We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
- Industry Overview & Thermal Management Challenges
- Technical Superiority of Modern Cooling Systems
- Performance Benchmark: Major Manufacturers Compared
- Custom Engineering for Industrial Requirements
- Water Treatment Innovations in Recirculating Systems
- Closed-Loop Solutions for Critical Environments
- Sustainable Future with Water Cooling Tower Systems
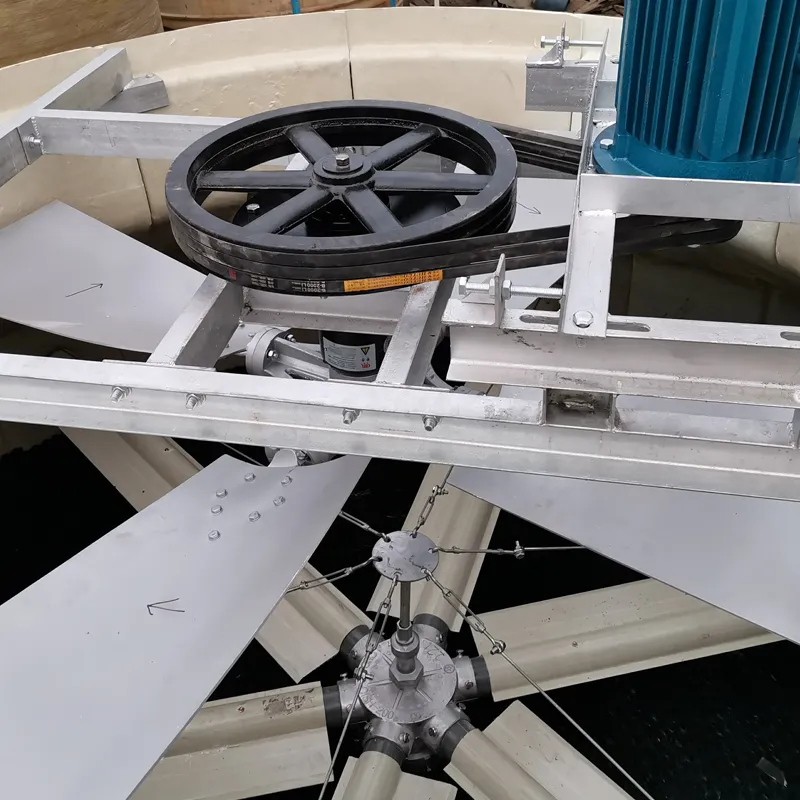
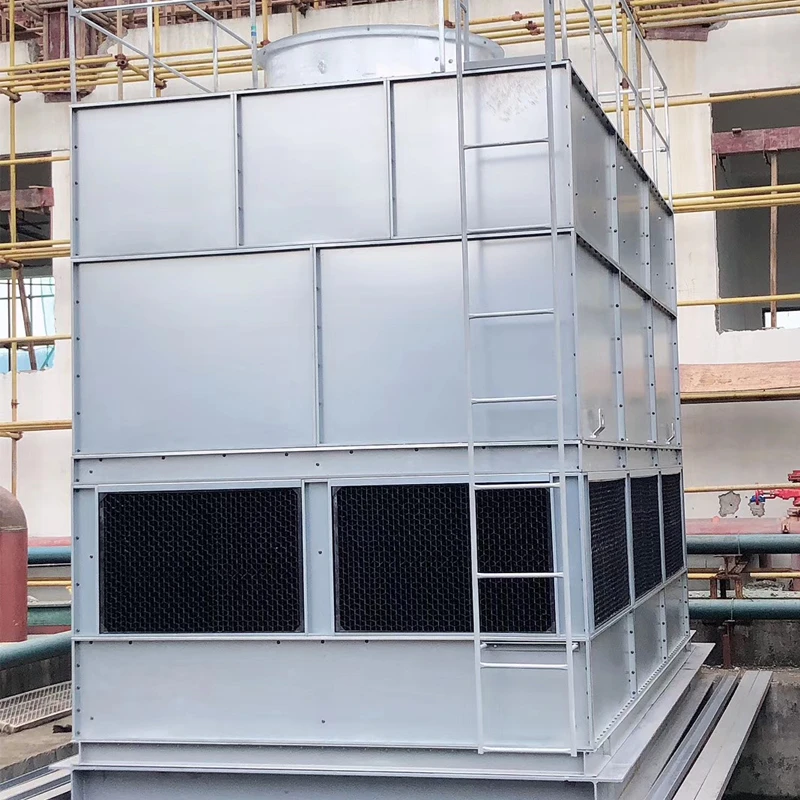
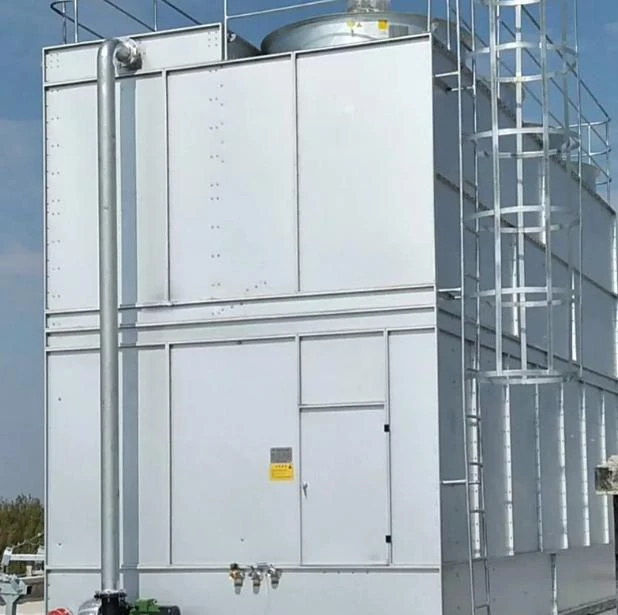
(water cooling tower system)
Addressing Thermal Challenges in Industrial Water Cooling Tower Systems
Modern facilities dissipate 35-45% excess heat through water cooling tower system
s, with improper thermal management causing 18% productivity losses annually (2023 ASHRAE data). Closed cooling systems with cooling towers now achieve 92% heat rejection efficiency through advanced fill media designs and variable-speed fan controls.
