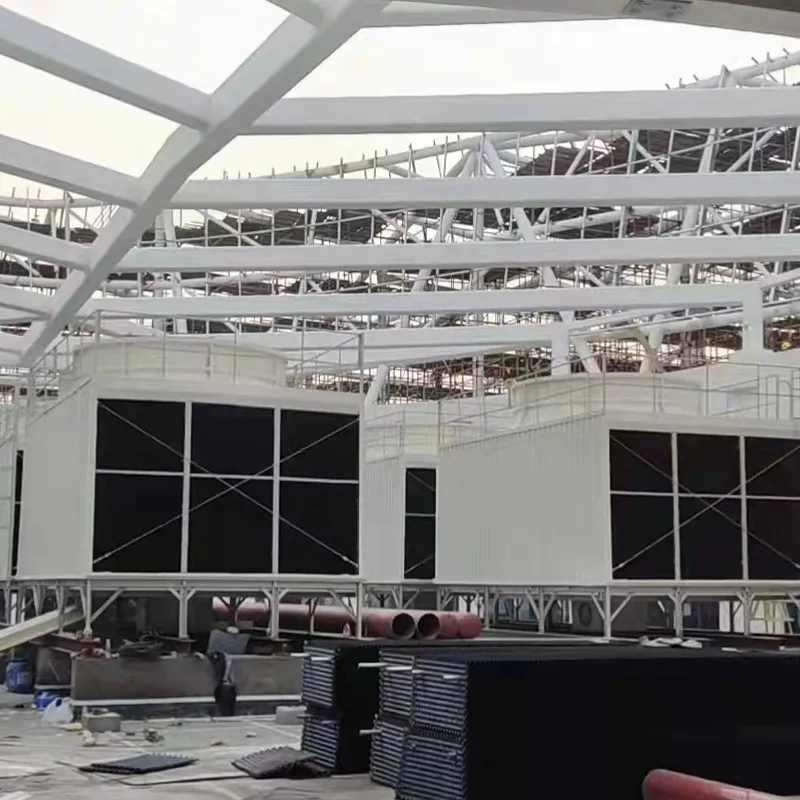
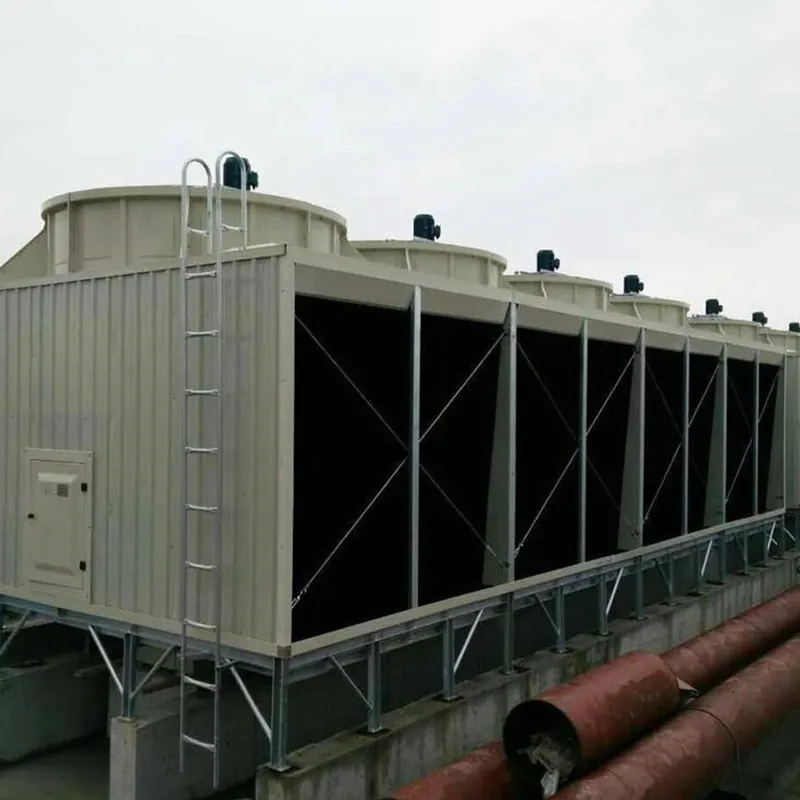
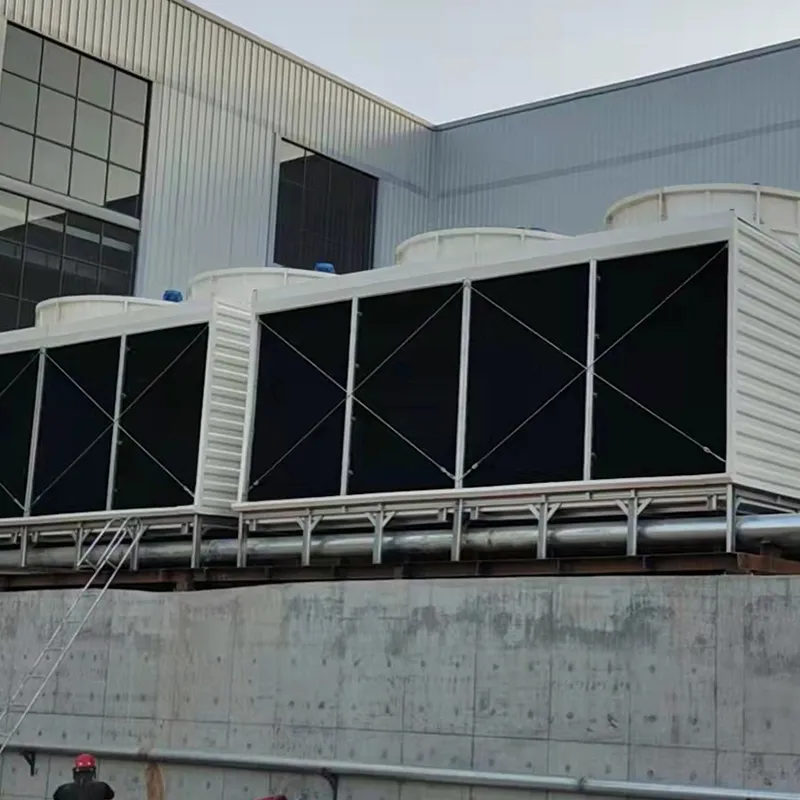
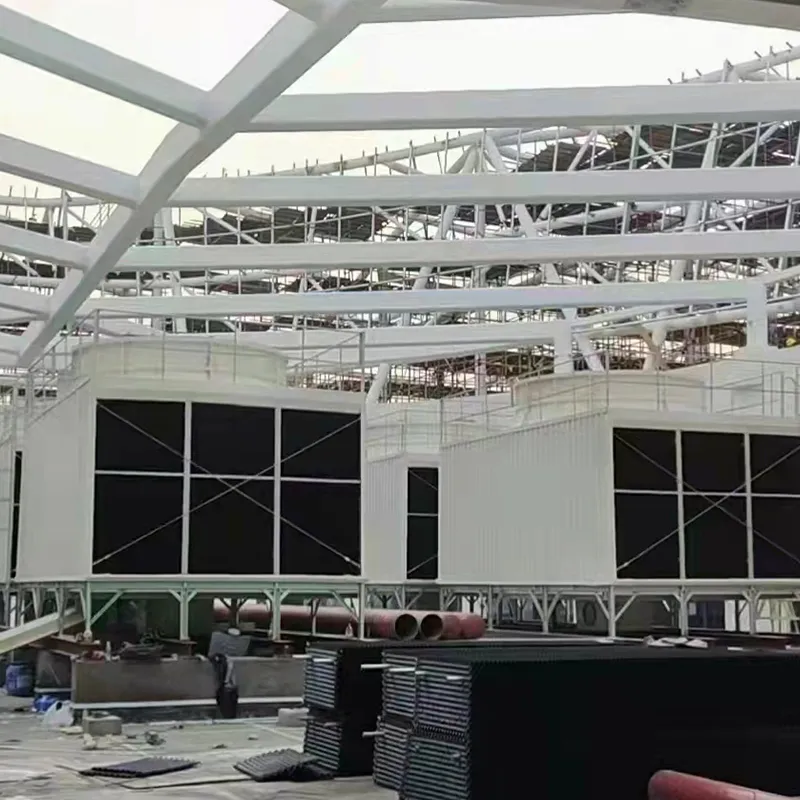
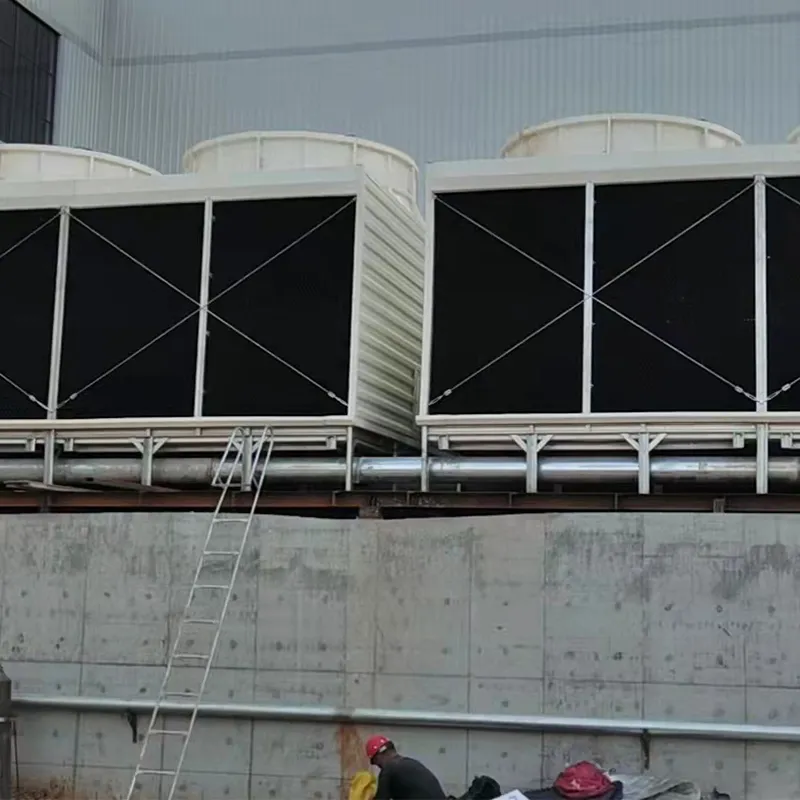
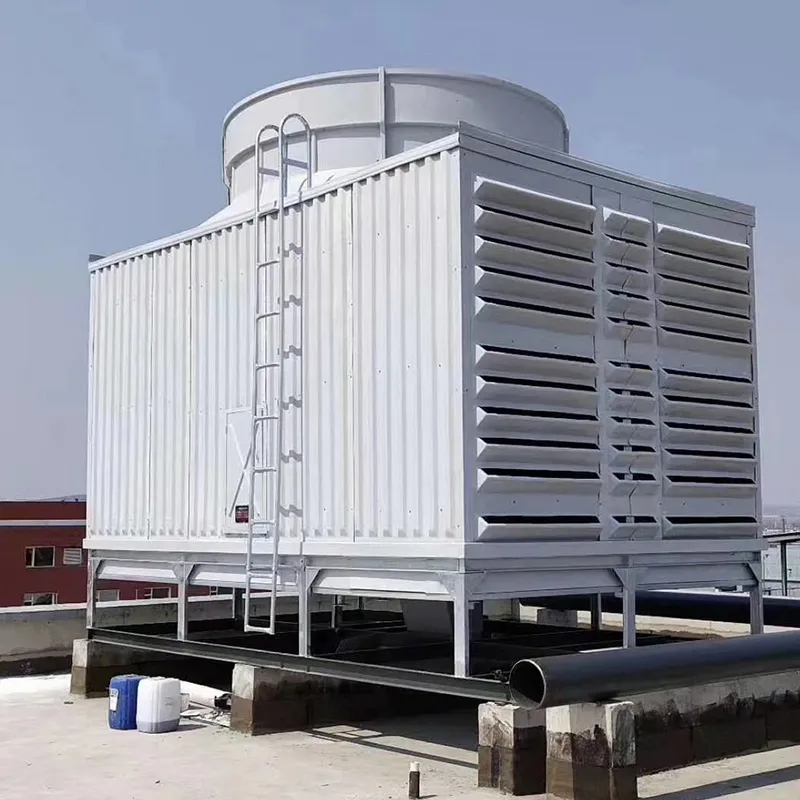
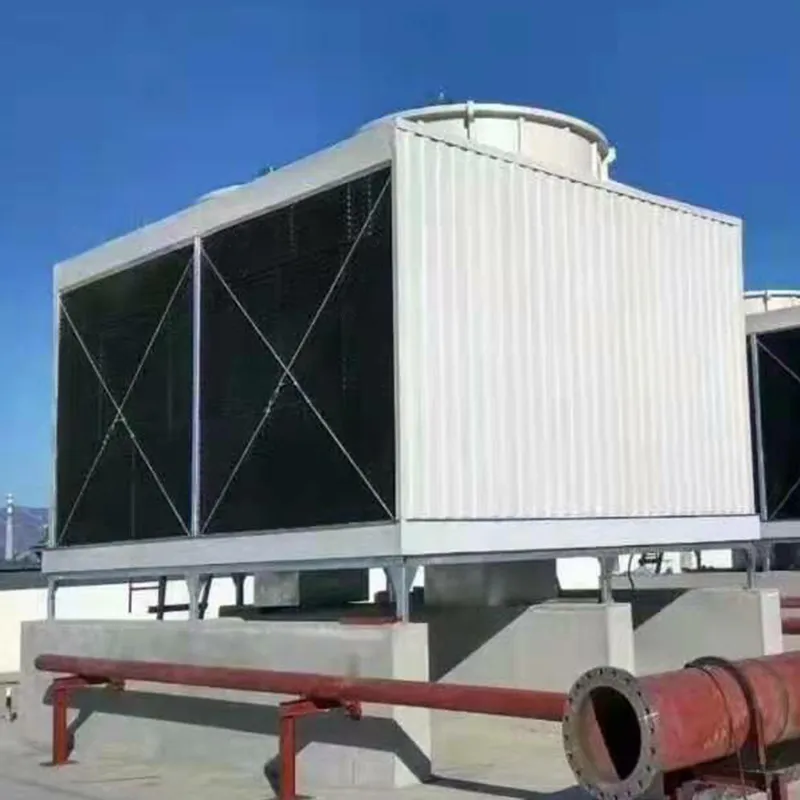
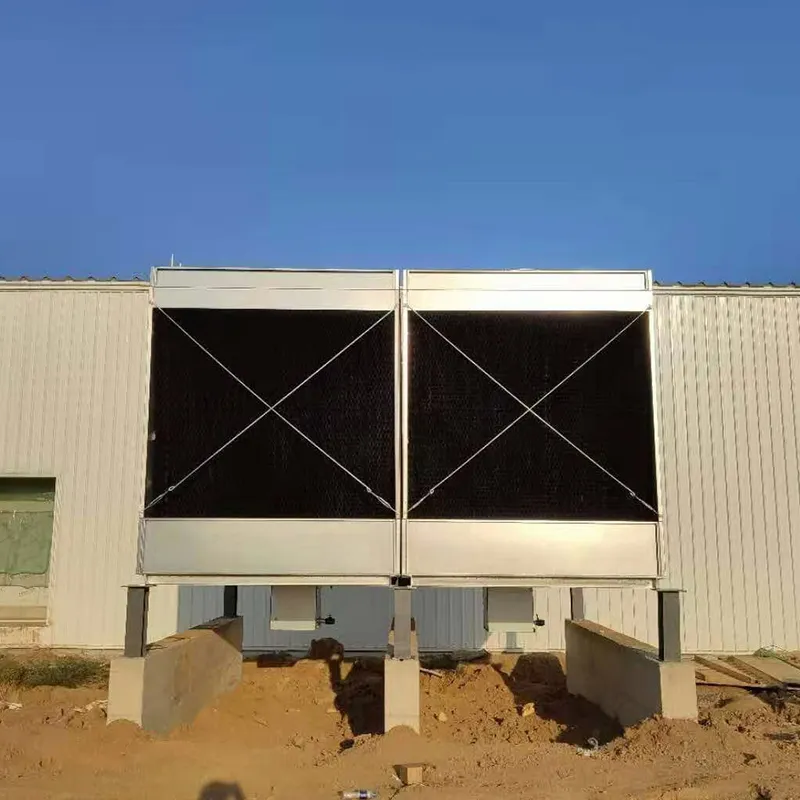
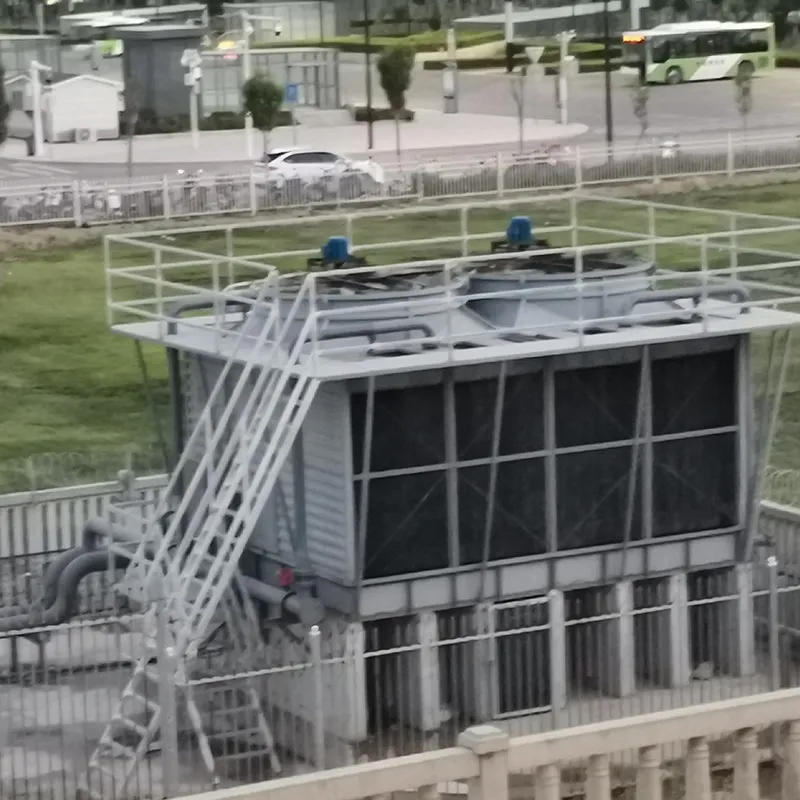
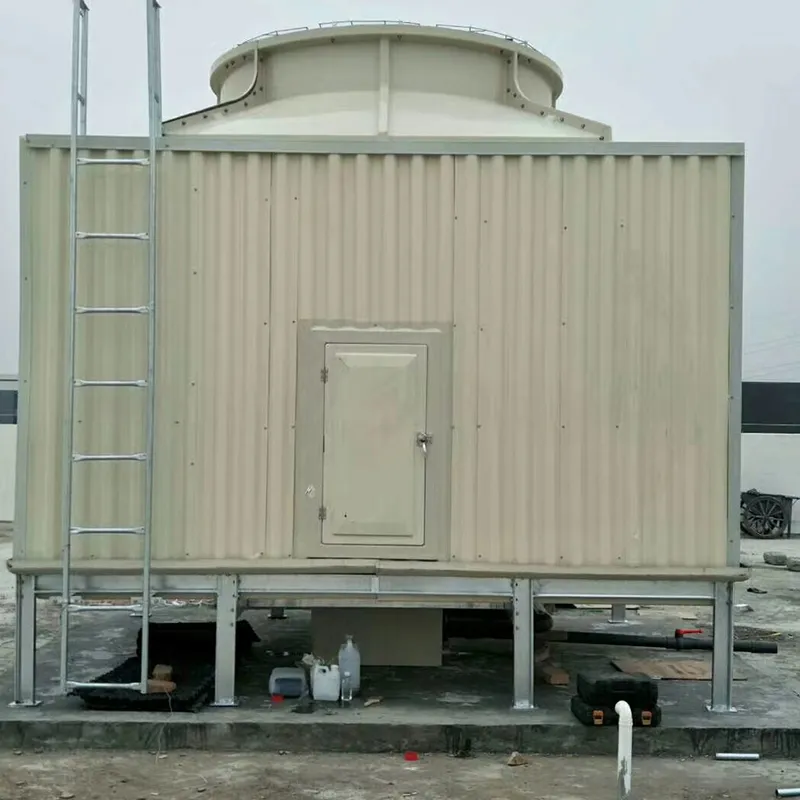
