We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
- The Fundamentals of Modern Cooling Systems
- Performance Metrics and Technological Breakthroughs
- Leading Manufacturers Comparison and Selection Guide
- Custom Engineering for Specialized Applications
- Real-World Industrial Application Studies
- Installation Best Practices and Maintenance Protocols
- Future Trends in Cooling Towers and Chillers Technology

(cooling towers and chillers)
The Fundamentals of Modern Cooling Towers and Chillers
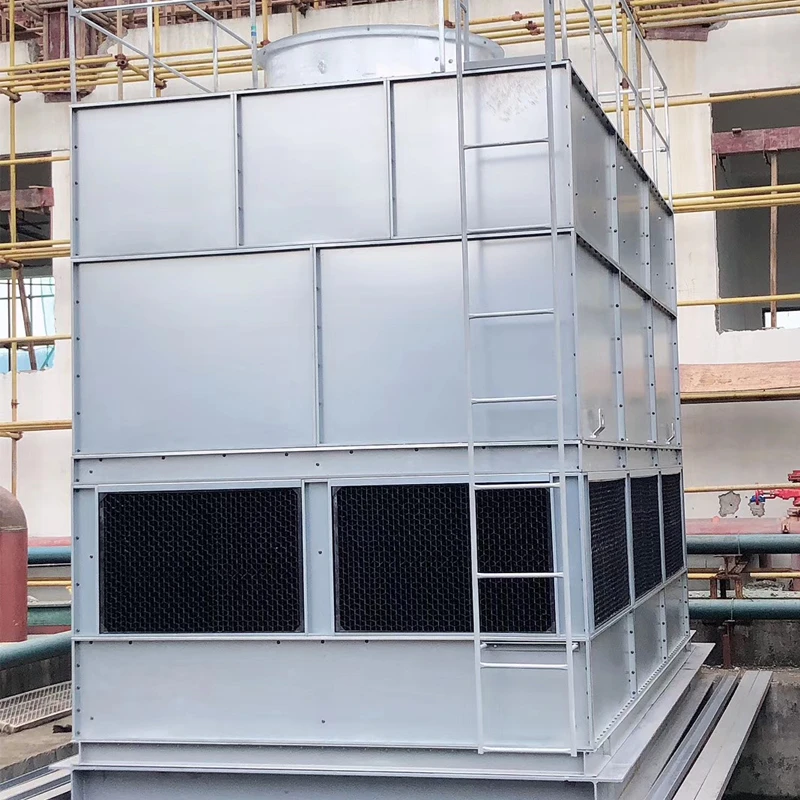
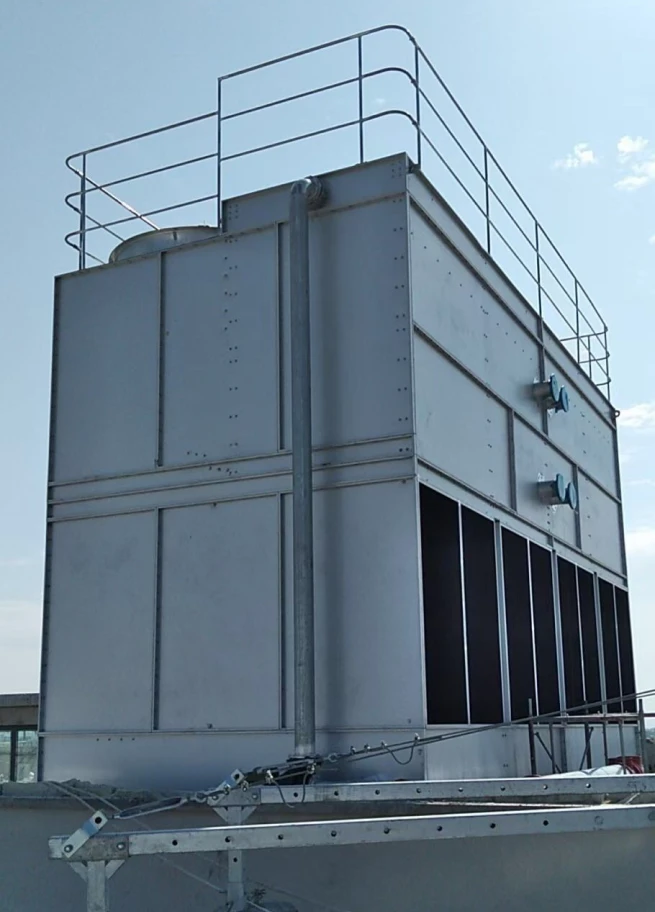
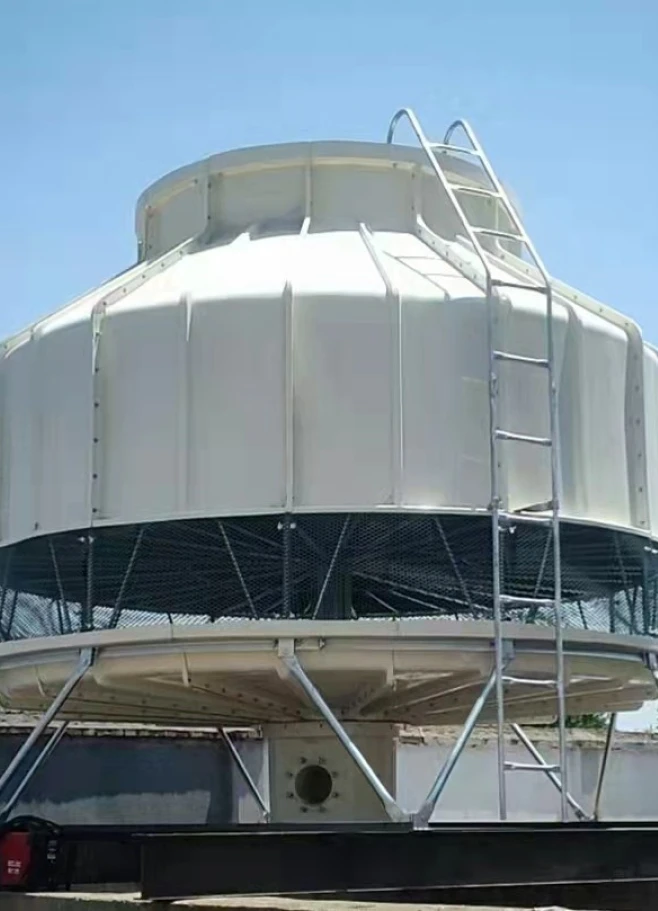
HVAC water chillers and cooling towers form the backbone of industrial climate control, with chillers removing heat from process water through refrigerant cycles and cooling towers dissipating this heat through evaporation. Counterflow cooling towers move air opposite to water flow for compact efficiency, while crossflow designs allow perpendicular airflow for lower pressure drops. These systems consume approximately 10-20% of commercial building energy according to Department of Energy statistics, making their optimization critical. Key components include:
- Compressor units using centrifugal or scroll technology
- Fill media that maximizes air-water contact
- Drift eliminators reducing water loss to 0.001%
- Variable frequency drives controlling pump speeds