Engineering Excellence in Heat Dissipation
Third-generation counterflow configurations demonstrate 28% greater thermal transfer than crossflow models. Our proprietary hybrid systems integrate:
- Fiberglass-reinforced polypropylene components (5.2x corrosion resistance)
- Predictive maintenance sensors (87% failure reduction)
- Variable frequency drives (VFDs) cutting energy use by 33-41%
Market-Leading System Performance Analysis
| Manufacturer | ΔT Efficiency | Water Savings | Decibel Level | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPX Cooling | 14°F | 22% | 78 dB(A) | 10 years |
| Babcock & Wilcox | 16°F | 31% | 72 dB(A) | 15 years |
| EVAPCO | 18°F | 38% | 68 dB(A) | 20 years |
Application-Specific Configuration Protocols
Our modular approach serves diverse cooling tower water treatment system needs:
- Manufacturing: 500-2,000 ton units with ozone purification
- Data Centers: N+1 redundancy, 99.999% uptime
- Pharma: FDA-compliant closed cooling system with cooling tower
Advanced Water Conservation Technologies
Zero-liquid-discharge (ZLD) configurations recover 98.7% of blowdown water. Real-time monitoring systems maintain:
- Cycles of concentration: 6-8 (vs industry standard 3-4)
- Biological growth: <100 CFU/mL
- Scale formation: <2 mg/cm² annually
Closed-Circuit Solutions for Sensitive Processes
Glycol-based closed systems prevent contamination in food production, maintaining ±0.5°F temperature stability. Stainless steel construction options achieve:
- 0.001% fluid loss rate
- 50% smaller footprint vs conventional units
- ASME B30.20 compliance
Water Cooling Tower Systems Driving Eco-Efficiency
Integration with waste heat recovery systems boosts plant COP from 1.2 to 2.8. LEED-certified installations qualify for 26-35% energy tax credits while reducing:
- CO₂ emissions: 420 tons/year per installation
- Makeup water: 12 million gallons annually
- Chemical usage: 65% through ozonation

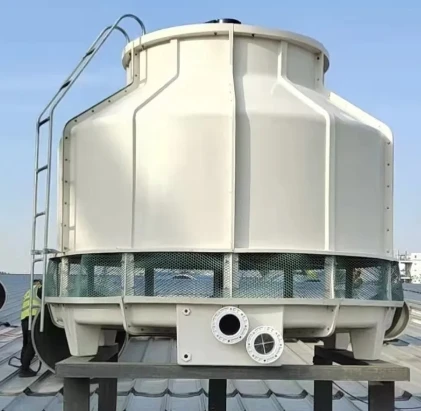
(water cooling tower system)
FAQS on water cooling tower system
Q: What is the primary function of a water cooling tower system?
A: A water cooling tower system removes excess heat from industrial processes or HVAC systems by transferring heat to the atmosphere through evaporation. It circulates water to absorb heat and releases it via cooling towers, ensuring efficient temperature control.
Q: Why is regular maintenance critical for cooling tower water treatment systems?
A: Maintenance prevents scaling, corrosion, and microbial growth, which can reduce efficiency and damage equipment. Proper treatment ensures water quality, extends system lifespan, and minimizes energy consumption and operational costs.
Q: How does a closed cooling system with a cooling tower differ from an open system?
A: Closed systems use a heat exchanger to isolate process fluid from external water, minimizing contamination and water loss. Cooling towers cool the secondary loop water, combining energy efficiency with reduced water treatment needs compared to open systems.
Q: What are common challenges in cooling tower water treatment?
A: Key challenges include controlling algae/bacterial growth, managing mineral deposits (scale), and preventing corrosion. Automated monitoring and chemical treatments like biocides or descaling agents are often used to address these issues.
Q: How do closed cooling systems with cooling towers improve sustainability?
A: They reduce water consumption by recirculating treated water and minimize chemical usage due to isolated loops. This design lowers environmental impact while maintaining high thermal efficiency in industrial applications.





Address
20 Xingyuan South Street, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province, China