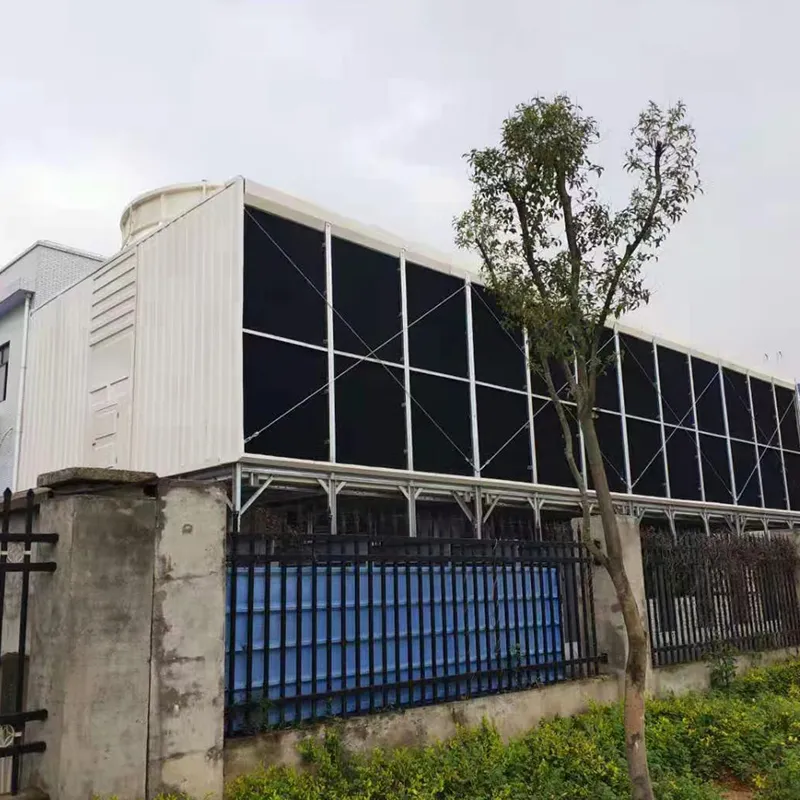
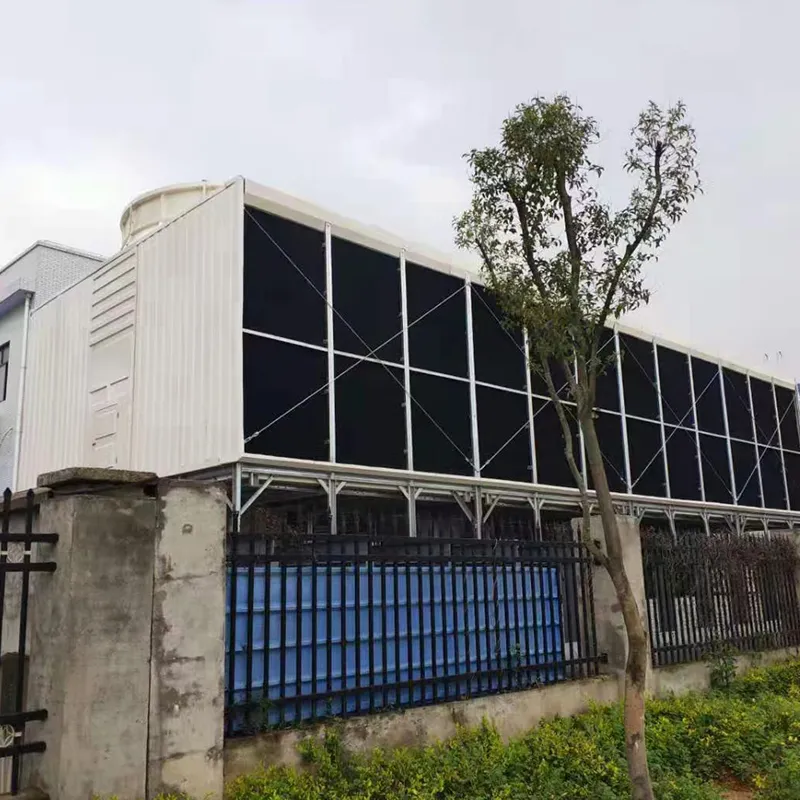
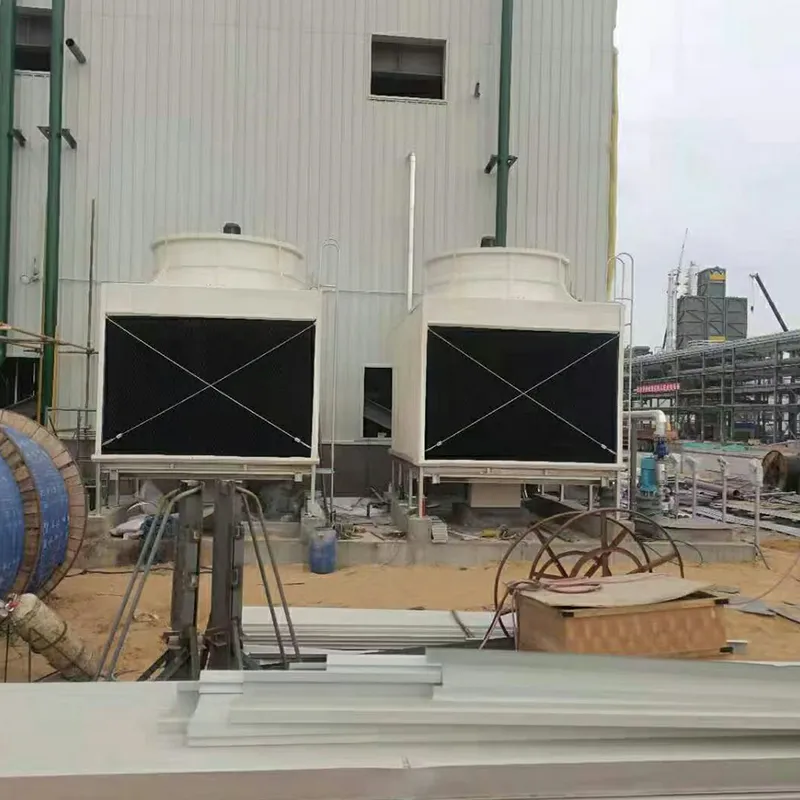
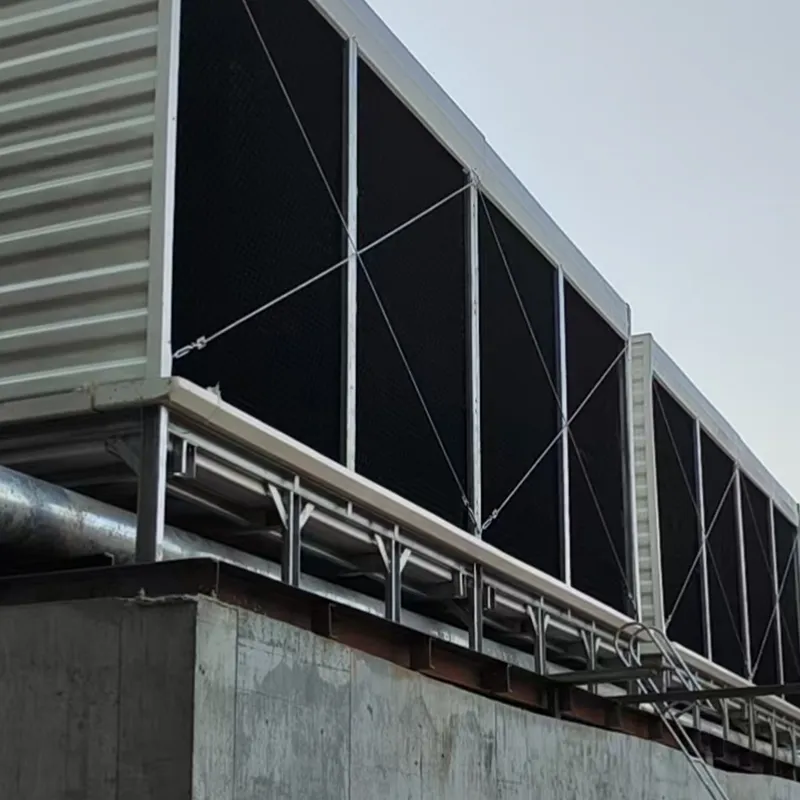
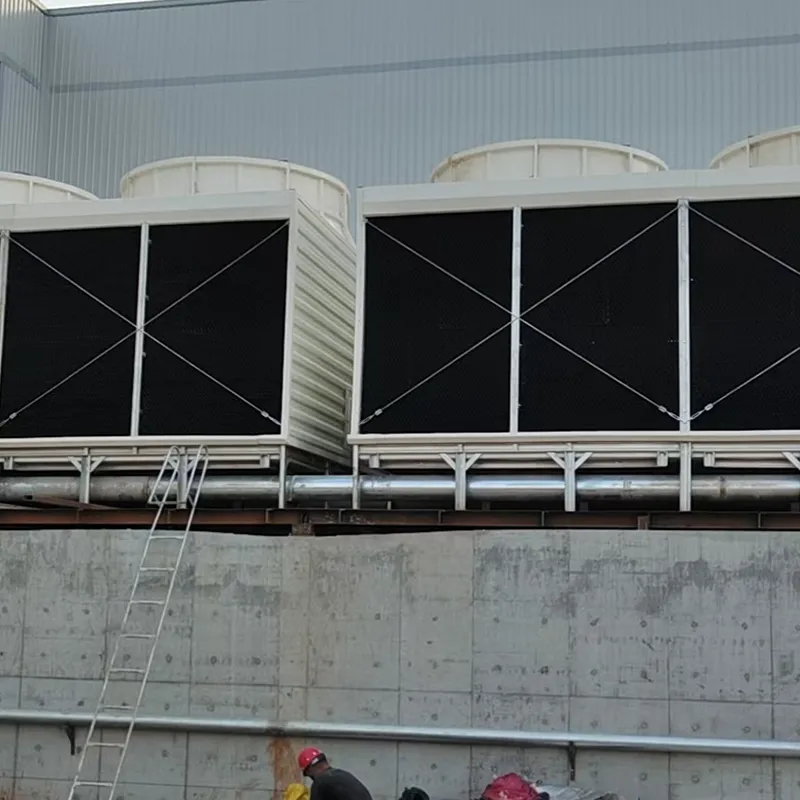
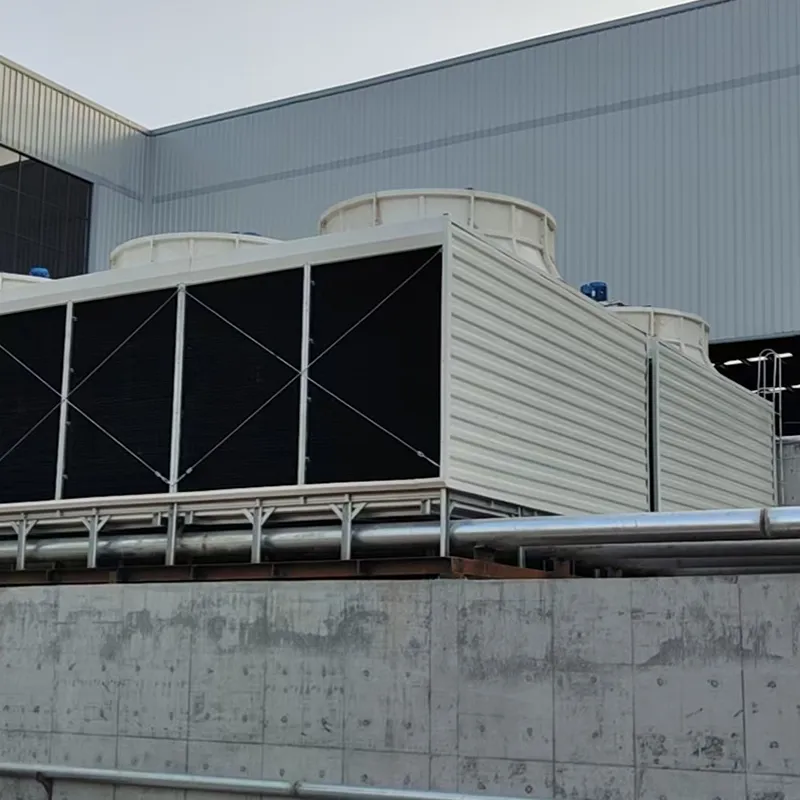
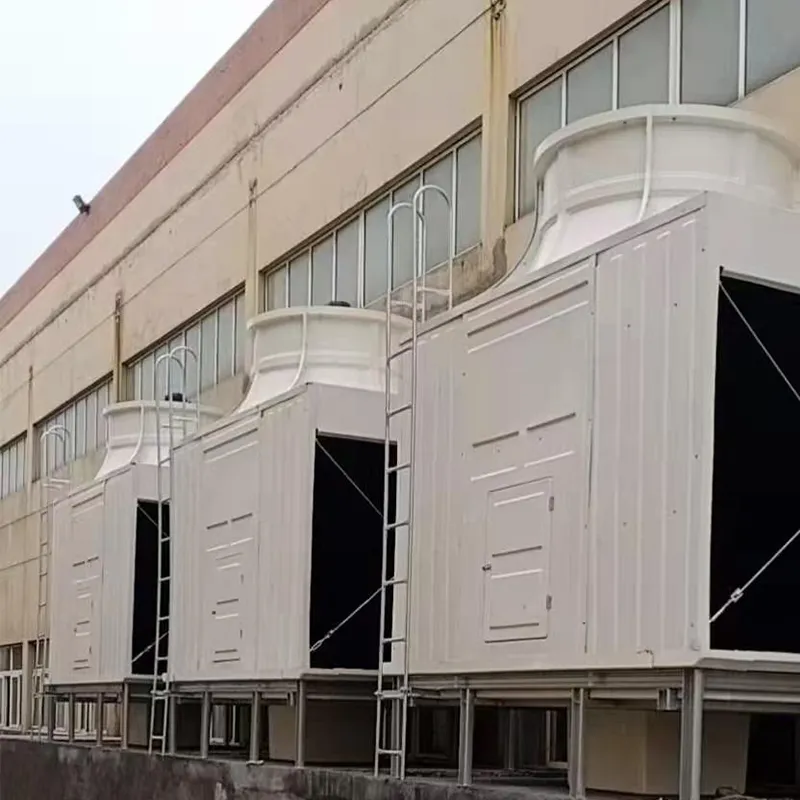
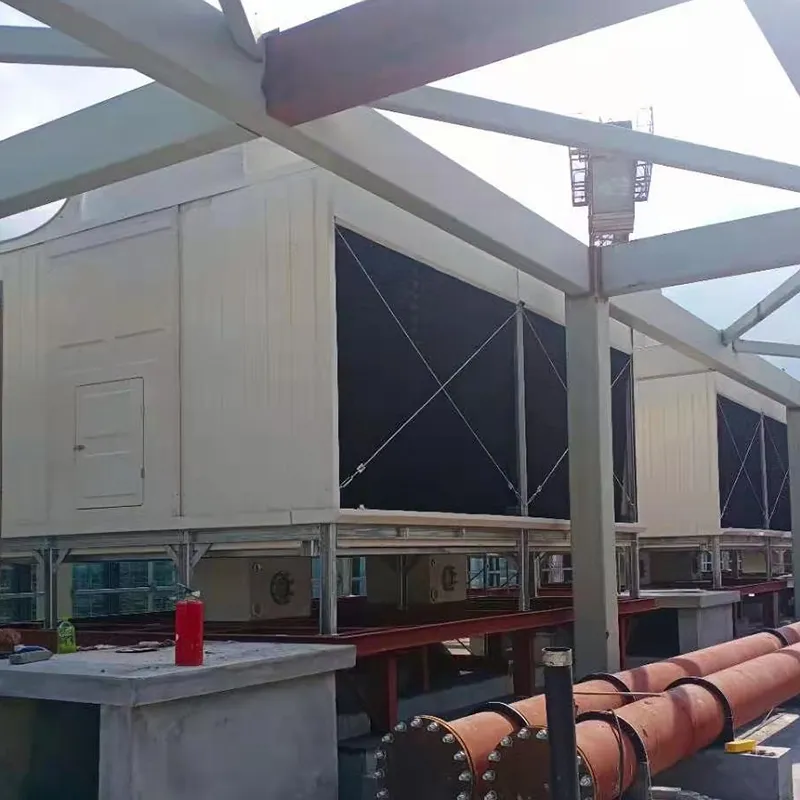
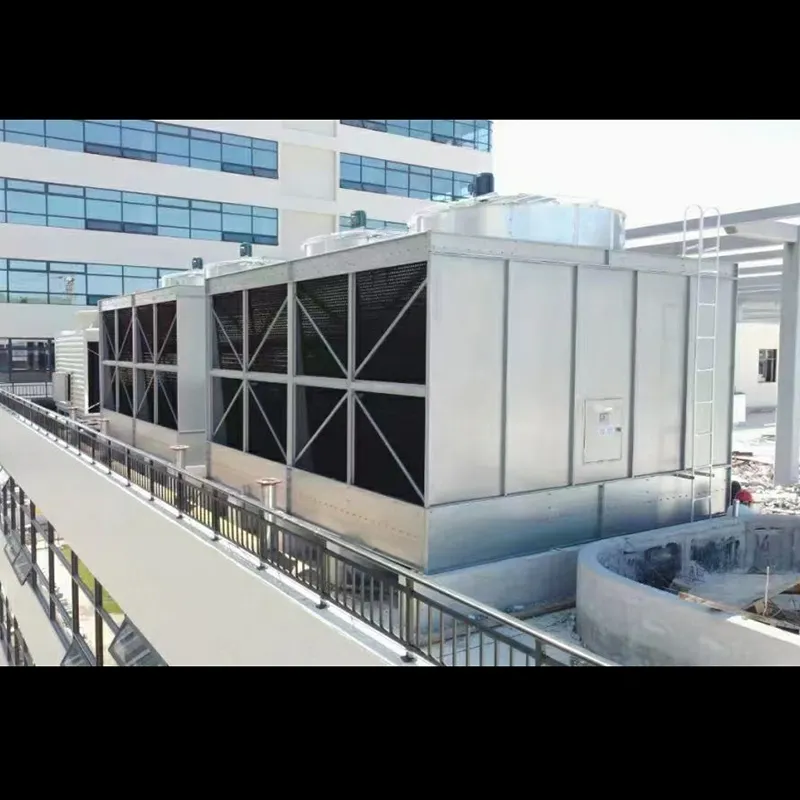
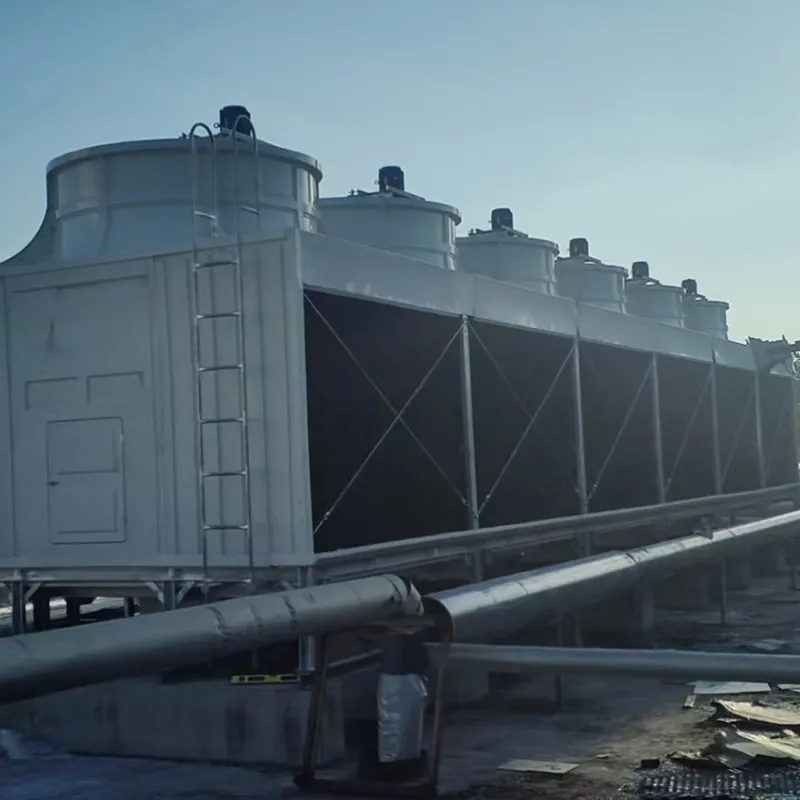