Performance Metrics and Technological Breakthroughs
Recent advancements deliver unprecedented efficiency in thermal exchange systems. Next-generation hybrid cooling towers combine wet and dry operations to cut water consumption by 40% during transitional seasons. Coefficient of Performance (COP) ratings exceeding 6.5 are now achievable with magnetic bearing chillers, while sound levels have dropped to 75 dBA through aerodynamic fan designs. Water treatment innovations include:
- Pulsed-power scale inhibition systems
- Automated biocide dosing controllers
- Self-cleaning strainer technology
According to ASHRAE testing, optimized chillers paired with counterflow towers demonstrate 30% better heat dissipation than standard configurations, validating their design superiority.
Leading Manufacturers Comparison and Selection Guide
| Brand | Chiller Efficiency (COP) | Tower Water Savings | Noise Reduction | Maintenance Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johnson Controls | 6.8 | 25% | 78 dBA | Quarterly |
| Trane Technologies | 6.5 | 32% | 75 dBA | Biannual |
| SPX Cooling | 6.2 | 38% | 82 dBA | Quarterly |
| Baltimore Aircoil | 5.9 | 27% | 80 dBA | Biannual |
Data shows Trane leads in water conservation while Johnson Controls achieves highest operational efficiency. Material selection proves critical - stainless steel components increase longevity by 40% in coastal environments compared to galvanized steel.
