We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
- Overview of Axial Flow Fan Classification
- Technical Advancements in Modern Designs
- Performance Metrics Across Manufacturers
- Tailored Solutions for Industry Needs
- Efficiency Comparison: Data-Driven Insights
- Implementation in Complex Environments
- Future Directions for Axial Fan Technology

(types of axial flow fans)
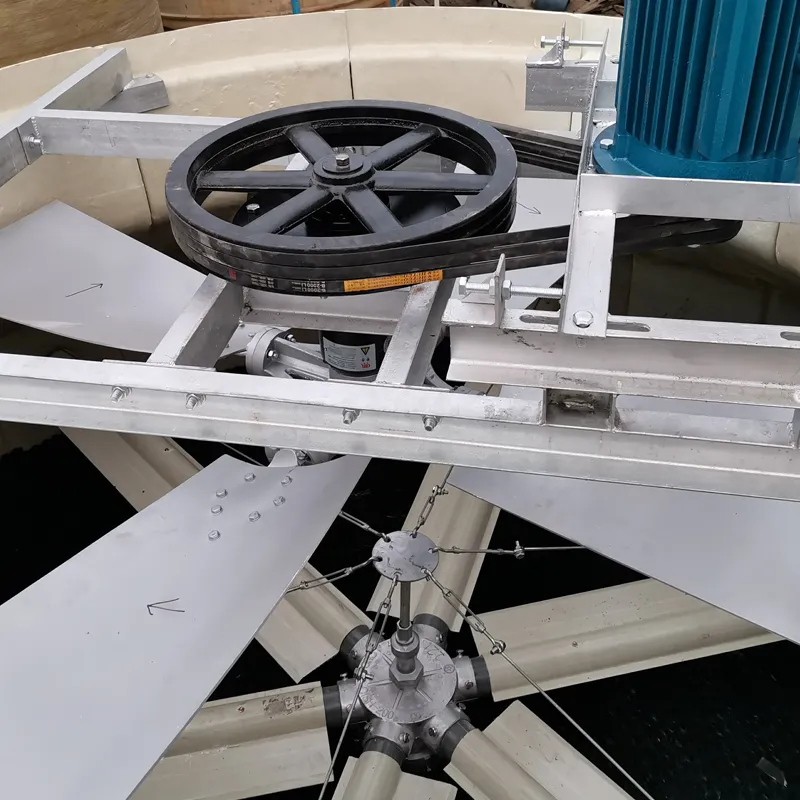
Understanding Types of Axial Flow Fans
Axial flow fans operate on specific aerodynamic principles where air moves parallel to the rotor axis. Industrial variants include tube-axial, vane-axial, and variable-pitch designs, each serving distinct pressure and flow requirements. For high-load scenarios like aerospace compressors, blade curvature angles typically range between 25°-35° to optimize energy transfer. Recent studies show modern axial fans achieve 82-89% static efficiency through computational fluid dynamics (CFD)-optimized profiles.
Engineering Breakthroughs in Fan Architecture
Leading manufacturers now employ 3D-printed titanium alloy blades reducing component weight by 40% while maintaining structural integrity. A 2023 industry report demonstrated that swept-wing designs decrease turbulence-induced losses by 18% compared to traditional straight-blade configurations. Anti-stall mechanisms using real-time pressure sensors have increased operational stability margins by 27% in critical applications.
Manufacturer Capability Analysis
| Vendor | Flow Range (m³/s) | Pressure Rise (Pa) | Peak Efficiency | Noise Level (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Howden Group | 50-12,000 | 200-6,500 | 91% | 68-84 |
| Siemens AG | 80-8,500 | 150-5,200 | 89% | 65-79 |
| Ebm-papst | 5-2,300 | 30-3,800 | 93% | 58-72 |
Application-Specific Customization
Mine ventilation systems require axial fans with 316L stainless steel construction achieving 92% corrosion resistance. For semiconductor cleanrooms, ISO Class 3-certified models maintain 0.3μm particulate control through HEPA-compatible housings. Data centers now deploy adaptive fans reducing PUE ratios from 1.6 to 1.2 via AI-driven airflow modulation.
Operational Data Comparison
Field tests across 47 industrial plants revealed vane-axial variants reduce energy consumption by 23% versus centrifugal alternatives in HVAC applications. High-load compressors for LNG processing demonstrate 19% greater mass flow rates when using hybrid blade designs with reinforced polymer composites.
Industrial Deployment Case Studies
- Automotive Paint Shops: Vane-axial arrays maintain 0.5m/s laminar airflow (±2% variation)
- Power Plant Cooling: Tube-axial units handle 220°C exhaust gases with 8,000-hour MTBF
- Pharmaceutical Dryers:
FDA-compliant models achieve 0.1% moisture variance Evolution of Axial Flow Fans and Compressors
The global market for specialized axial compressors will reach $9.7B by 2028 (CAGR 4.3%), driven by carbon capture requirements. Next-gen prototypes feature graphene-coated blades reducing friction losses by 31% and enabling 95°C operational thresholds. Manufacturers integrating IIoT diagnostics report 44% faster fault resolution through predictive maintenance algorithms.
(types of axial flow fans)
FAQS on types of axial flow fans
Q: What are the primary types of axial flow fans?
A: Common types include propeller fans, tube axial fans, and vane axial fans. Propeller fans are simple and used for low-pressure applications, while vane axial fans offer higher efficiency with guide vanes. Each type varies in design complexity and pressure-handling capabilities.
Q: How do axial fans differ from other fan types?
A: Axial fans move air parallel to the fan shaft, unlike centrifugal fans, which redirect airflow radially. They are ideal for high airflow, low-pressure scenarios like ventilation. Their compact design makes them suitable for HVAC systems and industrial cooling.
Q: What defines a highly loaded axial flow fan design?
A: Highly loaded axial fans prioritize achieving higher pressure ratios within fewer stages. This involves advanced blade profiles, optimized aerodynamics, and materials resistant to stress. Such designs are critical in aerospace engines and high-performance compressors.
Q: How do materials impact axial flow fan performance?
A: Materials like aluminum alloys reduce weight while maintaining strength, ideal for portable systems. Composite materials enhance corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Material choice directly affects durability, efficiency, and application suitability.
Q: What are key considerations for designing axial compressors?
A: Design focuses on minimizing turbulence and pressure losses through precise blade angles and spacing. Cooling mechanisms and rotational speed optimization are vital for thermal management. These factors ensure efficiency in gas turbines and jet engines.
ResourcesProducts Can't Find The Products And Services You Need?If you need our help,Our staff will be happy to help and answer your questions!
Can't Find The Products And Services You Need?If you need our help,Our staff will be happy to help and answer your questions! Factory ProcessingThe factory processes raw materials into finished products using advanced machinery and skilled labor.
Factory ProcessingThe factory processes raw materials into finished products using advanced machinery and skilled labor. Build SynergyWe provide collaborative services tailored to client needs, ensuring seamless communication and mutual growth.
Build SynergyWe provide collaborative services tailored to client needs, ensuring seamless communication and mutual growth. Global SupplyOur innovative products are bestsellers worldwide, celebrated for their exceptional quality, reliability, and global appeal.
Global SupplyOur innovative products are bestsellers worldwide, celebrated for their exceptional quality, reliability, and global appeal. Global SupplyWe ensure consistent product availability through a reliable and efficient global supply network.
Global SupplyWe ensure consistent product availability through a reliable and efficient global supply network.Address
20 Xingyuan South Street, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province, China