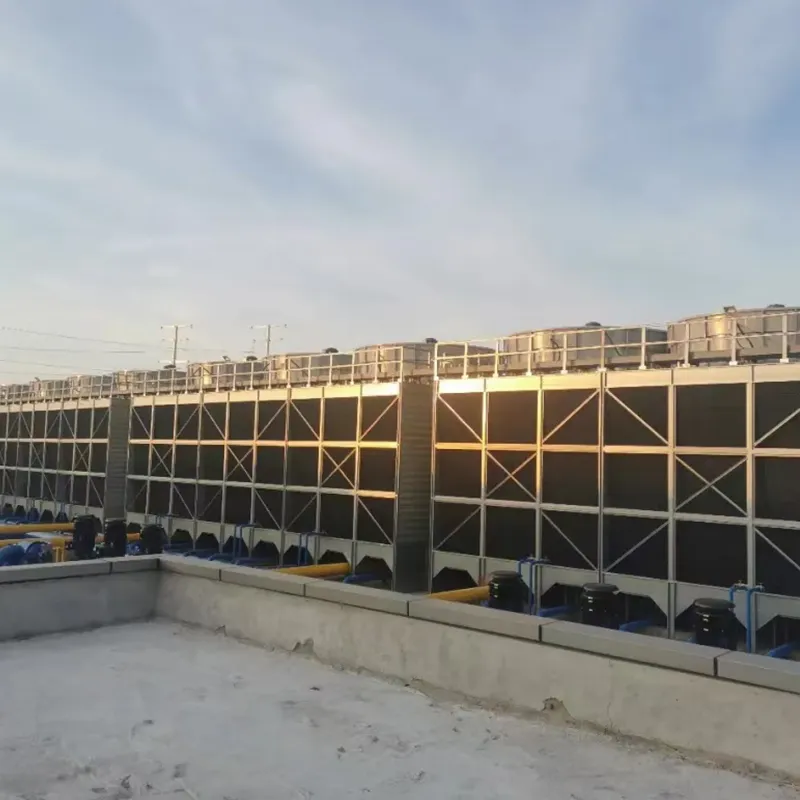
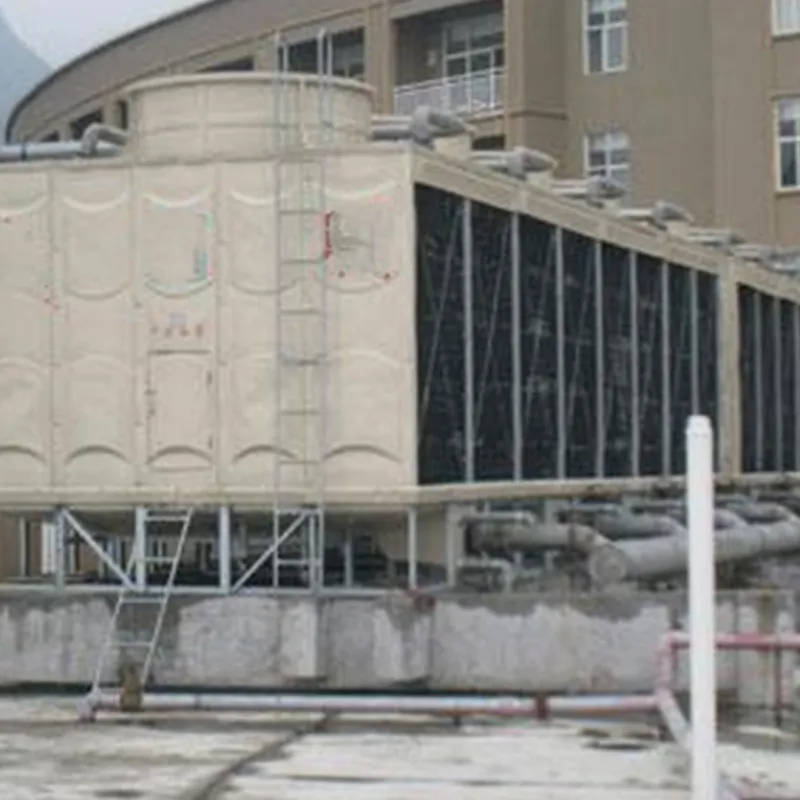
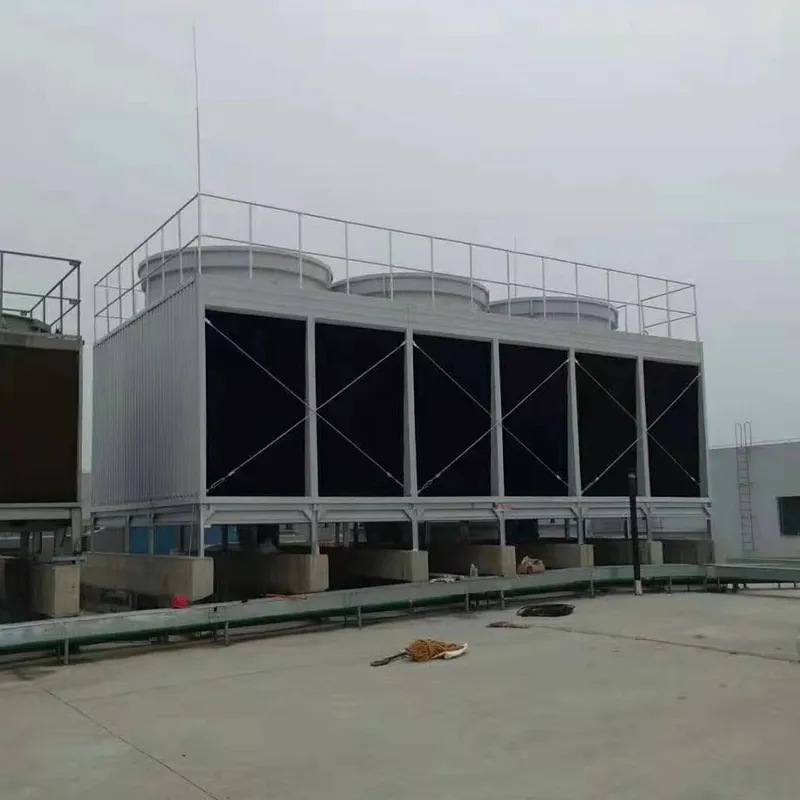
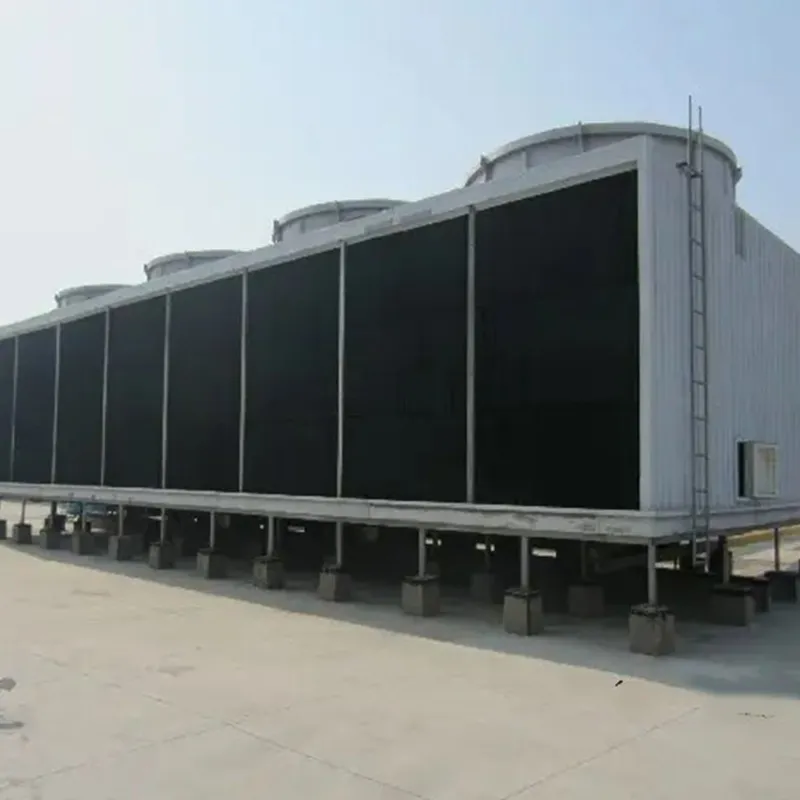
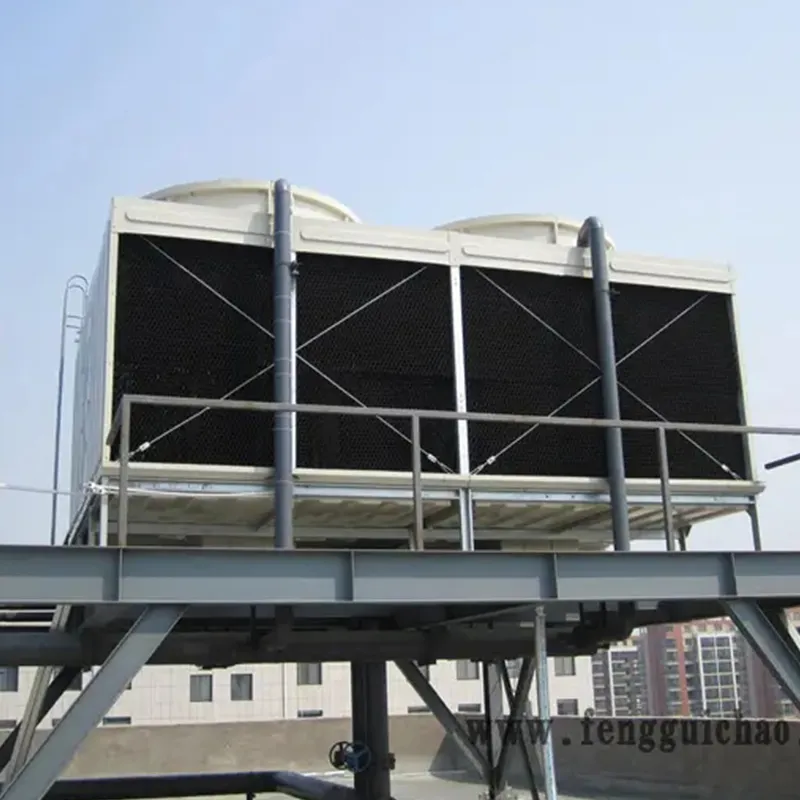
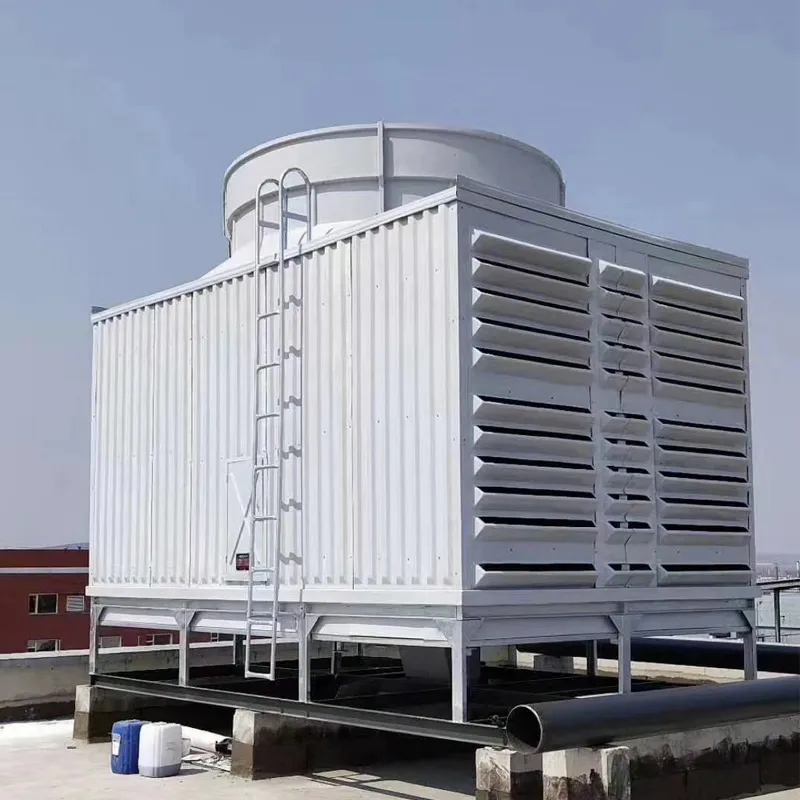
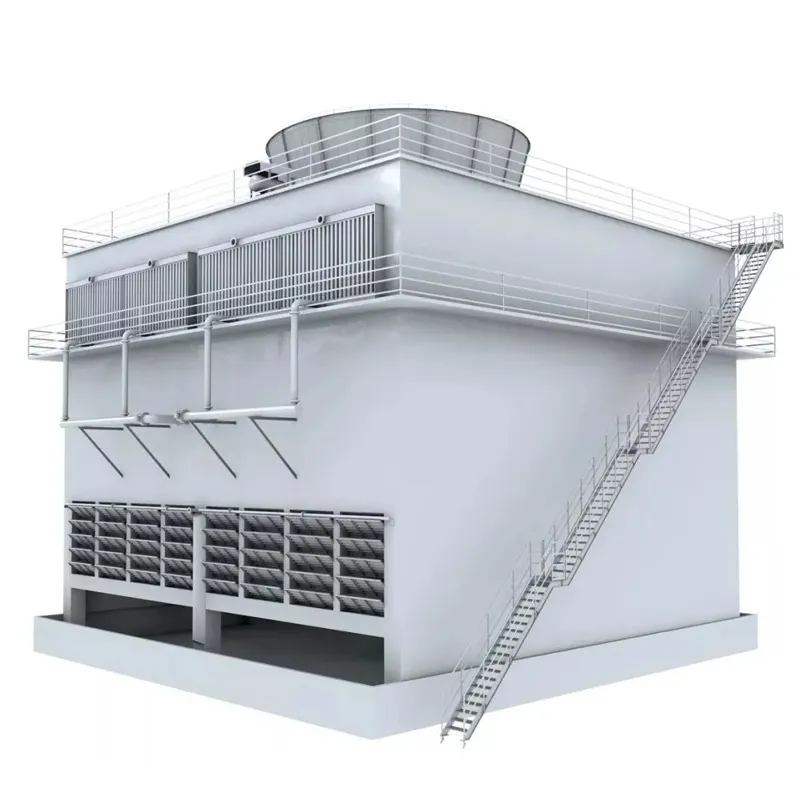
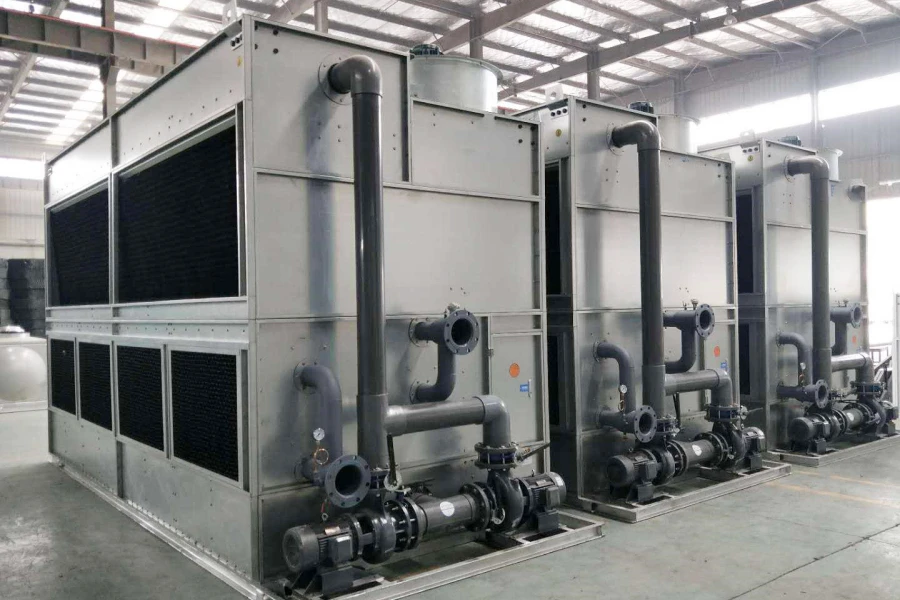
3. Tipi di torri di raffreddamento
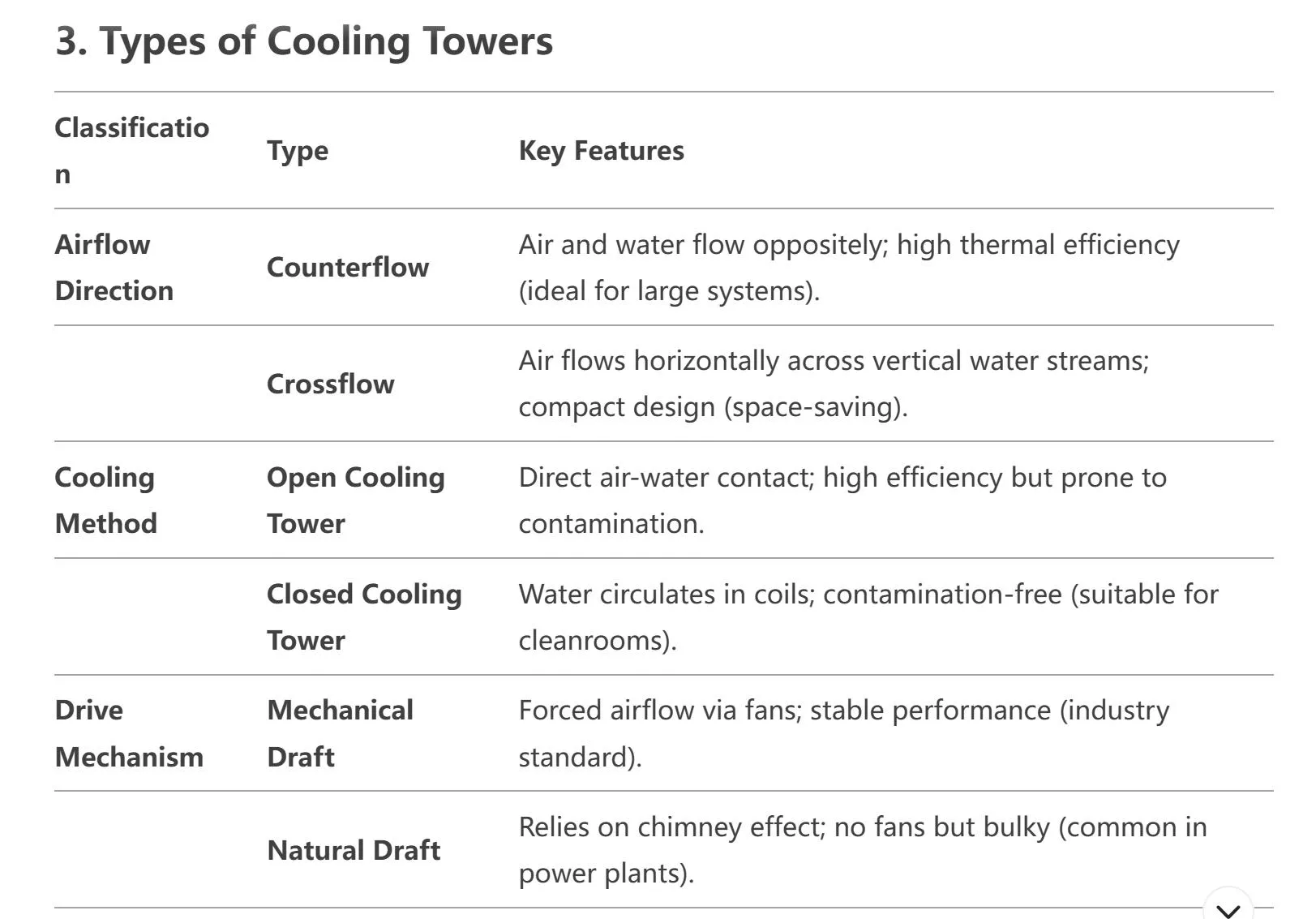
4. Componenti chiave e progettazione