Custom Engineering for Specialized Applications
Industrial processes require tailored solutions that standard units cannot provide. Pharmaceutical facilities implement duplex stainless steel chillers with triple redundancy to meet FDA validation requirements. Data centers utilize waterside economizers that leverage crossflow cooling towers during winter months, achieving PUE ratings below 1.1. Key customization factors include:
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for marine environments
- Seismic bracing for earthquake zones
- Low-temperature glycol mixtures (-20°F operation)
Industrial zones with limited space benefit from vertical counterflow towers occupying 40% less footprint than conventional designs while maintaining equivalent cooling capacity.
Real-World Industrial Application Studies
Dow Chemical implemented hybrid cooling towers at their Texas facility, achieving 43% reduction in makeup water consumption while lowering condenser temperatures by 4°F. This $2.3M retrofit generated payback in 2.7 years. Notable cases include:
- Phoenix Hospital: 3,000-ton centrifugal chillers with plate heat exchangers cut peak demand charges by $18,000/month
- Detroit Automotive Plant: Crossflow towers with fill treatment extend maintenance cycles from monthly to quarterly
- Singapore Datacenter: Seawater-cooled chillers operating at 0.5 kW/ton efficiency
Installation Best Practices and Maintenance Protocols
Proper installation ensures optimal performance of cooling systems. Foundation loading must accommodate 150% of operating weight to account for water-filled conditions during testing. Alignment tolerances for chiller compressors should not exceed 0.003 inches per ASHRAE guidelines. Quarterly maintenance should include:
- Infrared scanning of electrical components
- Vibration analysis on rotating equipment
- Water chemistry parameter monitoring
Automated monitoring systems reduce manual checks by 70% through predictive diagnostics identifying performance degradation before failures occur.
Future Trends in Cooling Towers and Chillers Technology
Cooling tower and chiller manufacturers are developing AI-driven optimization platforms that analyze weather patterns to anticipate thermal loading. Emerging technologies include:
- Adsorption cooling systems using waste heat streams
- Phase-change materials integrated into chiller designs
- Carbon fiber composite materials reducing structural weight by 50%
According to industry projections, next-generation HVAC water chillers and cooling towers will leverage IoT connectivity to achieve 15% additional efficiency gains through real-time operational adjustments based on fluctuating environmental conditions.

(cooling towers and chillers)
FAQS on cooling towers and chillers
Q: What is the primary difference between counterflow and crossflow cooling towers?
A: Counterflow cooling towers feature vertically opposite air-water movement, offering compact footprints and better efficiency. Crossflow towers have water falling vertically with horizontal air crossflow, simplifying maintenance and lowering pumping needs. The choice depends on space constraints and operational priorities.
Q: How do HVAC water chillers and cooling towers work together in a system?
A: Water chillers remove heat from building coolant loops using refrigerant cycles, while cooling towers dissipate chiller-generated heat into the atmosphere through evaporative cooling. Chillers handle internal heat transfer, while towers manage external heat rejection. This tandem operation maintains stable HVAC temperatures efficiently.
Q: When should industrial facilities use cooling towers versus chillers?
A: Cooling towers are ideal for large-scale heat rejection where water availability permits and ambient temperatures allow evaporation. Chillers are preferred for precise temperature control in critical processes like manufacturing. Hybrid systems often integrate both for optimized energy use.
Q: What are key advantages of modern cooling towers over older designs?
A: Modern towers offer superior energy efficiency through advanced fill media and variable-speed fans. They reduce water consumption via smart drift eliminators and require less chemical treatment. Upgraded designs also minimize noise pollution and maintenance downtime.
Q: Why maintain strict water treatment protocols for cooling towers and chillers?
A: Proper treatment prevents scale buildup that degrades heat transfer efficiency in chillers. It controls biological growth that causes corrosion in cooling tower components. Regular monitoring ensures system longevity and prevents costly repairs.





Address
20 Xingyuan South Street, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province, China