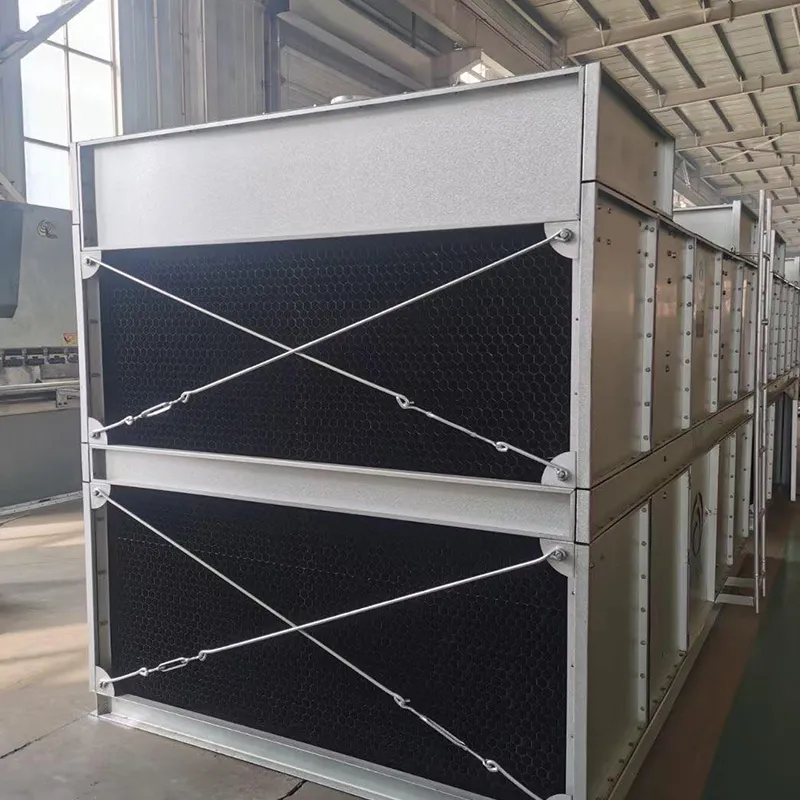
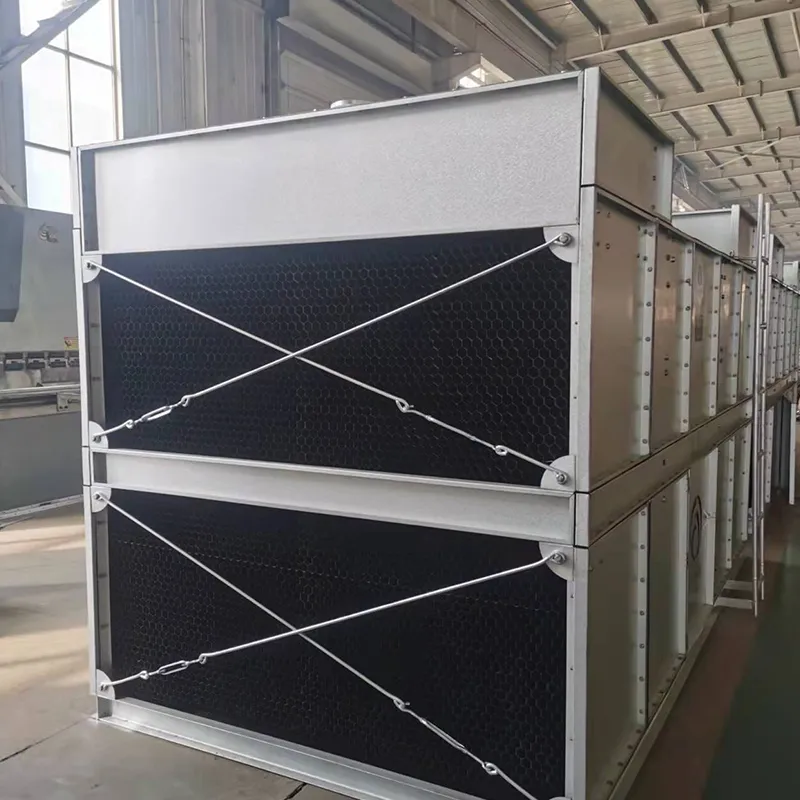
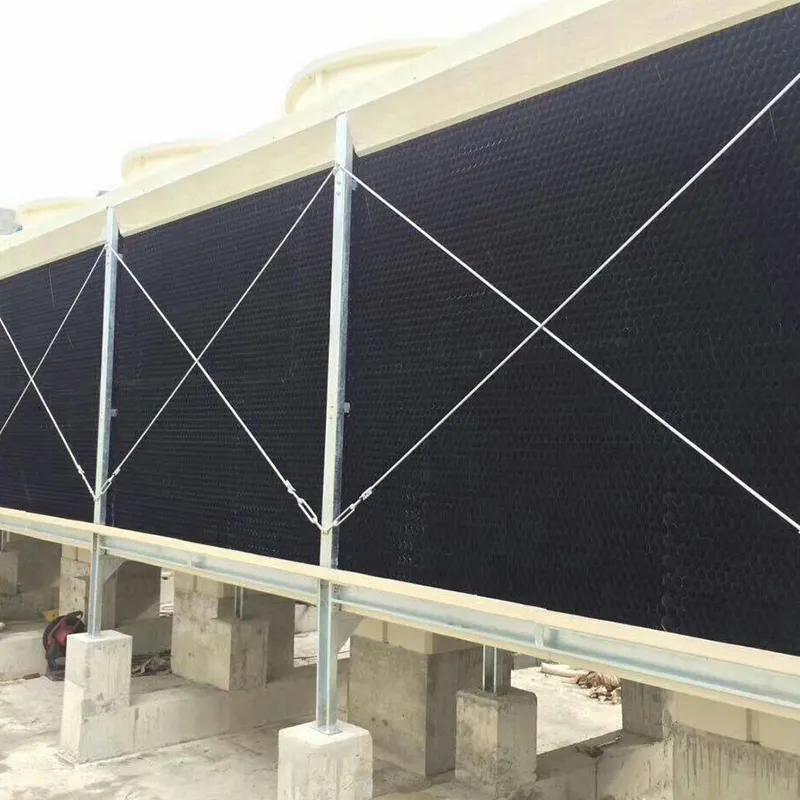
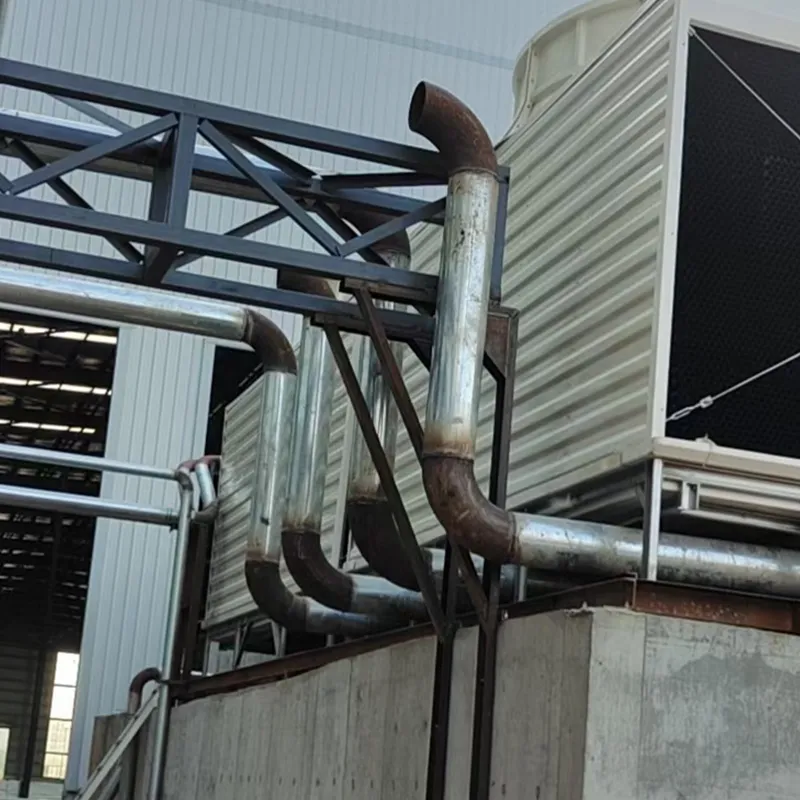
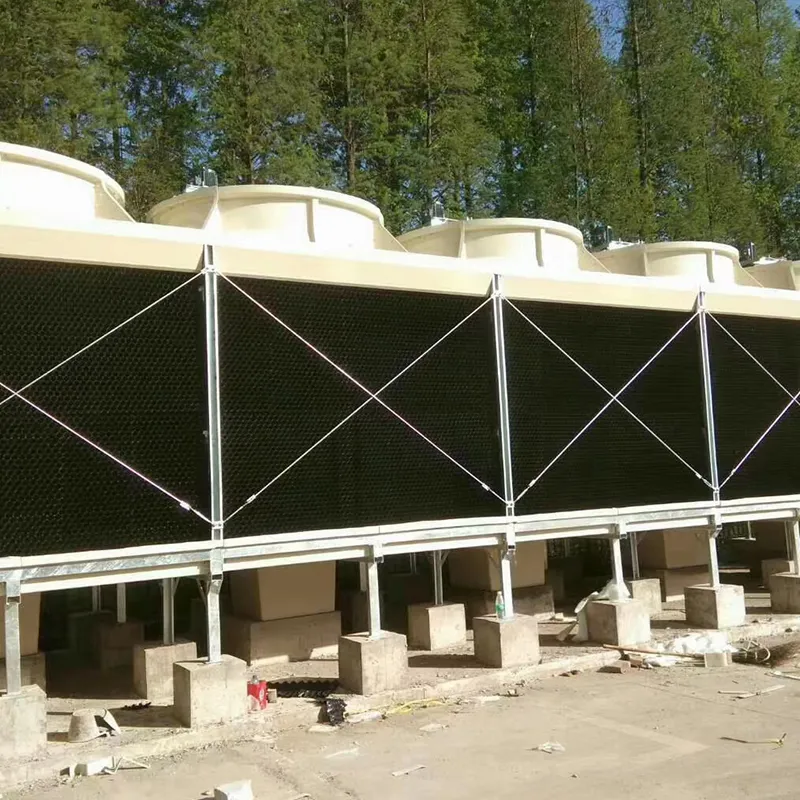
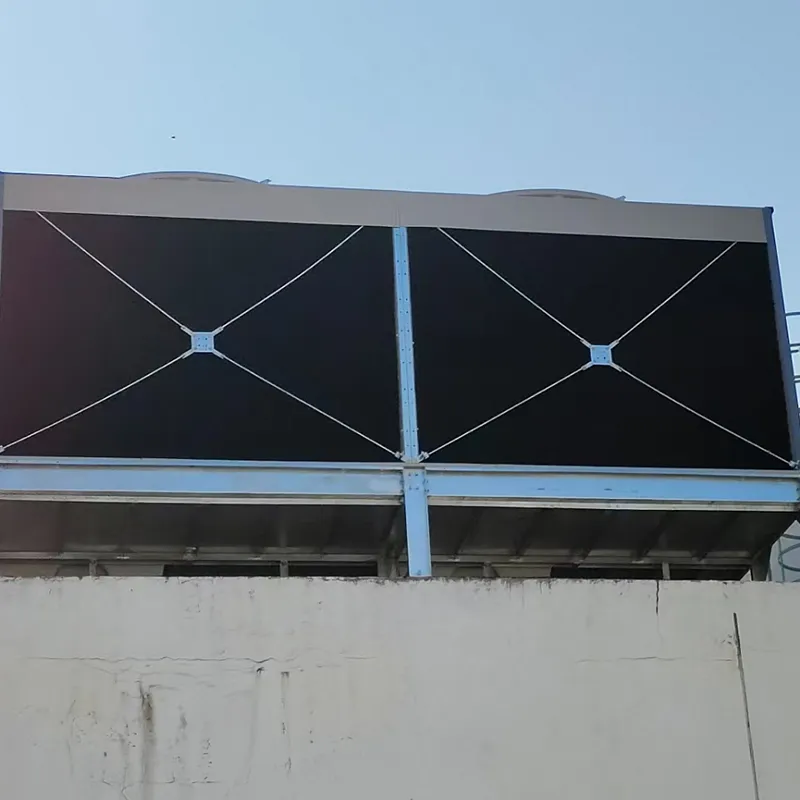
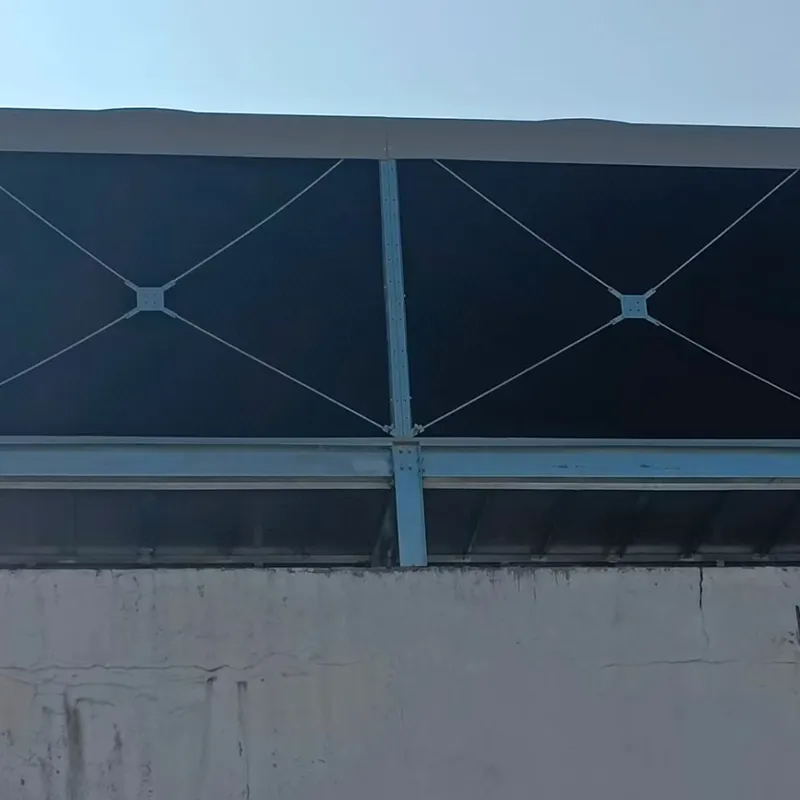
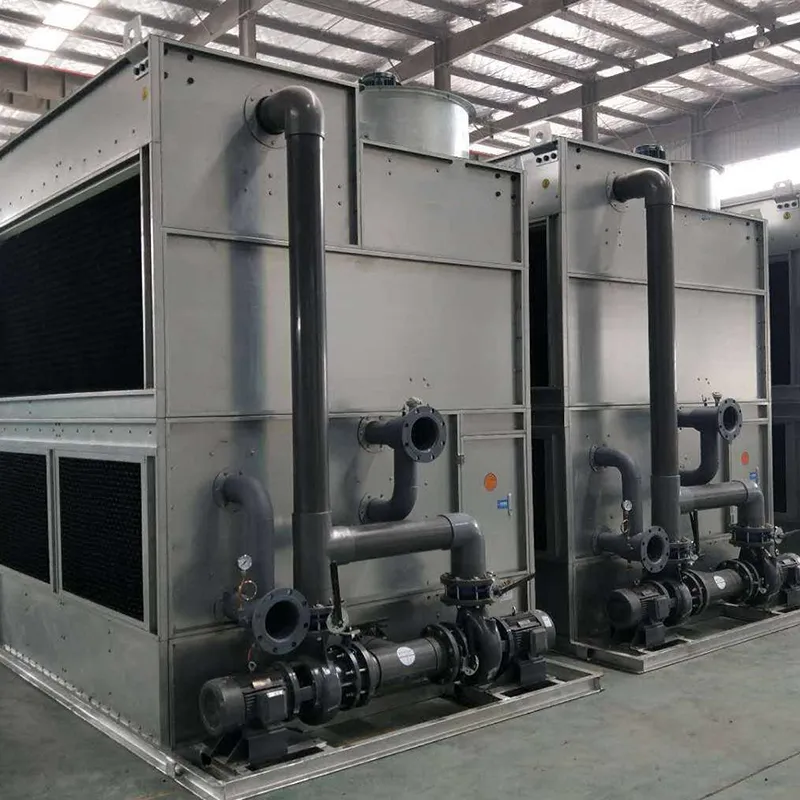
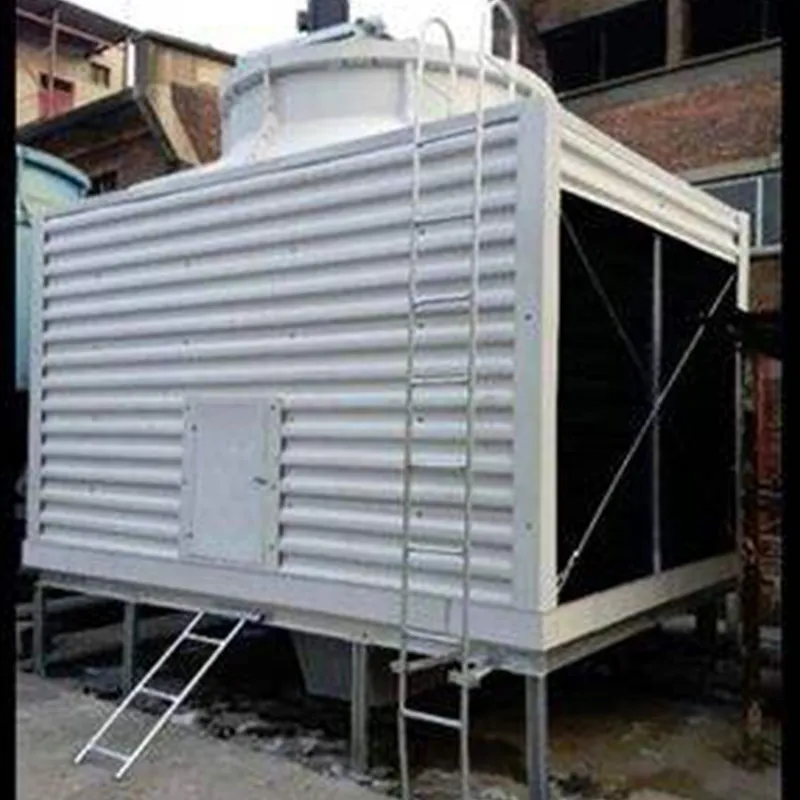
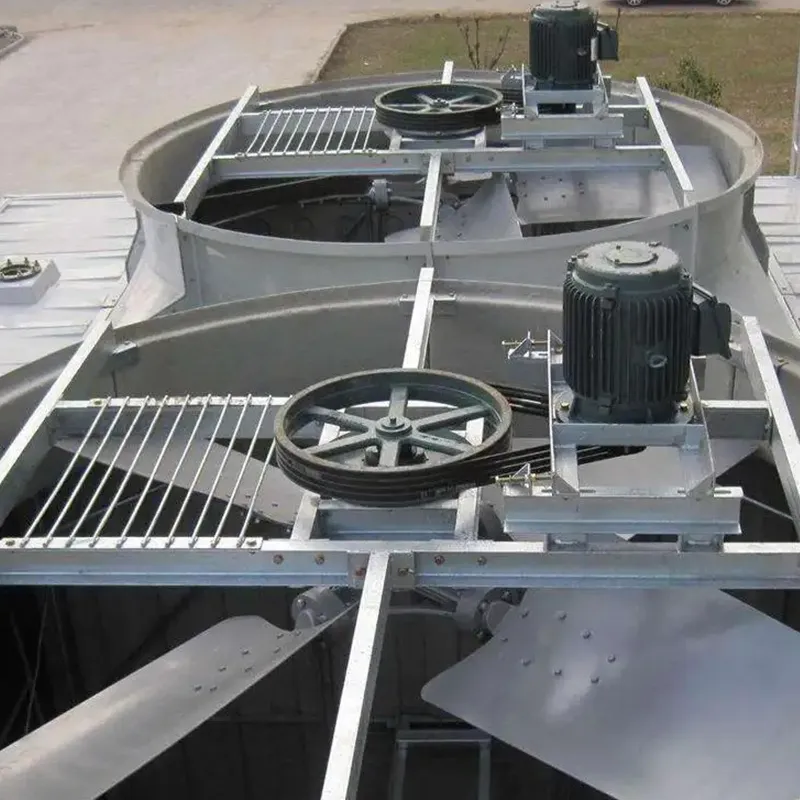
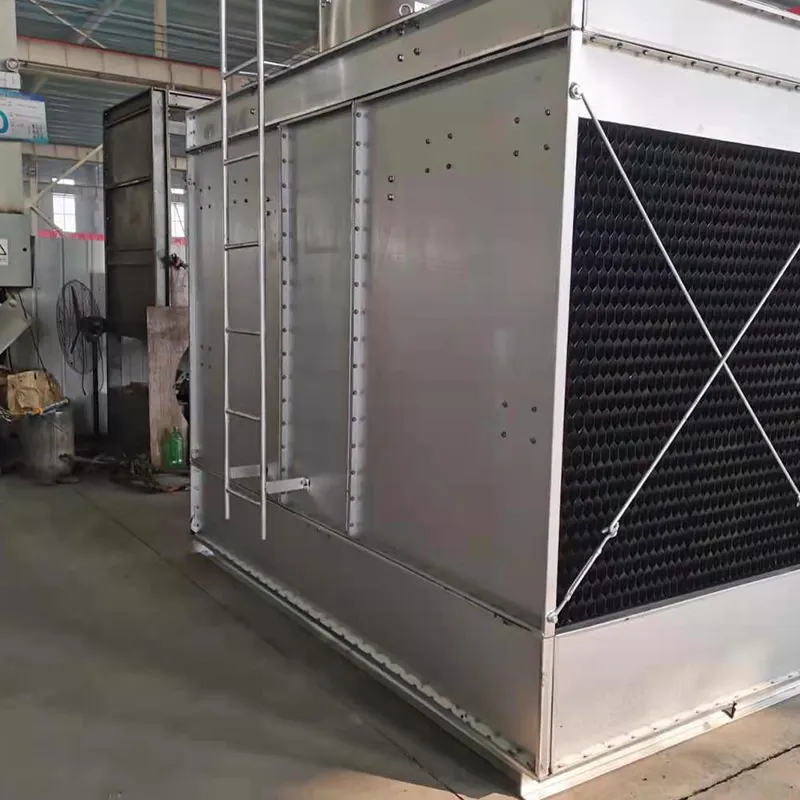
4.1 Componenti principali
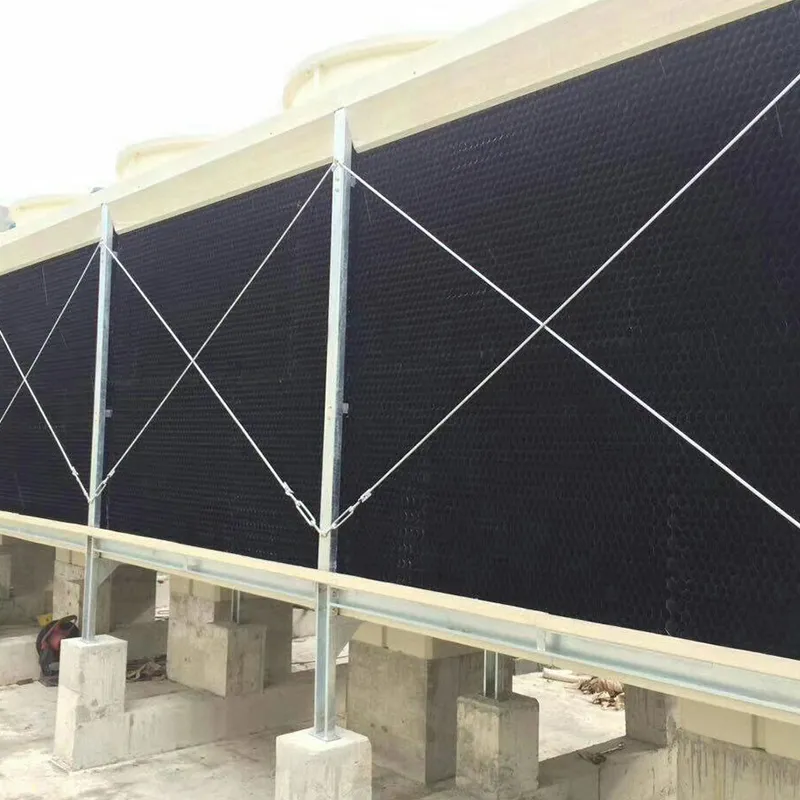
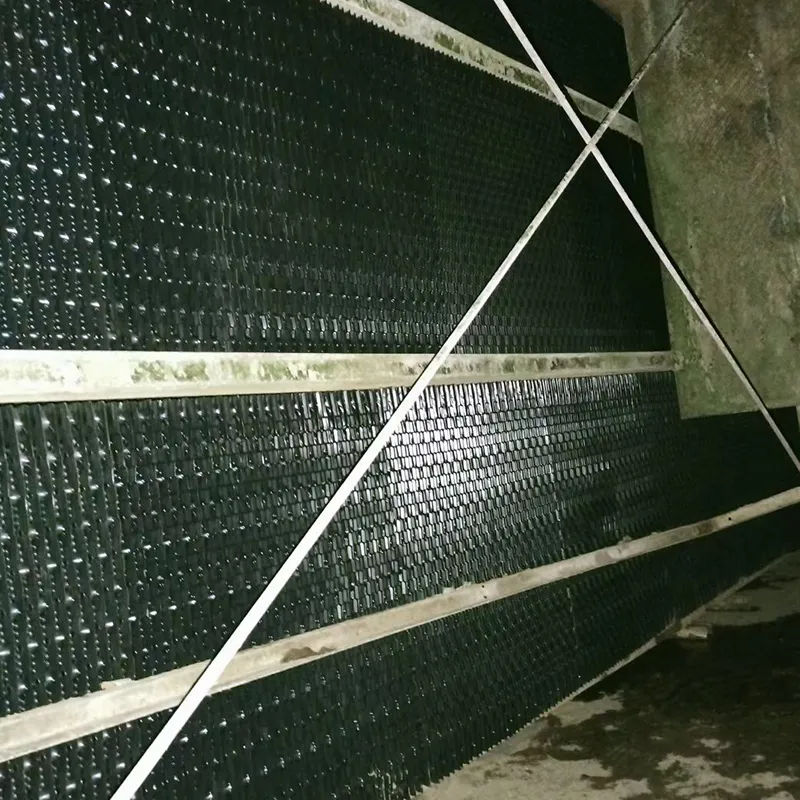
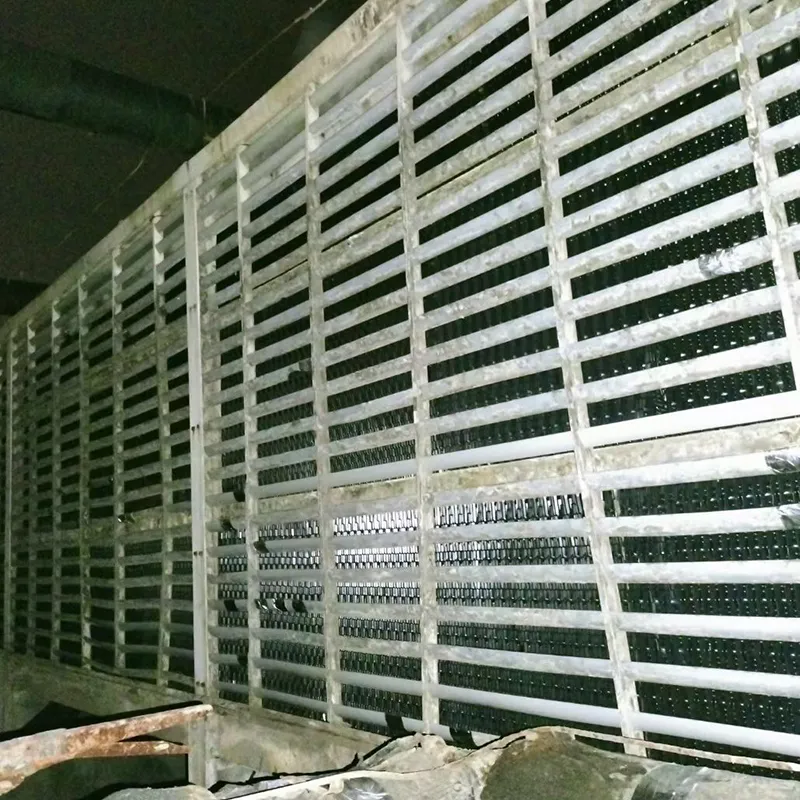
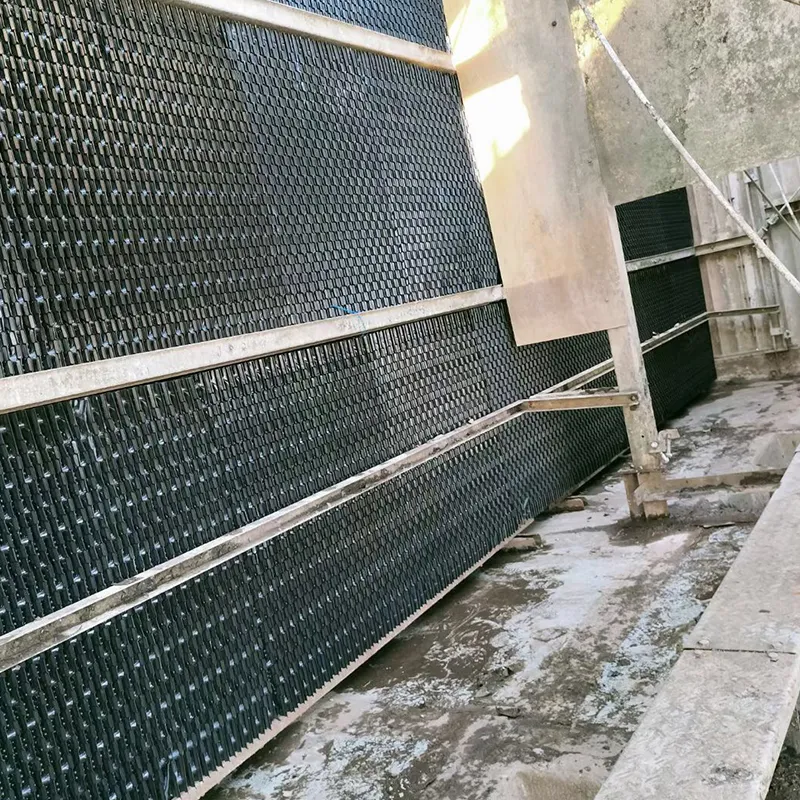
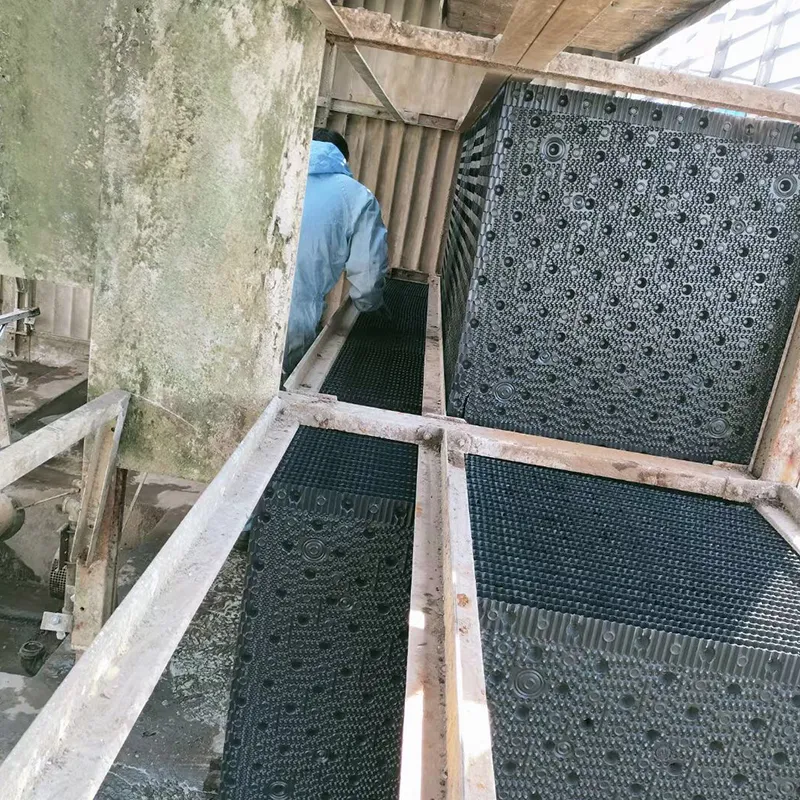
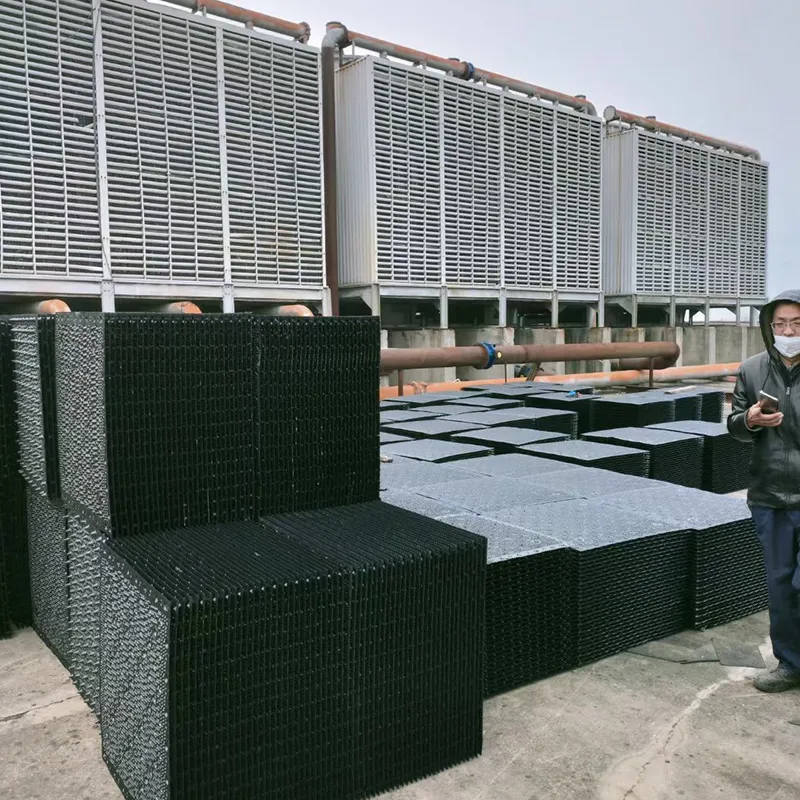
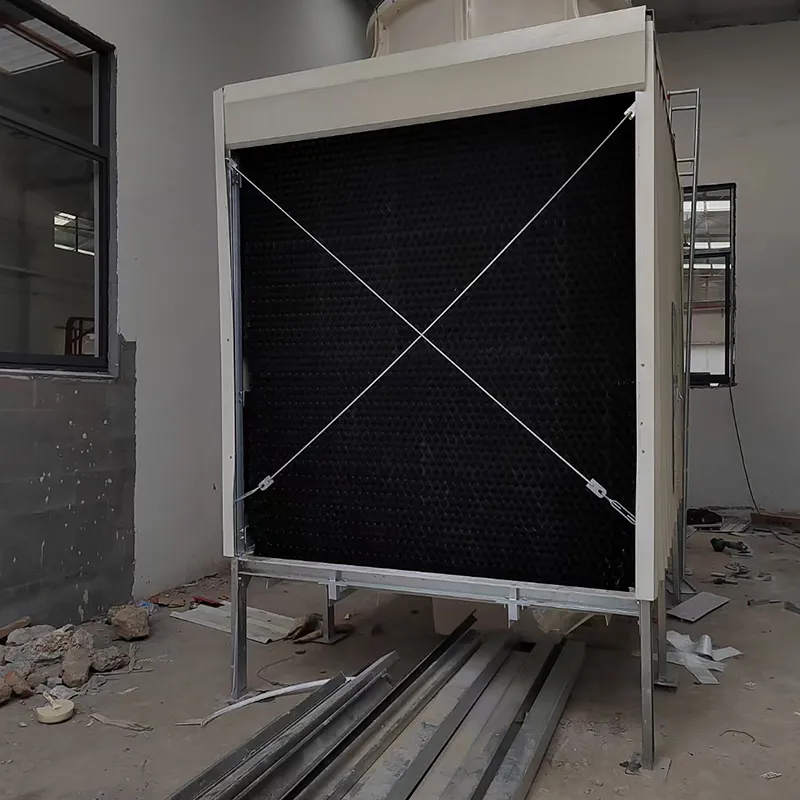
-Fill Media: PVC or PP modules to maximize air-water contact area.
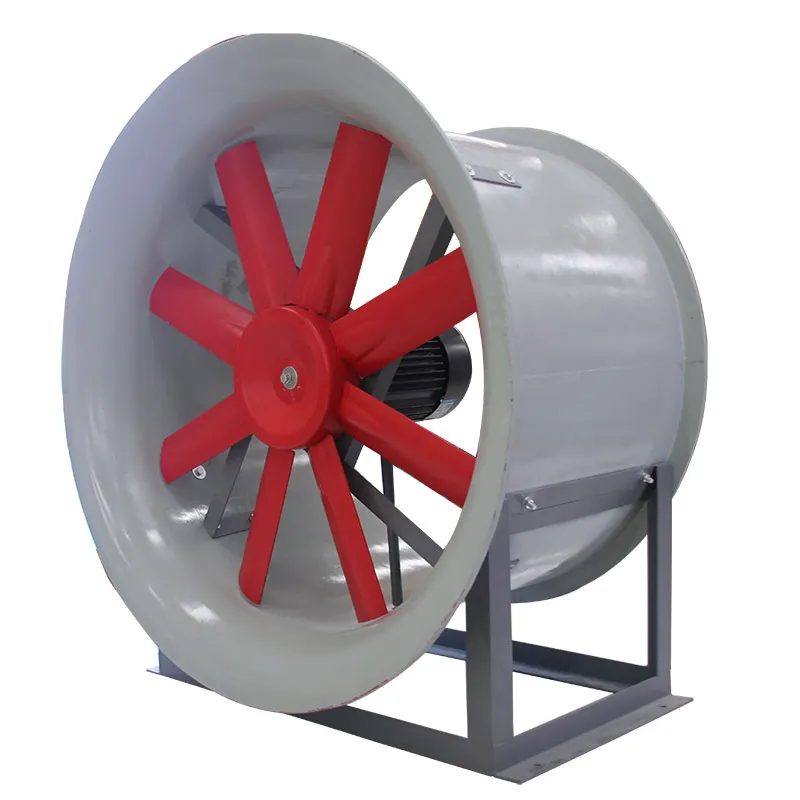
- Fan System: Axial/centrifugal fans (e.g., 7.5 kW motor for a 100 TR tower).
- Water Distribution: Rotary nozzles or fixed spray pipes.
- Drift Eliminator: Reduces water loss (<0.001% drift rate).
- Casing: FRP (corrosion-resistant) or galvanized steel (cost-effective).
4.2 Parametri di progettazione
- Cooling Capacity (TR): 1 TR = 3.516 kW; tower capacity = 1.2–1.3× chiller TR (to offset heat loss).
- Wet-Bulb Temperature (WBT): Critical design baseline (e.g., 28°C).
- Approach: Temperature difference between cooled water and WBT (typically 3–5°C).
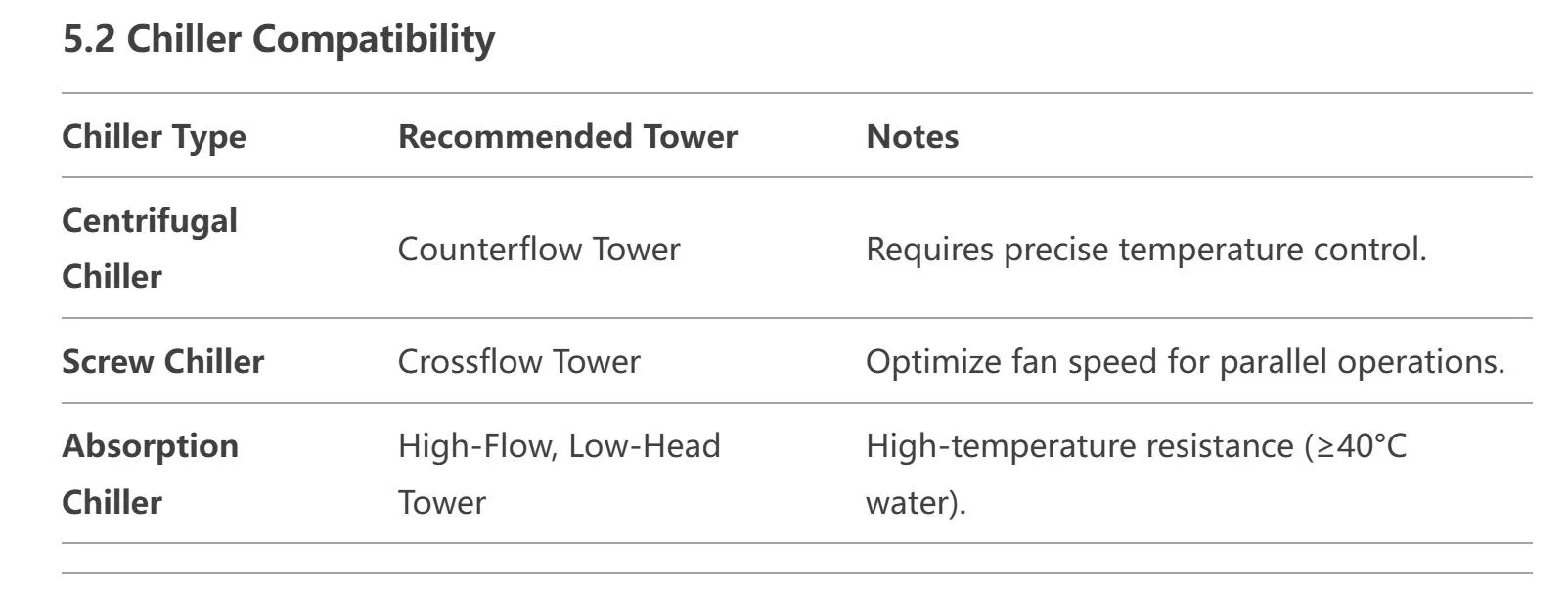
5. Linee guida per la selezione e la configurazione
5.1 Formula di dimensionamento
Tower Water Flow (m³/h) = \[ Chiller Capacity (TR) × 3024 × 1.3 \] ÷ 5000
Example: For a 500 TR chiller → ≈393 m³/h.
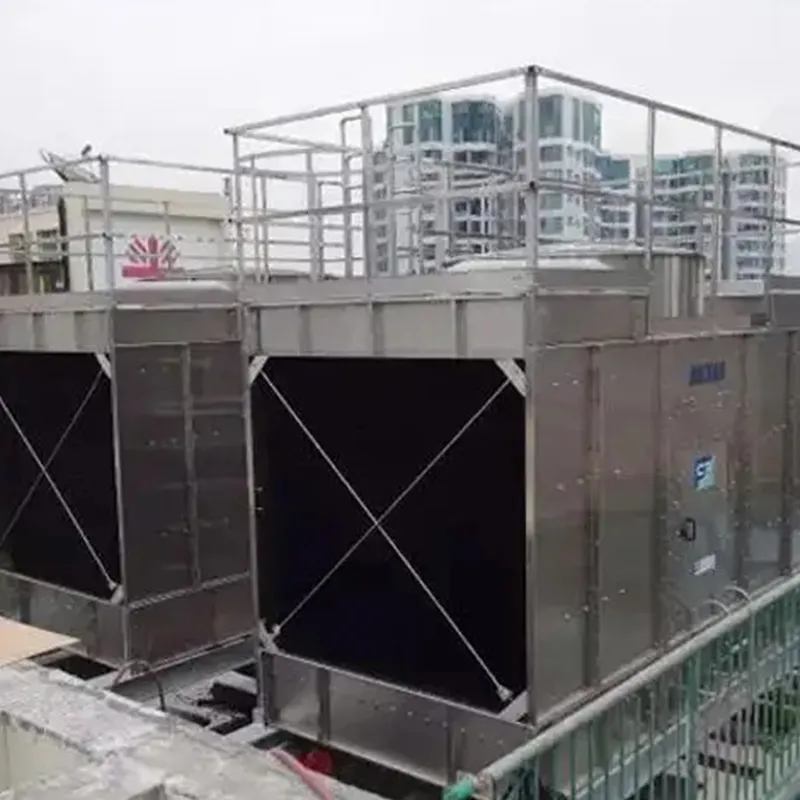
6. Efficienza energetica e sostenibilità
- Energy-Saving Technologies:
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) reduce fan power by 20–30%.
- High-efficiency fill media (15% higher heat transfer).
- Eco-Friendly Features:
- FRP compatible with low-GWP refrigerants (e.g., R-1233zd).
- Noise control ≤65 dB(A) @ 1m (ASHRAE compliant).
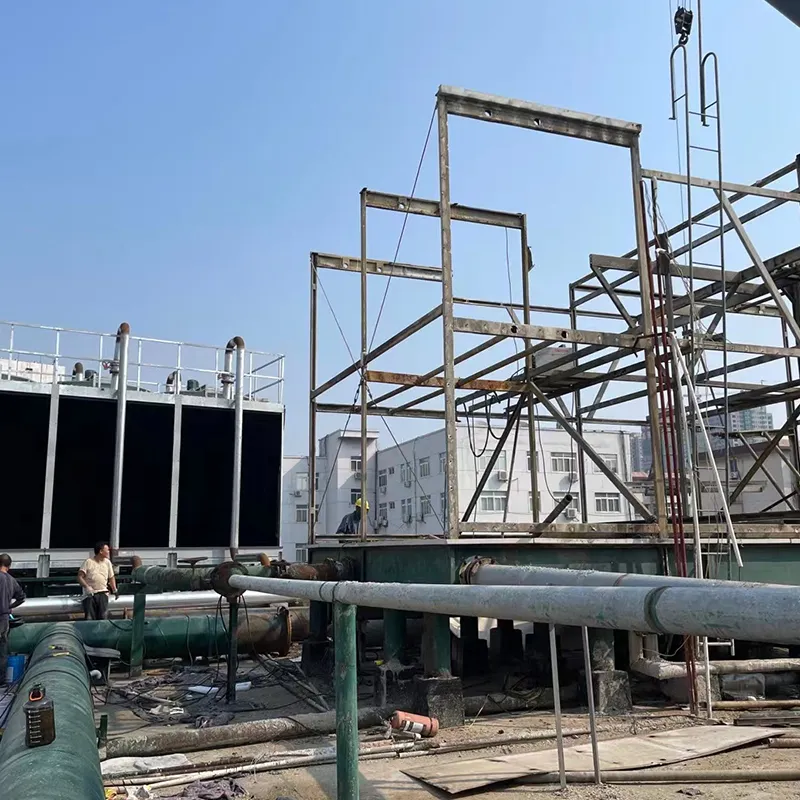
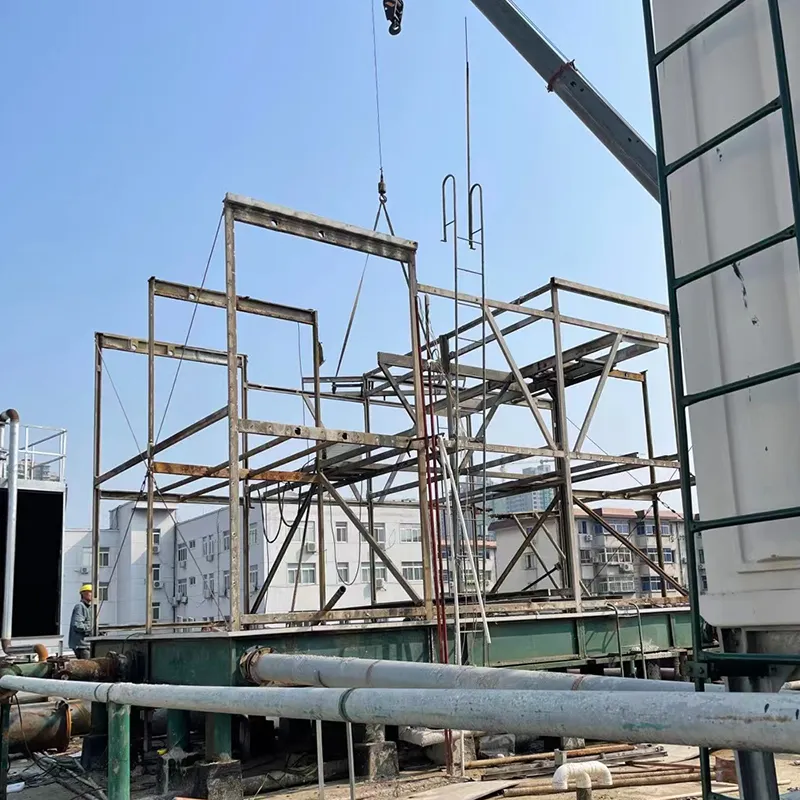
7. Manutenzione e risoluzione dei problemi
- Routine Maintenance:
- Weekly: Check water level/pH (6.5–8.5).
- Monthly: Clean fill media and filters.
- Common Issues:
- Reduced Efficiency: Clogged fills or fan imbalance.
- Abnormal Noise: Bearing wear or loose blades.
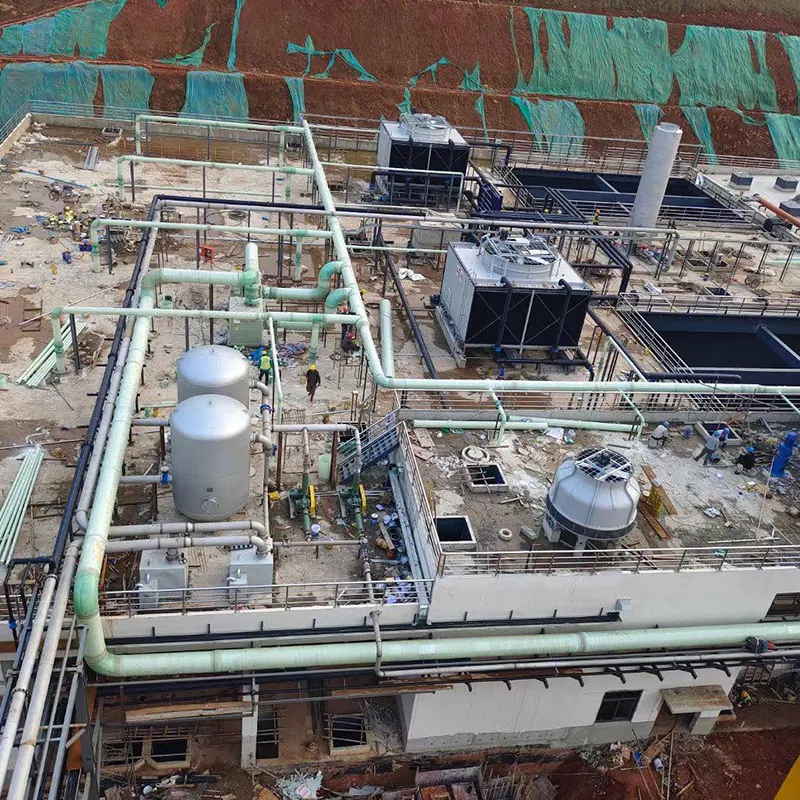
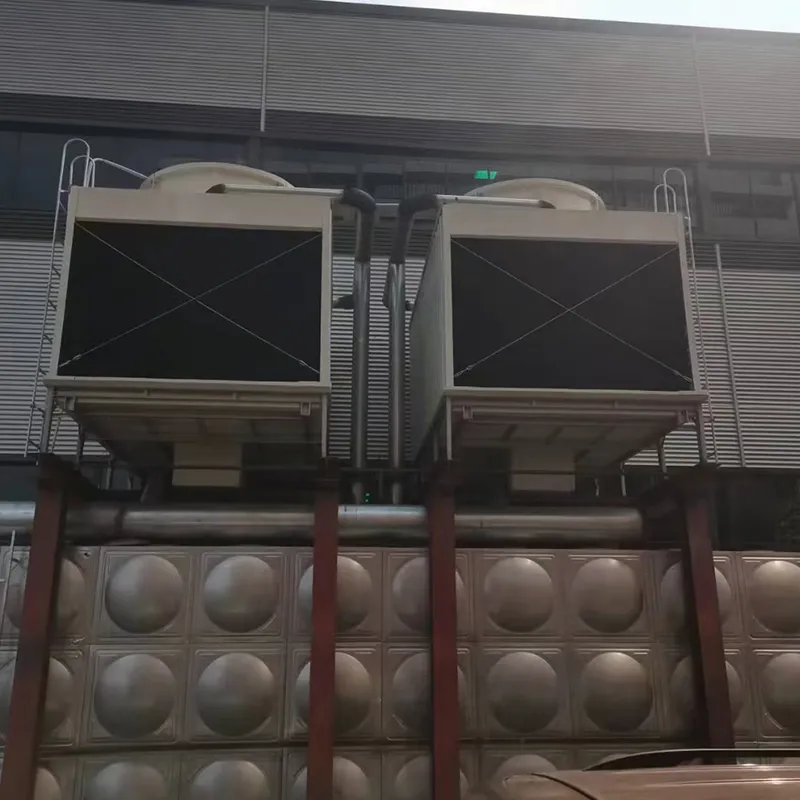
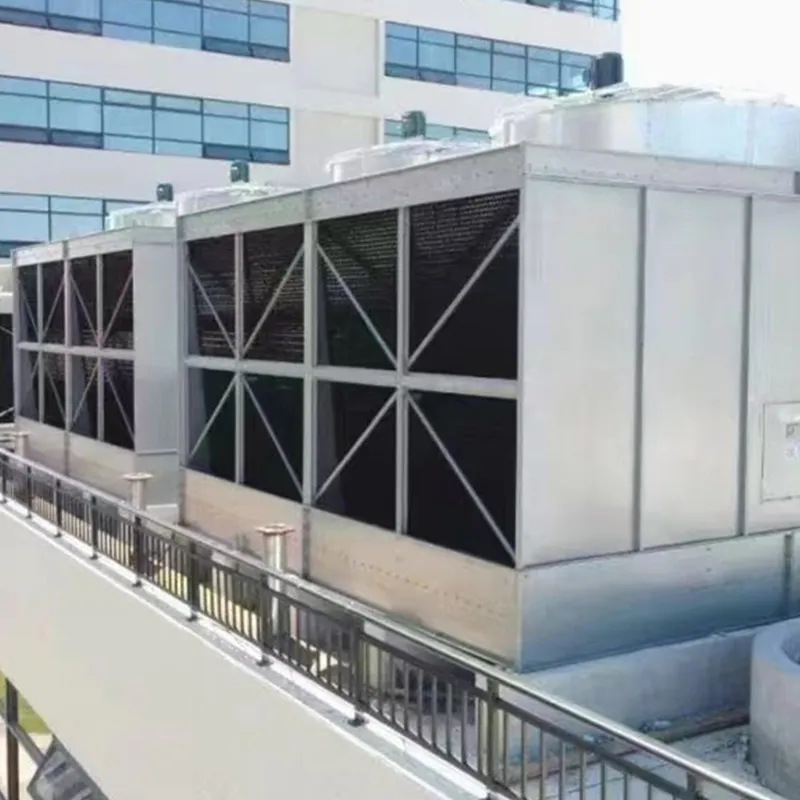
8. Applicazioni tipiche
- Commercial Buildings: Malls, offices (200–1,000 TR towers).
- Data Centers: Redundant N+1 configurations.
- Healthcare Facilities: Closed-loop towers for contamination control.
9. Riferimento dei costi (RMB)
| Capacity (TR) | Price Range (10,000 RMB) | Remarks |
|--------------------|------------------------------|---------------------------------------|
| 100 TR | 8–15 | FRP counterflow, standard config. |
| 500 TR | 40–70 | VFD fans + smart controls. |
| 1,000 TR | 80–150 | Modular design for parallel setups. |
10. Standard e certificazioni internazionali
- ASHRAE 90.1: Energy efficiency requirements.
- EN 13053: Ventilation system compliance (EU).
- LEED Certification: Credits for water/energy conservation.
Conclusione
Le torri di raffreddamento per l'aria condizionata sono fondamentali per l'efficienza dei sistemi HVAC. Le torri a flusso controcorrente sono adatte agli edifici commerciali ad alte prestazioni, mentre i modelli a flusso incrociato sono eccellenti per gli interventi di ristrutturazione in spazi limitati. È importante dare priorità ai sistemi di monitoraggio intelligenti (abilitati dall'IoT) e allineare i progetti agli obiettivi locali di WBT e sostenibilità.
Per consigli sui marchi (ad esempio BAC, SPX, EVAPCO) o confronti tecnici dettagliati, specificare i requisiti del progetto (zona climatica, budget, ecc.).
Cosa dicono di noi i nostri clienti







Indirizzo
20 Xingyuan South Street, contea di Zaoqiang, città di Hengshui, provincia di Hebei, Cina